|
Ring (diacritic)
A ring diacritic may appear above or below letters. It may be combined with some letters of the extended Latin alphabets in various contexts. Rings Distinct letter The character Å (å) is derived from an A with a ring. It is a distinct letter in the Danish, Norwegian, Swedish, Finnish, Walloon, and Chamorro alphabets. For example, the 29-letter Swedish alphabet begins with the basic 26 Latin letters and ends with the three letters Å, Ä, and Ö. Overring The character Ů (ů; a Latin U with overring, or kroužek in Czech Republic) is a grapheme in Czech preserved for historic reasons, which identifies a vowel shift. For example, the word for "horse" used to be written ''kóň'', which evolved, along with pronunciation, into ''kuoň''. Ultimately, the vowel disappeared completely, and the ''uo'' evolved into ''ů'', modern form ''kůň''. The letter ''ů'' now has the same pronunciation as the letter '' ú'' (long ), but changes to a short ''o'' when a word i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle Symbol (other)
Circle symbol may refer to (in ascending order of size, approximately): * , ring diacritic * , white bullet * , function composition * , degree symbol * , masculine ordinal indicator *, music symbol denoting either a diminished triad or diminished seventh chord The diminished seventh chord is a four-note chord (a seventh chord) composed of a root note, together with a minor third, a diminished fifth, and a diminished seventh above the root: (1, 3, 5, 7). For example, the diminished seve ... * , superscript lowercase letter o * , white circle Unicode symbol * , dotted circle * , lowercase vowel letters in the Latin, Greek (omicron), and Cyrillic alphabets * , Semitic/Phoenician letter Ayin, the ancestor of the Greek, Latin, Cyrillic etc. letters * , uppercase vowel letters in the Latin, Greek, and Cyrillic alphabets * , heavy circle Unicode symbol * , O mark, large circle Unicode symbol * , medium white circle Unicode symbol See also * Circle (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vowel Shift
A vowel shift is a systematic sound change in the pronunciation of the vowel sounds of a language. The best-known example in the English language is the Great Vowel Shift, which began in the 15th century. The Greek language also underwent a vowel shift near the beginning of the Common Era, which included iotacism. Among the Semitic languages, the Canaanite languages underwent a shift in which Proto-Semitic *ā became ō in Proto-Canaanite (a language likely very similar to Biblical Hebrew). A vowel shift can involve a merger of two previously different sounds, or it can be a chain shift. US examples One of the several major vowel shifts that is currently underway in the US is the Northern Cities Vowel Shift. This change pattern is characterized by the longer and lower vowels moving forward and upward, while the shorter vowels move downward and backward. This vowel rotation, for example, is noticeable as the vowel sound in “coffee” is moving toward the vowel in “fath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialectologist
Dialectology (from Greek , ''dialektos'', "talk, dialect"; and , ''-logia'') is the scientific study of linguistic dialect, a sub-field of sociolinguistics. It studies variations in language based primarily on geographic distribution and their associated features. Dialectology treats such topics as divergence of two local dialects from a common ancestor and synchronic variation. Dialectologists are ultimately concerned with grammatical, lexical and phonological features that correspond to regional areas. Thus they usually deal not only with populations that have lived in certain areas for generations, but also with migrant groups that bring their languages to new areas (see language contact). Commonly studied concepts in dialectology include the problem of mutual intelligibility in defining languages and dialects; situations of diglossia, where two dialects are used for different functions; dialect continua including a number of partially mutually intelligible dialects; and pluri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 233
The international standard ISO 233 establishes a system for romanization of Arabic and Syriac. It was supplemented by ISO 233-2 in 1993. 1984 edition The table below shows the consonants for the Arabic language. ISO 233-2:1993 ISO 233-2:1993 is an ISO schema for the simplified transliteration of Arabic characters into Roman characters. This transliteration system was adopted as an amendment to ISO 233:1984. It is used mainly in library context, and was introduced because ISO 233 was not meeting the indexing purposes, which are essential for the consistency of library catalogs. According to ISO 233-2(1993), Arabic words are vocalized prior to romanization. ISO 233-2 is used in French libraries and in North African libraries, and is recommended by ISSN for establishing key titles when cataloguing serials. ISO 233-3:1999 ISO 233-3:1999 is dedicated to "Persian language – Simplified transliteration". ISO/R 233:1961 ISO/R 233 is an earlier standard that has been wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
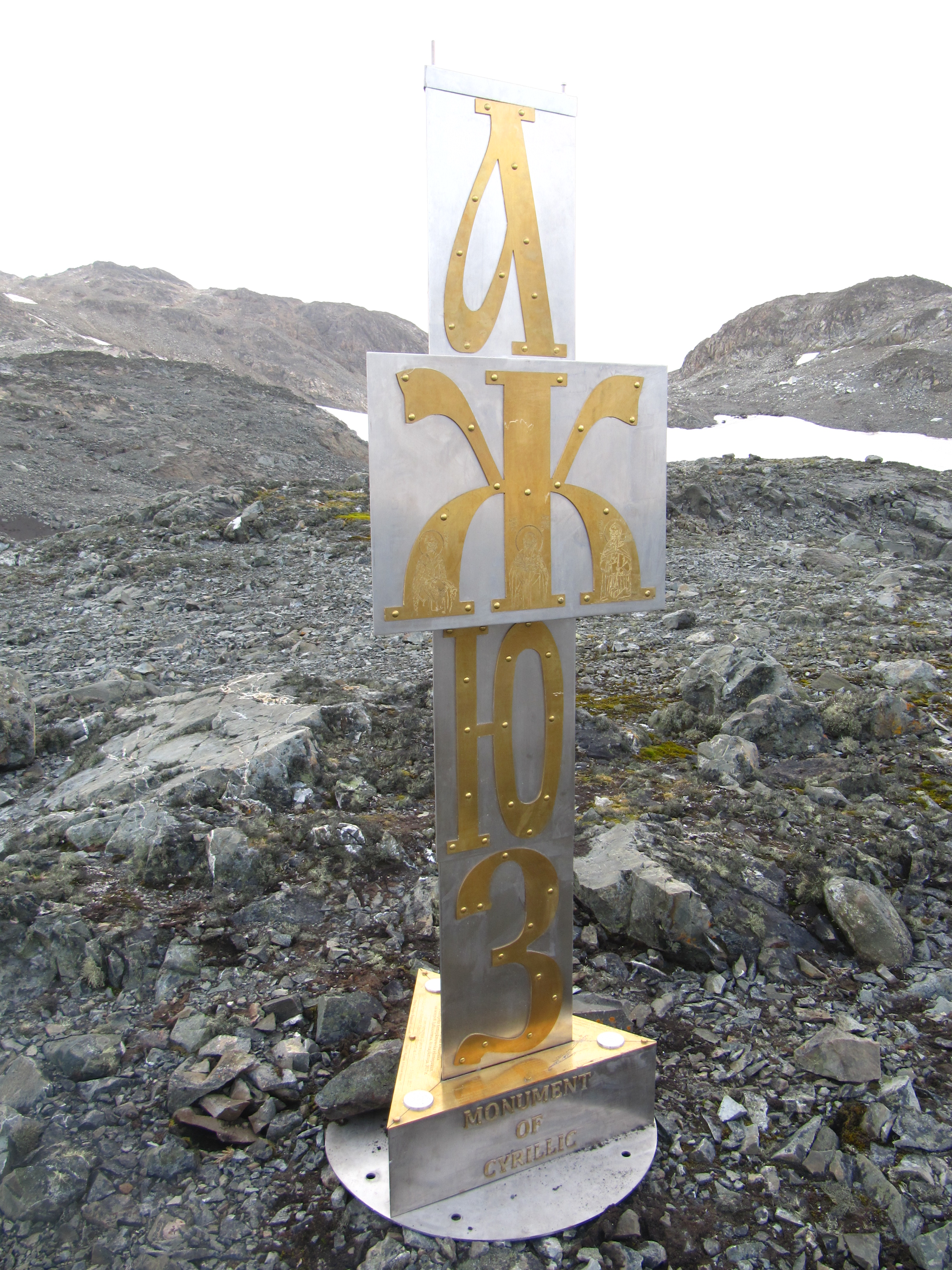
Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union, following the Latin and Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of tsar Simeon I the Great, probably by disciples of the two Byzantine brothers Saint Cyril and Saint Methodius, who had previously created the Glagoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
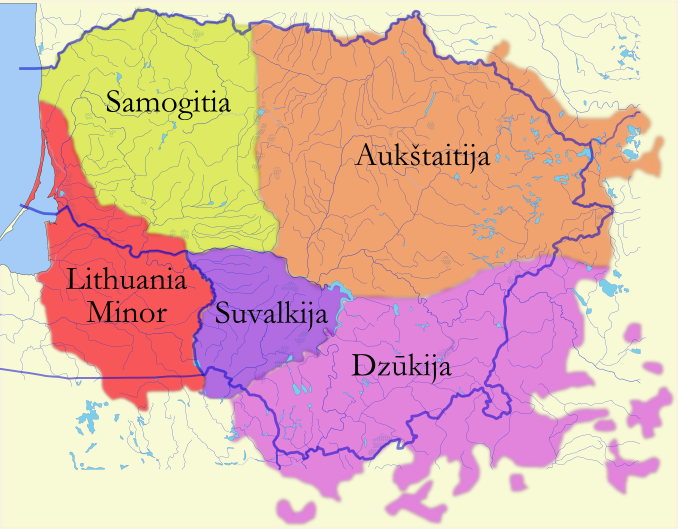
Lithuania Minor
Lithuania Minor ( lt, Mažoji Lietuva; german: Kleinlitauen; pl, Litwa Mniejsza; russian: Ма́лая Литва́), or Prussian Lithuania ( lt, Prūsų Lietuva; german: Preußisch-Litauen, pl, Litwa Pruska), is a historical ethnography, ethnographic region of Prussia (region), Prussia, where Prussian Lithuanians (or Lietuvininkai) lived, now located in Lithuania and the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. Lithuania Minor encompassed the northeastern part of the region and got its name from the territory's substantial Lithuanian language, Lithuanian-speaking population. Prior to the Northern Crusades, invasion of the Teutonic Knights in the 13th century, the main part of the territory later known as Lithuania Minor was inhabited by the tribes of Scalovians, Skalvians and Nadruvians. The land depopulated during the incessant war between Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania and the Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights, Teutonic Order. The war ended with the Treaty of Melno and the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Language
Lithuanian ( ) is an Eastern Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the official language of Lithuania and one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.8 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 200,000 speakers elsewhere. Lithuanian is closely related to the neighbouring Latvian language. It is written in a Latin script. It is said to be the most conservative of the existing Indo-European languages, retaining features of the Proto-Indo-European language that had disappeared through development from other descendant languages. History Among Indo-European languages, Lithuanian is conservative in some aspects of its grammar and phonology, retaining archaic features otherwise found only in ancient languages such as Sanskrit (particularly its early form, Vedic Sanskrit) or Ancient Greek. For this reason, it is an important source for the reconstruction of the Proto-Indo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emiliano-Romagnolo Language
Emilian-Romagnol is a linguistic continuum part of the Gallo-Romance languages spoken in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna. It is divided into two main varieties: Emilian and Romagnol. While first registered under a single code in ISO standard 639-3, in 2009 this was retired in favour of two distinct codes for the two varieties, due to the cultural and literary split between the two parts of the region, making Emilian and Romagnol distinct ethnolinguistic entities. Since 2015, Emilian and Romagnol are considered, with separated entries, definitely endangered languages according to the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger. Description As part of the Gallo-Italic languages, Emilian-Romagnol is most closely related to the Lombard, Piedmontese and Ligurian languages, all of which are spoken in neighboring regions. Among other Gallo-Italic languages, Emilian-Romagnol is characterized by systematic raising and diphthongization of latin stressed vowel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
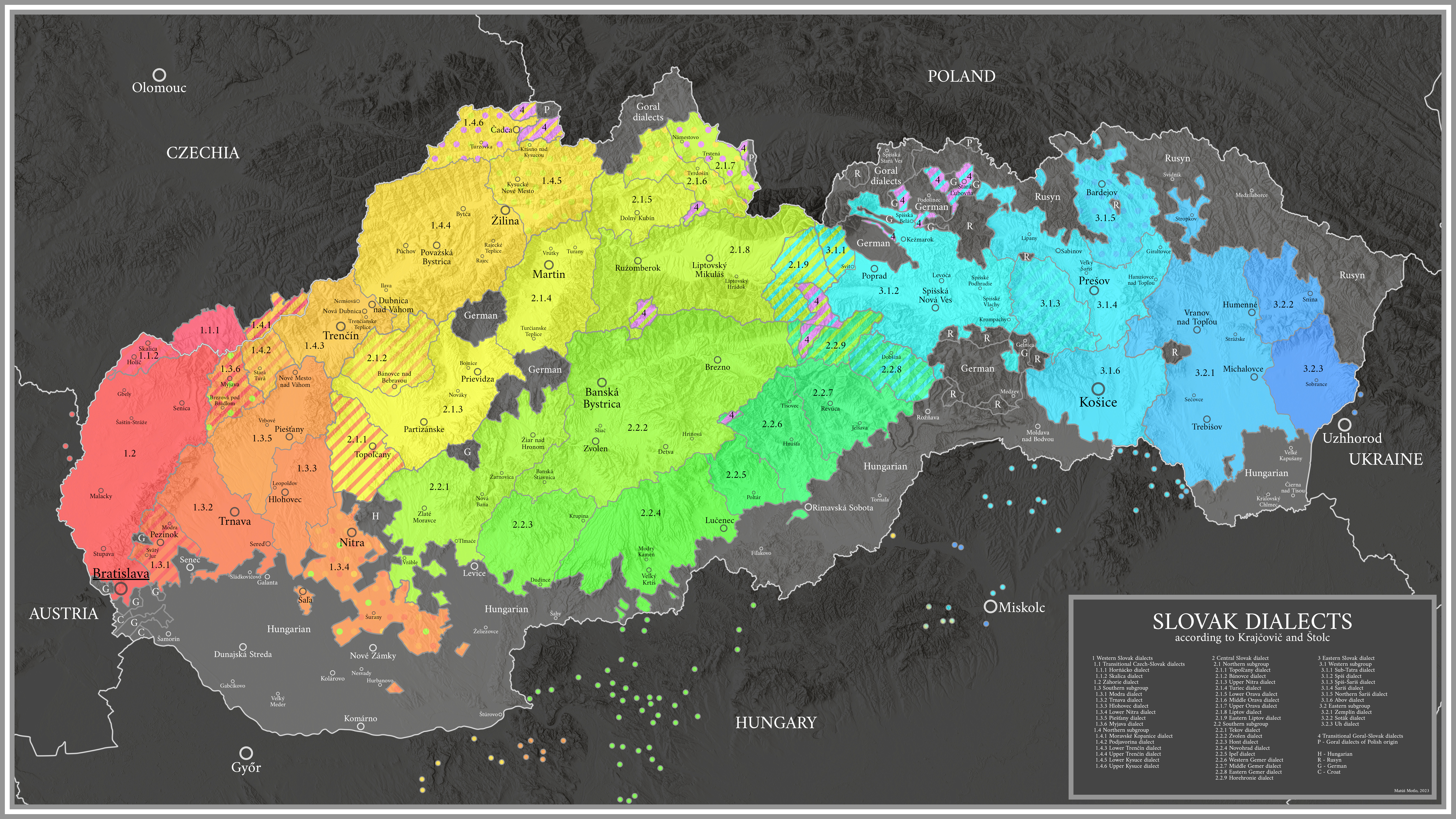
Slovak Language
Slovak () , is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of the larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by approximately 5 million people as a native language, primarily ethnic Slovaks, it serves as the official language of Slovakia and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Slovak is closely related to Czech, to the point of mutual intelligibility to a very high degree, as well as Polish. Like other Slavic languages, Slovak is a fusional language with a complex system of morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German and other Slavic languages. The Czech–Slovak group developed within West Slavic in the high medieval period, and the standardization of Czech and Slovak within the Czech–Slovak dialect continuum emerged in the early modern period. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moravian Language
Moravian dialects ( cs, moravská nářečí, moravština) are the varieties of Czech spoken in Moravia, a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic. There are more forms of the Czech language used in Moravia than in the rest of the Czech Republic. The main four groups of dialects are the Bohemian-Moravian group, the Central Moravian group, the Eastern Moravian group and the Lach (Silesian) group (which is also spoken in Czech Silesia). While the forms are generally viewed as regional variants of Czech, some Moravians (108,469 in the 2011 Census) claim them to be one separate Moravian language. Southeastern Moravian dialects form a dialect continuum with the closely related Slovak language, and are thus sometimes viewed as dialects of Slovak rather than Czech. Until the 19th century, the language used in Slavic-speaking areas of Moravia was referred to as “Moravian” or as “Czech”. When regular censuses started in Austria-Hungary in 1880, the choice of main-com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |