|
Rikuzentakata City Museum
is a city located in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. In the census of 2010, the city had a population of 23,302 (2005: 24,709), and a population density of 100 persons per km². The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami caused extensive damage to the city. , the city had an estimated population of 19,062, and a population density of 82 persons per km² in 7,593 households. The total area of the city is . Geography Rikuzentakata is located in the far southeast corner of Iwate Prefecture, bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the east. The city contained Lake Furukawanuma until the 2011 tsunami destroyed it. Parts of the coastal area of the city are within the borders of the Sanriku Fukkō National Park. Neighboring municipalities Iwate Prefecture * Ōfunato * Ichinoseki * Sumita Miyagi Prefecture * Kesennuma Climate Rikuzentakata has a humid climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') bordering on an oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfb'') with warm summers and cold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
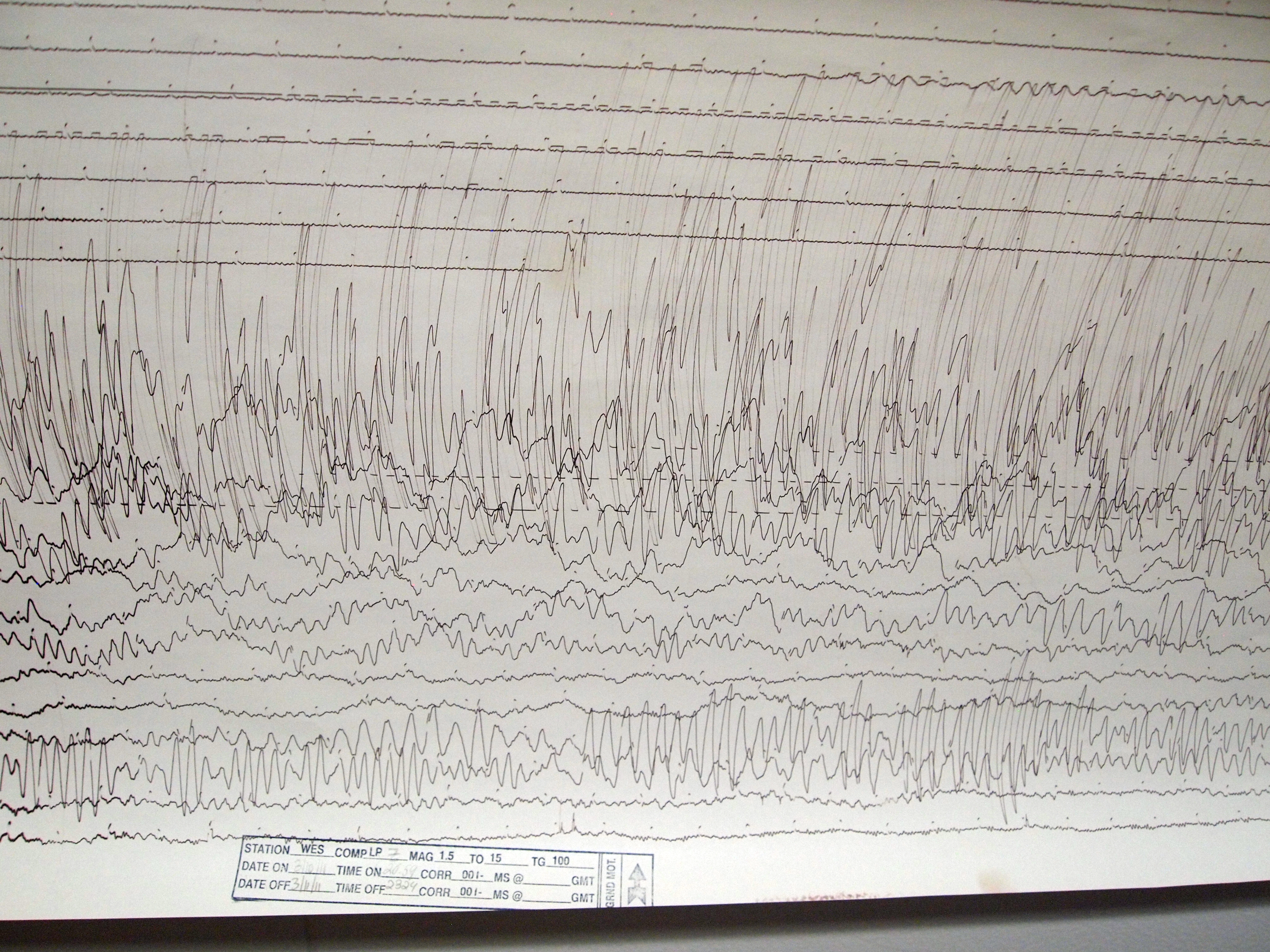
2011 Tōhoku Earthquake And Tsunami
The occurred at 14:46 JST (05:46 UTC) on 11 March. The magnitude 9.0–9.1 (M) undersea megathrust earthquake had an epicenter in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region, and lasted approximately six minutes, causing a tsunami. It is sometimes known in Japan as the , among other names. The disaster is often referred to in both Japanese and English as simply 3.11 (read in Japanese). It was the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan, and the fourth most powerful earthquake in the world since modern record-keeping began in 1900. The earthquake triggered powerful tsunami waves that may have reached heights of up to in Miyako in Tōhoku's Iwate Prefecture,Yomiuri Shimbun evening edition 2-11-04-15 page 15, nearby Aneyoshi fishery port (姉吉漁港)(Google map E39 31 57.8, N 142 3 7.6) 2011-04-15大震災の津波、宮古で38.9 m…明治三陸上回るby okayasu Akio (岡安 章夫) and which, in the Sendai area, traveled at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emishi
The (also called Ebisu and Ezo), written with Chinese characters that literally mean "shrimp barbarians," constituted an ancient ethnic group of people who lived in parts of Honshū, especially in the Tōhoku region, referred to as in contemporary sources. The first mention of the Emishi in literature that can be corroborated with outside sources dates to the 5th century AD, in which they are referred to as (毛人 - "hairy people") in Chinese records. Some Emishi tribes resisted the rule of various Japanese Emperors during the Asuka, Nara and early Heian periods (7th–10th centuries AD). The origin of the Emishi is disputed. They are often thought to have descended from some tribes of the Jōmon people. Some historians believe that they were related to the Ainu people, but others disagree with this theory and see them as a completely distinct ethnicity.Aston, W.G., trans. Nihongi: Chronicles of Japan from the Earliest Times to AD 697. Tokyo: Charles E.Tuttle Co., 1972 (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jōmon Period
The is the time in Japanese history, traditionally dated between 6,000–300 BCE, during which Japan was inhabited by a diverse hunter-gatherer and early agriculturalist population united through a common Jōmon culture, which reached a considerable degree of sedentism and cultural complexity. The name "cord-marked" was first applied by the American zoologist and orientalist Edward S. Morse, who discovered sherds of pottery in 1877 and subsequently translated it into Japanese as ''Jōmon''.Mason, 14 The pottery style characteristic of the first phases of Jōmon culture was decorated by impressing cords into the surface of wet clay and is generally accepted to be among the oldest in the world. The Jōmon period was rich in tools and jewelry made from bone, stone, shell and antler; pottery figurines and vessels; and lacquerware.Imamura, K. (1996) ''Prehistoric Japan: New Perspectives on Insular East Asia''. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press It is often compared to pre-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutsu Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and Aomori Prefectures and the municipalities of Kazuno and Kosaka in Akita Prefecture. Mutsu Province is also known as or . The term is often used to refer to the combined area of Mutsu and the neighboring province Dewa, which together make up the entire Tōhoku region. History Invasion by the Kinai government Mutsu, on northern Honshū, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the largest as it expanded northward. The ancient regional capital of the Kinai government was Tagajō in present-day Miyagi Prefecture. * 709 ('' Wadō 2, 3rd month''), an uprising against governmental authority took place in Mutsu and in nearby Echigo Province. Troops were dispatched to subdue the revolt. * 712 (''Wadō 5''), Mutsu was separated from Dewa Province. Empress Genmei's ''Daijō-kan'' made cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Meteorological Agency
The , abbreviated JMA, is an agency of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. It is charged with gathering and providing results for the public in Japan that are obtained from data based on daily scientific observation and research into natural phenomena in the fields of meteorology, hydrology, seismology and volcanology, among other related scientific fields. Its headquarters is located in Minato, Tokyo. JMA is responsible for gathering and reporting weather data and forecasts for the general public, as well as providing aviation and marine weather. JMA other responsibilities include issuing warnings for volcanic eruptions, and the nationwide issuance of earthquake warnings of the Earthquake Early Warning (EEW) system. JMA is also designated one of the Regional Specialized Meteorological Centers of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). It is responsible for forecasting, naming, and distributing warnings for tropical cyclones in the Northwestern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand. Precipitation Locations with oceanic climates tend to feature frequent cloudy conditions with precipitation, low hanging clouds, and frequent fronts and storms. Thunderstorms are normally few, since strong daytime heating and hot and cold air masses meet infrequently in the region. In most areas with an oceanic climate, precipitation comes in the form of rain for the majority of the year. However, some areas with this climate see some snowfall annually during winter. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humid Subtropical Climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° and are located poleward from adjacent tropical climates. It is also known as warm temperate climate in some climate classifications. Under the Köppen climate classification, ''Cfa'' and ''Cwa'' climates are either described as humid subtropical climates or warm temperate climates. This climate features mean temperature in the coldest month between (or ) and and mean temperature in the warmest month or higher. However, while some climatologists have opted to describe this climate type as a "humid subtropical climate", Köppen himself never used this term. The humid subtropical climate classification was officially created under the Trewartha climate classification. In this classification, climates are termed humid subtropical when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kesennuma, Miyagi
is a city in Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 59,803 and a population density of in 26,390 households. The total area of the city is . Large sections of the city were destroyed by the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami and major fires on March 11, 2011. Geography Kesennuma is in the far northeastern corner of Miyagi Prefecture. The city wraps around the western part of Kesennuma Bay and also includes the island of Ōshima. Its deeply indented rias coastline forms the southern boundary of the Sanriku Fukkō National Park, which stretches north to Aomori Prefecture. The city borders Hirota Bay, Kesennuma Bay, and the Pacific Ocean to the east and Minamisanriku, Miyagi to the south. Iwate Prefecture makes up the remainder of its borders, with the city of Ichinoseki to the west, and the city of Rikuzen-Takata to the north. The highest point in Kesennuma is the high Mount Ōmori, on the border with Motoyoshi, while the lowest point is at sea lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumita, Iwate
is a town located in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 5,315, and a population density of 16 persons per km² in 2142 households. The total area of the town is . Geography Sumita is located in a basin in southeastern Iwate Prefecture in the southern Kitakami Mountains, surrounded by peaks with an elevation of between 600 and 1500 meters an all sides. Approximately 90% of the town’s area is covered by forest and mountains. Neighboring municipalities Iwate Prefecture * Ōfunato *Rikuzentakata *Ichinoseki * Tōno *Kamaishi *Ōshū Climate Sumita has a humid climate (Köppen climate classification ''Dfa'') with warm summers and cold winters. The average annual temperature in Sumita is 10.4 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1379 mm with September as the wettest month and January as the driest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 23.1 °C, and lowest in January, at around -1.2 °C. Demographic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichinoseki, Iwate
is a city located in Iwate Prefecture, in the Tōhoku region of northern Japan. , the city had a population of 114,476 and a population density of 91 persons per km² in 46,375 households. It is currently the second largest city by population in the prefecture, after Morioka. The total area of the city was . Geography Ichinoseki is located inland in the south of Iwate Prefecture, a little over two hours north of Tokyo by the Tōhoku Shinkansen. A large volume of extremely stable granite rock runs beneath the city, and is the center of the site is being promoted as a suitable location for construction of the International Linear Collider (ILC). Neighboring municipalities Iwate Prefecture *Ōshū *Rikuzentakata * Sumita *Hiraizumi Miyagi Prefecture *Kesennuma *Kurihara * Tome Akita Prefecture * Higashinaruse Climate Ichinoseki has a humid climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') with warm summers and cold winters. The average annual temperature in Ichinoseki is 10.9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |