|
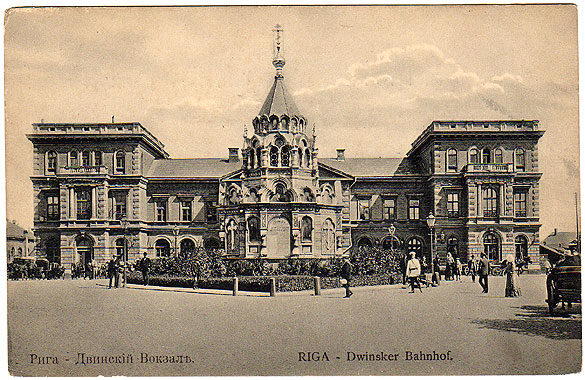
Riga Central Station
__NOTOC__ Riga Central Station ( lv, Rīgas Centrālā stacijа) is the main railway station in Riga, Latvia. It is known as the main point of Riga due to its central location, and most forms of public transport stop in this area. Part of the building is a shopping centre. Three rail mainlines depart the station to the east: * Riga–Skulte * Riga–Lugaži, through to the Estonian border crossing at Valka * Riga- Krustpils, which then splits into lines to Daugavpils and Zilupe, including international routes to the Russian, Belarusian & Lithuanian borders at Zilupe, & Turmantas. Two rail mainlines depart the station to the west: * Riga–Jelgava, including lines through to Liepāja & the Lithuanian border at Meitene * Riga–Tukums, including trains through to Ventspils History The first railway station in Riga was constructed to serve as the western terminal station of the new railway line from Riga to Daugavpils which was financed by British contractors and led by Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rīga
Riga (; lv, Rīga , liv, Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city of Latvia and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava (river), Daugava river where it meets the Baltic Sea. Riga's territory covers and lies above sea level, on a flat and sandy plain. Riga was founded in 1201 and is a former Hanseatic League member. Riga's historical centre is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, noted for its Art Nouveau/Jugendstil architecture and 19th century wooden architecture. Riga was the European Capital of Culture in 2014, along with Umeå in Sweden. Riga hosted the 2006 Riga summit, 2006 NATO Summit, the Eurovision Song Contest 2003, the 2006 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships, 2006 IIHF Men's World Ice Hockey Championships, 2013 World Women's Curling Championship and the 2021 IIHF World Championship. It is home to the European Union's office of Body of European Regulators of Electronic Communic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liepāja Station
Liepāja Station is the railway station for Liepāja on the Jelgava – Liepāja Railway. History The station was built in 1871 as the first station in the Libau–Romny Railway, Libau being the German German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) ** Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Ge ... name of the city in use at the time. References Liepāja Railway stations in Latvia Railway stations opened in 1871 {{Latvia-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daugava
, be, Заходняя Дзвіна (), liv, Vēna, et, Väina, german: Düna , image = Fluss-lv-Düna.png , image_caption = The drainage basin of the Daugava , source1_location = Valdai Hills, Russia , mouth_location = Gulf of Riga, Baltic Sea , mouth_coordinates = , subdivision_type1 = Country , subdivision_name1 = Belarus, Latvia, Russia , length = , source1_elevation = , mouth_elevation = , discharge1_avg = , basin_size = , pushpin_map = , pushpin_map_size = , pushpin_map_caption = , pushpin_map_alt = The Daugava ( ltg, Daugova; german: Düna) or Western Dvina (russian: Западная Двина, translit=Západnaya Dviná; be, Заходняя Дзвіна; et, Väina; fi, Väinäjoki) is a large river rising in the Valdai Hills of Russia that flows through Belarus and Latvia into the Gulf of Riga of the Baltic Sea. It rises close to the source of the Volga. It is in length, of which are in Latvia and are in Russia. It is a westward-flowing river, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torņakalns Station
Torņakalns Station is a railway station in the neighbourhood of Torņakalns in Riga, Latvia, located on the western bank of the Daugava River. Torņakalns Station is located on the Riga–Jelgava and Riga–Tukums railway lines. The station opened in 1868 as the northern terminus of the Riga–Jelgava railway line. From 1872, however, all trains were continued from the station via the Iron Bridge across the Daugava to the current Riga Central Station. In 1877, Torņakalns Station also became the eastern terminus of the Torņakalns–Tukums railway line. History The terminal of Riga–Jelgava Railway, was opened in 1868 and called ''Riga-Mitauer Bahnhof'' back then. This was a very important station, which secured the connection of Riga with Zemgale, but in 1872 one year after construction of the railway bridge across the Daugava , be, Заходняя Дзвіна (), liv, Vēna, et, Väina, german: Düna , image = Fluss-lv-Düna.png , image_caption = The drai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Police Station
A police station (sometimes called a "station house" or just "house") is a building which serves to accommodate police officers and other members of staff. These buildings often contain offices and accommodation for personnel and vehicles, along with locker rooms, temporary holding cells and interview/interrogation rooms. Names Large departments may have many stations to cover the area they serve. The names used for these facilities include: *Barracks for many American state police and highway patrol stations and in Ireland *District office, typically used by American state police forces like the California Highway Patrol, but also used by smaller departments like the Calgary Police Service *Precinct house, or precinct, for some urban police departments in the United States such as the New York City Police Department, Memphis Police Department, and Newark Police Department, where stations are in charge of precincts *Police house *Police office, especially in Scotland *Statio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post Office
A post office is a public facility and a retailer that provides mail services, such as accepting letters and parcels, providing post office boxes, and selling postage stamps, packaging, and stationery. Post offices may offer additional services, which vary by country. These include providing and accepting government forms (such as passport applications), and processing government services and fees (such as road tax, postal savings, or bank fees). The chief administrator of a post office is called a postmaster. Before the advent of postal codes and the post office, postal systems would route items to a specific post office for receipt or delivery. During the 19th century in the United States, this often led to smaller communities being renamed after their post offices, particularly after the Post Office Department began to require that post office names not be duplicated within a state. Name The term "post-office" has been in use since the 1650s, shortly after the legali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telegraph Office
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pigeon post is not. Ancient signalling systems, although sometimes quite extensive and sophisticated as in China, were generally not capable of transmitting arbitrary text messages. Possible messages were fixed and predetermined and such systems are thus not true telegraphs. The earliest true telegraph put into widespread use was the optical telegraph of Claude Chappe, invented in the late 18th century. The system was used extensively in France, and European nations occupied by France, during the Napoleonic era. The electric telegraph started to replace the optical telegraph in the mid-19th century. It was first taken up in Britain in the form of the Cooke and Wheatstone telegraph, initially used mostly as an aid to railway signalling. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Felsko
Johann Daniel Felsko (also Felskau; lv, Johans Daniels Felsko; — ) was a Baltic German architect, urban planner and the chief architect of Riga for 35 years in the period 1844—79. The most significant accomplishment of his creative work is the development of the center of Riga. Early life Johann Felsko was born 30 October 1813 in Riga as son of mason Johan Jakob Felskau (1779—1858), who 1805 emigrated from Königsberg, East Prussia, to settle in Riga. Johann's mother was Therese Luise Heydemann (died 1868) from Schönberg in Courland. Johann Felsko married Georgine Wilhelmine Groos from Copenhagen, Denmark in 1842; they had three children, two of them being architect Karl Johann (1844—1918) and painter Oskar Eduard Daniel (born 1848). Education Johann Felsko learned the building profession by being an apprentice to architect of Riga and master of the craft Johann Daniel Gottfriedt, until Gottfriedt died 1831. His education continued into the arts of technical d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg–Warsaw Railway
Saint Petersburg–Warsaw Railway (() (transliteration: Sankt-Peterburgo–Varshavskaya zheleznaya doroga)) is a long railway, built in the 19th century by the Russian Empire to connect Russia with Central Europe. At the time the entire railway was within the Russian Empire: Warsaw was under a Russian partition of Poland. Due to territorial changes, the line now lies within five countries and crosses the eastern border of the European Union three times. Therefore, no passenger trains follow the entire route. Passenger trains between Saint Petersburg and Warsaw today travel through Brest instead and a new line called Rail Baltica is under development to improve the direct connection between Poland and Lithuania. History Construction In February 1851 the Tsarist Government of Russia made a decision to build the St. Petersburg–Warsaw railway line with a length of approximately 1,250 kilometers. It was built to Russian gauge. Construction was completed in 1862. The first sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Arkadyevich Suvorov
Alexander Arkadyevich Suvorov, Prince Italsky, Count Rymniksky (russian: Алекса́ндр Арка́дьевич Суво́ров; 13 June 1804, Saint Petersburg – 12 February 1882, Saint Petersburg), was a Russian general, diplomat and politician. Life Education His parents were Arkadi Suvorov and his wife Elena Aleksandrovna Naryshkina, making him the grandson of Alexander Suvorov. His father was drowned in 1811 when Alexander was still a child. He was then sent to the Jesuit college in Saint Petersburg, where he was raised (as was then the fashion) alongside other sons of Russian aristocrats. Three years later, due to a change in his attitude towards the Jesuits, his uncle Cyril A. Naryshkin (who had himself been taught by the Jesuits) withdrew Alexander from the school and educated him himself, inviting the best teachers. Alexander's mother Elena was then living in Florence and wanted him beside her, so he moved to Italy, where (aged 13) he was placed in a school run b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor-General Of Baltic Provinces
The governor-general of the Baltic provinces or governor-general of Estonia, Livonia, and Courland () was the military commander of the Riga Military District and the highest administrator of the Baltic governorates of Estonia, Livonia and Courland sporadically under Russian rule in the 19th century. List of Russian governors-general of the Baltic provinces Governors-general of Riga * Anikita Repnin (1710–1726) appointed by Peter I of Russia * Peter Lacy (1729-1740) Governors-general of Livonia * Vladimir Petrovich Dolgorukiy (1758–1761)Eric Amburger: ''Geschichte der Behördenorganisation Russlands von Peter dem Grossen bis 1917'lk. 387-388/ref> * George Browne (1762–1791) * Nicholas Repnin (1792–1796) as the Governor-General of Livonia and Estonia Governors-general of Livonia, Estonia and Courland in Riga * Peter Ludwig von der Pahlen (1800–1801) Governor-General of Courland since 1795 * Sergei Fyodorovich Golitsyn ( ru) (1801–1803) * Friedrich Wilhelm von B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foundation Stone
The cornerstone (or foundation stone or setting stone) is the first stone set in the construction of a masonry foundation. All other stones will be set in reference to this stone, thus determining the position of the entire structure. Over time a cornerstone became a ceremonial masonry stone, or replica, set in a prominent location on the outside of a building, with an inscription on the stone indicating the construction dates of the building and the names of architect, builder, and other significant individuals. The rite of laying a cornerstone is an important cultural component of eastern architecture and metaphorically in sacred architecture generally. Some cornerstones include time capsules from, or engravings commemorating, the time a particular building was built. History The ceremony typically involved the placing of offerings of grain, wine and oil on or under the stone. These were symbolic of the produce and the people of the land and the means of their subsistence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |