|
Riess Spiral
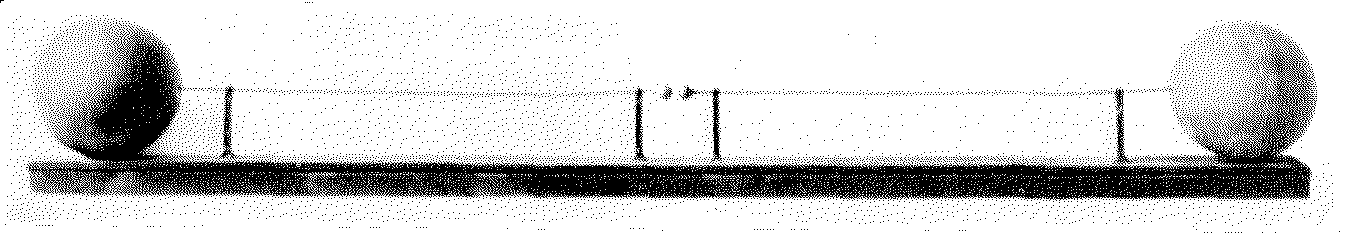
Riess spirals, or Knochenhauer spirals, are a pair of spirally wound conductors with metal balls at their ends. Placing one above the other forms an induction coil. Heinrich Hertz used them in his discovery of radio waves.Jed Buchwald, ''The Creation of Scientific Effects: Heinrich Hertz and Electric Waves'', 1994: Ch. 14: "A Novel Device", p. 219. They are named for German physicists Peter Theophil Riess Peter Theophil Riess (27 June 1804 – 22 October 1883) was a German physicist, known mostly for his work in electricity, particularly friction electricity, but also in the field of electromagnetic induction. In the latter work he developed two ... and K. W. Knochenhauer. References {{reflist External links Riess spiral pair Laboratory equipment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induction Coil
An induction coil or "spark coil" (archaically known as an inductorium or Ruhmkorff coil after Heinrich Rühmkorff) is a type of electrical transformer used to produce high-voltage pulses from a low-voltage direct current (DC) supply. p.98 To create the flux changes necessary to induce voltage in the secondary coil, the direct current in the primary coil is repeatedly interrupted by a vibrating mechanical contact called an interrupter. Invented in 1836 by Nicholas Callan, with additional research by Charles Grafton Page and others, the induction coil was the first type of transformer. It was widely used in x-ray machines, spark-gap radio transmitters, arc lighting and quack medical electrotherapy devices from the 1880s to the 1920s. Today its only common use is as the ignition coils in internal combustion engines and in physics education to demonstrate induction. Construction and function An induction coil consists of two coils of insulated wire wound around a common i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Hertz
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz ( ; ; 22 February 1857 – 1 January 1894) was a German physicist who first conclusively proved the existence of the electromagnetic waves predicted by James Clerk Maxwell's Maxwell's equations, equations of electromagnetism. The unit of frequency, cycle per second, was named the "hertz" in his honor.IEC History . Iec.ch. Biography Heinrich Rudolf Hertz was born in 1857 in Hamburg, then a sovereign state of the German Confederation, into a prosperous and cultured Hanseatic (class), Hanseatic family. His father was Gustav Ferdinand Hertz. His mother was Anna Elisabeth Pfefferkorn. While studying at the Gelehrtenschule des Johanneums in Hamburg, Hertz showed an aptitude for sciences as well as languages, learning Arabic. He studied sciences and engineering in th ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Theophil Riess
Peter Theophil Riess (27 June 1804 – 22 October 1883) was a German physicist, known mostly for his work in electricity, particularly friction electricity, but also in the field of electromagnetic induction. In the latter work he developed two devices, the spark micrometer (sometimes called the Riess micrometer) and the Riess spiral coils, both of which were used by Heinrich Hertz in his experiments to prove the propagation of electromagnetic waves. Riess was the son of a wealthy jeweller in Berlin. He received his doctorate in 1831 from the University of Berlin. In the early years after graduation he stayed with his father who was ill and helped run the business. Even after his father died, he never sought an academic teaching position. However he was a fellow (Mitglied) of the Berlin Academy, the first Jewish member of that academy, and under its auspices, and within its journal, Riess published prolifically. He also published several books, as well as many articles in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |