|
Riesenburg
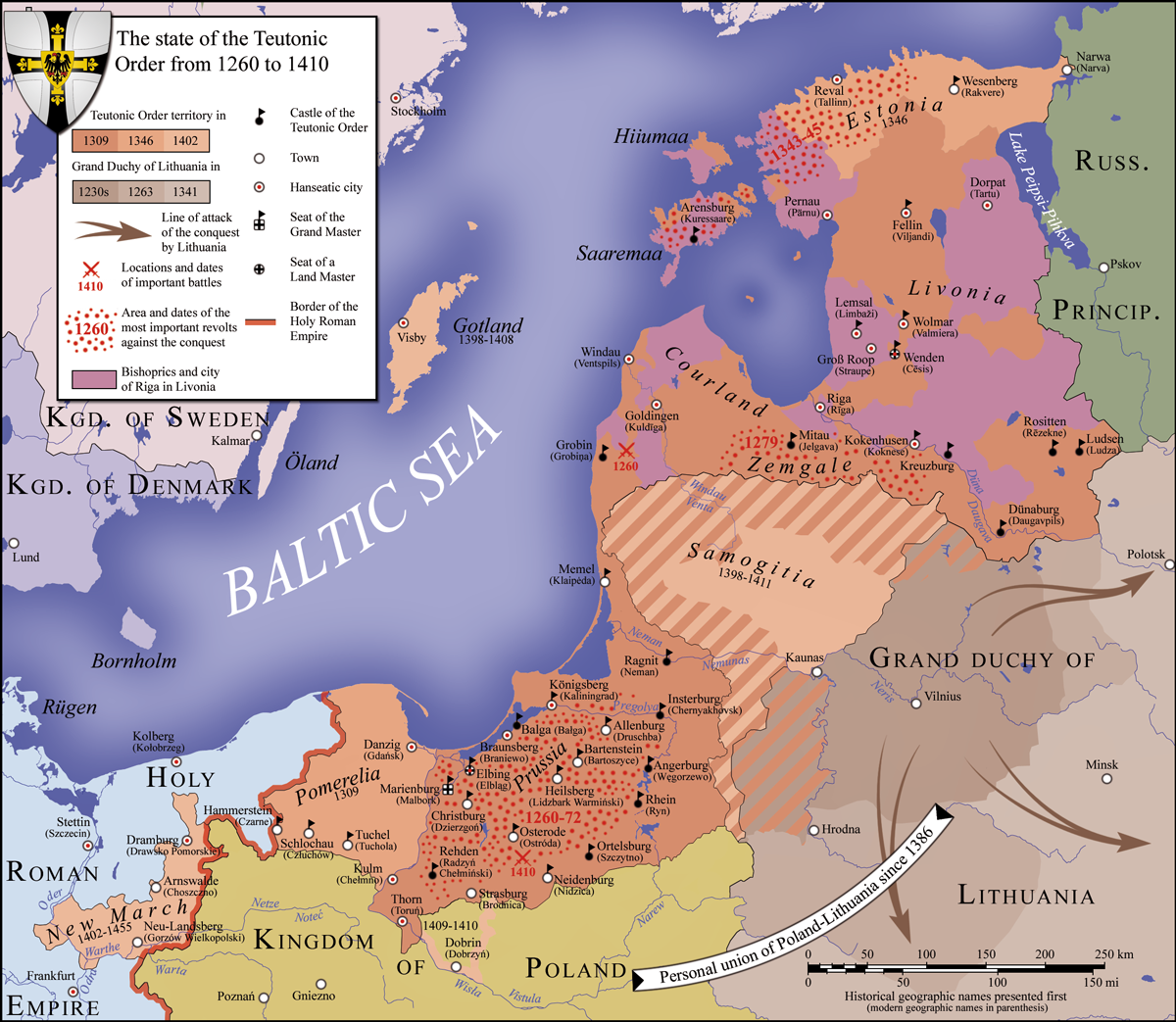
Prabuty (german: Riesenburg) is a town in Kwidzyn County within the Pomeranian Voivodeship of northern Poland. Before World War I, the town belonged to the German province of West Prussia. It was ceded to Poland in 1945. Between 1975 and 1998, Prabuty was part of the Elbląg Voivodeship. Geographical location Prabuty is located approximately 18 kilometers east of Kwidzyn, 100 kilometers southeast of Gdańsk, 100 kilometers west of Olsztyn, and 133 kilometers southwest of Kaliningrad. Prabuty is a rail junction on the Warszawa–Gdynia railway. History In 1236, the Teutonic Knights under Henry III, Margrave of Meissen, destroyed an Old Prussian fortress between the lakes Dzierzgoń and Liwieniec. The settlement was first mentioned in 1250 as ''Riesenburg''. The village grew around the castle and received Culm law city rights on 30 October 1330 from bishop Rudolf of Pomerania (1322–1332). In 1379 the town was visited by Lithuanian duke Švitrigaila.''Słownik geograficzny Kr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivodeships Of Poland
A voivodeship (; pl, województwo ; plural: ) is the highest-level administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as "province". The Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998, which went into effect on 1 January 1999, created sixteen new voivodeships. These replaced the 49 former voivodeships that had existed from 1 July 1975, and bear a greater resemblance (in territory, but not in name) to the voivodeships that existed between 1950 and 1975. Today's voivodeships are mostly named after historical and geographical regions, while those prior to 1998 generally took their names from the cities on which they were centered. The new units range in area from under (Opole Voivodeship) to over (Masovian Voivodeship), and in population from nearly one million (Opole Voivodeship) to over five million (Masovian Voivodeship). Administrative authority at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gdynia
Gdynia ( ; ; german: Gdingen (currently), (1939–1945); csb, Gdiniô, , , ) is a city in northern Poland and a seaport on the Baltic Sea coast. With a population of 243,918, it is the List of cities in Poland, 12th-largest city in Poland and the second-largest in the Pomeranian Voivodeship after Gdańsk. Gdynia is part of a conurbation with the spa town of Sopot, the city of Gdańsk, and suburban communities, which together form a metropolitan area called the Tricity, Poland, Tricity (''Trójmiasto'') with around 1,000,000 inhabitants. Historically and culturally part of Kashubia and Pomerelia, Eastern Pomerania, Gdynia for centuries remained a small fishing village. By the 20th-century it attracted visitors as a seaside resort town. In 1926, Gdynia was granted city rights after which it enjoyed demographic and urban development, with a Modernist architecture, modernist cityscape. It became a major seaport city of Poland. In 1970, 1970 Polish protests, protests in and aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Peace Of Thorn (1466)
The Peace of Thorn or Toruń of 1466, also known as the Second Peace of Thorn or Toruń ( pl, drugi pokój toruński; german: Zweiter Friede von Thorn), was a peace treaty signed in the Hanseatic city of Thorn (Toruń) on 19 October 1466 between the Polish king Casimir IV Jagiellon and the Teutonic Knights, which ended the Thirteen Years' War, the longest of the Polish–Teutonic Wars. The treaty was signed in the Artus Court, and afterward a mass was held in the Gothic Franciscan Church of the Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary to celebrate the peace treaty. Background The treaty concluded the Thirteen Years' War which had begun in February 1454 with the revolt of the Prussian Confederation, led by the cities of Danzig (Gdańsk), Elbing (Elbląg), Kulm (Chełmno) and Toruń, and the Prussian gentry Gentry (from Old French ''genterie'', from ''gentil'', "high-born, noble") are "well-born, genteel and well-bred people" of high social class, especially in the past. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Chojnice (1454)
The Battle of Chojnice (or Battle of Konitz) occurred on 18 September 1454 near the town of Chojnice, between Poland and the Teutonic Knights during the Thirteen Years' War. The battle was won by the Teutonic Knights. Background The Teutonic army had around 9,000 cavalry and 6,000 infantry under Bernhard von Zinnenberg. The Polish army had 16,000 cavalry, a few thousand servants (who could and usually were used in battles), a few hundred infantry, plus 500 mercenaries and burghers from Gdańsk and 2,000 mercenaries hired by the Prussian Confederacy, all under the command of King Casimir IV, advised by chancellor Jan Koniecpolski and Piotr of Szczekociny. The Polish commanders were counting on the battle being won by the Polish heavy cavalry, not caring much about either artillery or infantry. They had not thought that their opponents could change their traditional strategy, or that the Teutonic soldiers besieged in Chojnice could be anything more than spectators. Bernard v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466)
The Thirteen Years' War (german: Dreizehnjähriger Krieg; pl, wojna trzynastoletnia), also called the War of the Cities, was a conflict fought in 1454–1466 between the Prussian Confederation, allied with the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, and the State of the Teutonic Order. The war began as an uprising by Prussian cities and local nobility to win independence from the Teutonic Knights. In 1454 Casimir IV married Elisabeth of Habsburg and the Prussian Confederation asked Poland's King Casimir IV Jagiellon for help and offered to accept the king as protector instead of the Teutonic Order. When the King assented, war broke out between supporters of the Prussian Confederation, backed by Poland, and backers of government by the Teutonic Knights. The Thirteen Years' War ended in the victory of the Prussian Confederation and Poland and in the Second Peace of Thorn (1466). This was soon followed by the War of the Priests (1467–1479), a drawn-out dispute over the independence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Poland (1385–1569)
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, including the Kingdom of Poland proper. The Polish Crown was at the helm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1569 to 1795. Major political events The Kingdom of Poland has been traditionally dated back to c. 966, when Mieszko I and his pagan Slavic realm joined Christian Europe (Baptism of Poland), establishing the state of Poland, a process started by his Polan Piast dynasty ancestors. His oldest son and successor, Prince Bolesław I Chrobry, Duke of Poland, became the first crowned King of Poland in 1025. Union of Krewo The Union of Krewo was a set of prenuptial agreements made in the Kreva Castle on August 13, 1385. Once Jogaila confirmed the prenuptial agreements on August 14, 1385, Poland and Lithuania formed a personal uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casimir IV Jagiellon
Casimir IV (in full Casimir IV Andrew Jagiellon; pl, Kazimierz IV Andrzej Jagiellończyk ; Lithuanian: ; 30 November 1427 – 7 June 1492) was Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1440 and King of Poland from 1447, until his death. He was one of the most active Polish-Lithuanian rulers, under whom Poland, by defeating the Teutonic Knights in the Thirteen Years' War recovered Pomerania, and the Jagiellonian dynasty became one of the leading royal houses in Europe. The great triumph of his reign was bringing Prussia under Polish rule. The rule of Casimir corresponded to the age of "new monarchies" in western Europe. By the 15th century, Poland had narrowed the distance separating it from western Europe and become a significant factor in international relations. The demand for raw materials and semi-finished goods stimulated trade, producing a positive balance, and contributed to the growth of crafts and mining in the entire country. He was a recipient of the English Order of the Gart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian Confederation
The Prussian Confederation (german: Preußischer Bund, pl, Związek Pruski) was an organization formed on 21 February 1440 at Kwidzyn (then officially ''Marienwerder'') by a group of 53 nobles and clergy and 19 cities in Prussia, to oppose the arbitrariness of the Teutonic Knights. It was based on an earlier similar organization, the Lizard Union established in 1397 by the nobles of Chełmno Land. In 1454, the leader of the Confederation, Johannes von Baysen (Jan Bażyński), formally asked King Casimir IV Jagiellon, to incorporate Prussia into the Kingdom of Poland. This marked the beginning of the Thirteen Years' War between the Order's State and Poland, with the cities co-financing the military costs of the latter. Background According to the 1411 First Peace of Thorn which followed the Teutonic Knights' defeat in the Battle of Grunwald, the Teutonic Order had to pay high reparations to the Kingdom of Poland. The monastic state imposed high taxes on the cities to raise t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squire
In the Middle Ages, a squire was the shield- or armour-bearer of a knight. Use of the term evolved over time. Initially, a squire served as a knight's apprentice. Later, a village leader or a lord of the manor might come to be known as a "squire", and still later, the term was applied to members of the landed gentry. In contemporary American usage, "squire" is the title given to justices of the peace or similar local dignitaries. ''Squire'' is a shortened version of the word ''esquire'', from the Old French (modern French ), itself derived from the Late Latin ("shield bearer"), in medieval or Old English a ''scutifer''. The Classical Latin equivalent was ("arms bearer"). Knights in training The most common definition of ''squire'' refers to the Middle Ages. A squire was typically a young boy, training to become a knight. A boy became a page at the age of 7 then a squire at age 14. Squires were the second step to becoming a knight, after having served as a page. Boys s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Švitrigaila
Švitrigaila (before 1370 – 10 February 1452; sometimes spelled Svidrigiello) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1430 to 1432. He spent most of his life in largely unsuccessful dynastic struggles against his cousins Vytautas and Sigismund Kęstutaitis. Etymology of the name The name might be made of the roots Swede, Swedish rike - a kingdom or Latin rex, regis - a king and a suffix -aila, -ielo or a root of Prussian gailis - white, Lithuanian galas - phalos as by possibility in Ashurbanipal or English roots all, whole. The name coincides with his ruled lands - part of modern Russia, from Rus' people. His brothers' names were made following the same pattern: Skirgaila, Karigaila, Jogaila. Early life and Vitebsk rebellion Švitrigaila was born to Algirdas, Grand Duke of Lithuania, and his second wife Uliana of Tver. His date of birth is unknown, but it is believed that he was the youngest or second youngest son of Algirdas. He first appeared in politics in October 1382 when h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culm Law
Kulm law, Culm law or Chełmno Law (german: Kulmer Recht; lat, Jus Culmense vetus; pl, Prawo chełmińskie) was a legal constitution for a municipal form of government used in several Central European cities during the Middle Ages. It was initiated on 28 December 1233 in the Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights by Hochmeister Hermann von Salza and Hermann Balk when the towns of Thorn (Toruń) and Chełmno (Kulm) received German town law, in particular as a modification of Magdeburg rights. Named after the town it was signed in, the original document (''Kulmer Handfeste'') was lost in 1244 when the town hall burned due to an attack by Swantopolk II, Duke of Pomerania. The renewed charter of 1 October 1251 was based on a copy in Thorn, but the rights were reduced. This type of law was mostly granted by the Teutonic Order to cities within their monastic state, but also adopted by cities elsewhere, mainly in the neighboring independent Duchy of Masovia. In addition, the Kulm law w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Prussians
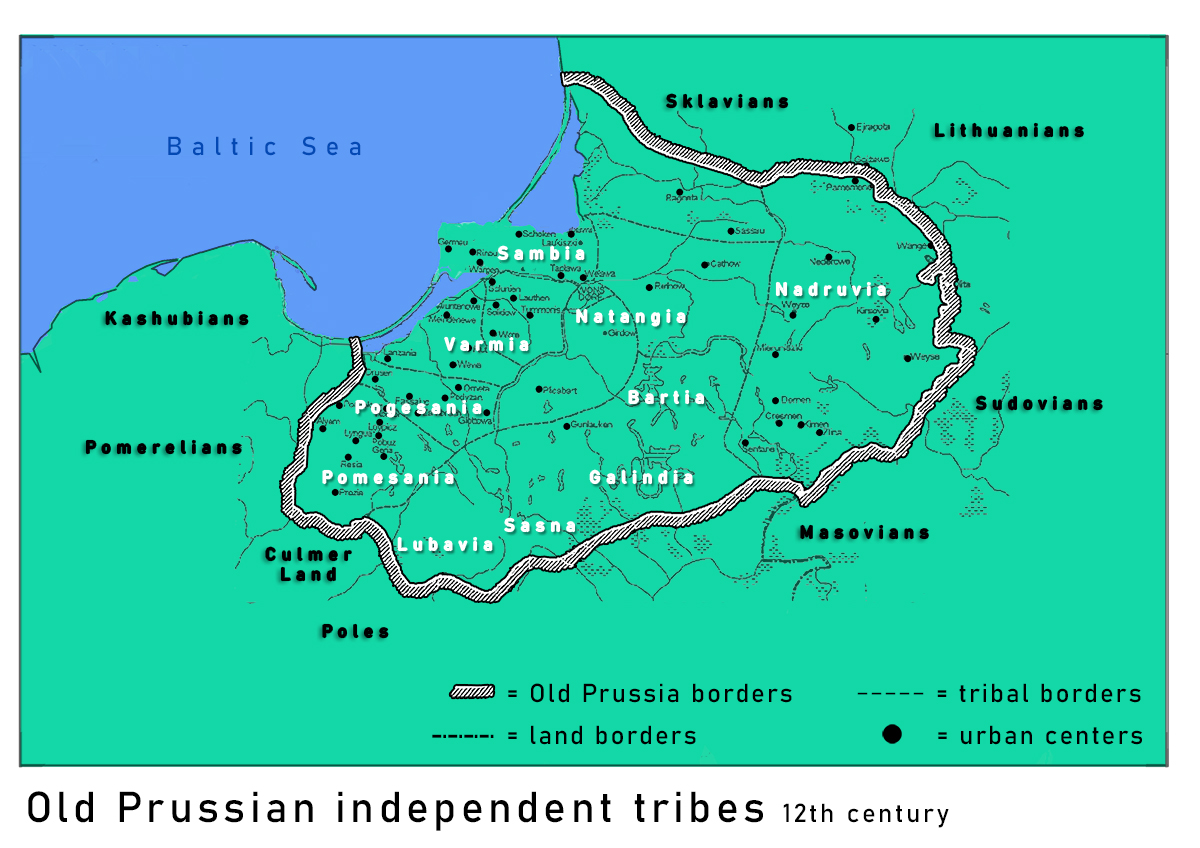
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians (Old Prussian: ''prūsai''; german: Pruzzen or ''Prußen''; la, Pruteni; lv, prūši; lt, prūsai; pl, Prusowie; csb, Prësowié) were an indigenous tribe among the Baltic peoples that inhabited the region of Prussia, at the south-eastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon to the east. The Old Prussians, who spoke an Indo-European language now known as Old Prussian and worshipped pre-Christian deities, lent their name, despite very few commonalities, to the later, predominantly Low German-speaking inhabitants of the region. The duchy of the Polans under Mieszko I, which was the predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland, first attempted to conquer and baptize the Baltic tribes during the 10th century, but repeatedly encountered strong resistance. Not until the 13th century were the Old Prussians subjugated and their lands conquered by the Teutonic Order. The remaining Old Prus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |