|
Ricinulei From Fernandez
Ricinulei is a small order of arachnids. Like most arachnids, they are predatory, eating small arthropods. They occur today in west-central Africa (''Ricinoides'') and the Neotropics (''Cryptocellus'' and ''Pseudocellus'') as far north as Texas. As of 2021, 91 extant species of ricinuleids have been described worldwide, all in the single family Ricinoididae. In older works they are sometimes referred to as Podogona. Due to their obscurity they do not have a proper common name, though in academic literature they are occasionally referred to as hooded tickspiders. In addition to the three living genera, there are fossil species from the upper Carboniferous of Euramerica and the Cretaceous Burmese amber. Description The most important general account of ricinuleid anatomy remains the 1904 monograph by Hans Jacob Hansen and William Sørensen. Useful further studies can be found in, e.g., the work of Pittard and Mitchell, Gerald Legg and L. van der Hammen. Body Ricinulei are typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
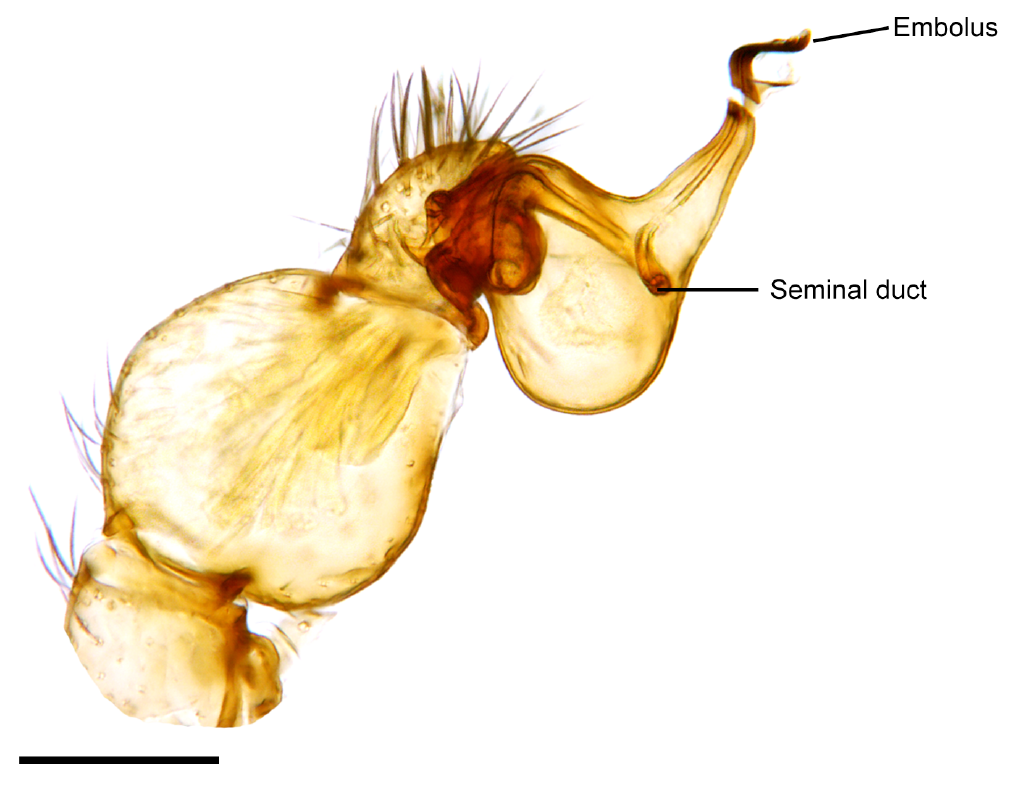
Cryptocellus Goodnighti
''Cryptocellus goodnighti'' is an arachnid species in the genus ''Cryptocellus ''Cryptocellus'' is an arachnid genus in the order Ricinulei, first described by John Westwood in 1874. It is native to the Neotropics The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physic ...''. It occurs in Costa Rica.On the female of Cryptocellus goodnighti Arachnida: Ricinulei. Norman I. Platnick, The Journal of Arachnology, 1993, Volume 21, no. 1, pages 79-80article Retrieved 26 March 2016 References External links * * Arthropods of Central America Ricinulei Animals described in 1981 {{Arachnid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Zoology
The ''Journal of Zoology'' is a scientific journal concerning zoology, the study of animals. It was founded in 1830 by the Zoological Society of London and is published by Wiley-Blackwell. It carries original research papers, which are targeted towards general readers. Some of the articles are available via open access, depending on the author's wishes. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 2.322, ranking it 36th out of 175 journals in the category "Zoology". From around 1833, it was known as the ''Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London'' (). From 1965 to 1984, it was known as the ''Journal of Zoology: Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London'' (). See also * List of zoology journals This is a list of scientific journals which cover the field of zoology. A * '' Acta Entomologica Musei Nationalis Pragae'' * '' Acta Zoologica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae'' * '' Acta Zoologica Bulgarica'' * ''Acta Zoologica Mex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod Structure & Development
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. Their nervous system is "ladder-lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part, or natural prolongation, that protrudes from an organism's body. In arthropods, an appendage refers to any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment, including antennae, mouthparts (including mandibles, maxillae and maxillipeds), gills, locomotor legs ( pereiopods for walking, and pleopods for swimming), sexual organs (gonopods), and parts of the tail (uropods). Typically, each body segment carries one pair of appendages. An appendage which is modified to assist in feeding is known as a maxilliped or gnathopod. In vertebrates, an appendage can refer to a locomotor part such as a tail, fins on a fish, limbs (legs, flippers or wings) on a tetrapod; exposed sex organ; defensive parts such as horns and antlers; or sensory organs such as auricles, proboscis ( trunk and snout) and barbels. Appendages may become ''uniramous'', as in insects and centipedes, where each appendage comprises a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles: the coxa, the trochanter, the femur, the short patella, the tibia, and the tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs, as in spiders, or chelate weapons ( pincers) of great size, as in scorpions. The pedipalps of Solifugae are covered in setae, but have not been studied in detail. Comparative studies of pedipalpal morphology may suggest that leg-like pedipalps are primitive in arachnids. At present, the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelicerae
The chelicerae () are the mouthparts of the subphylum Chelicerata, an arthropod group that includes arachnids, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. Commonly referred to as "jaws", chelicerae may be shaped as either articulated fangs, or similarly to pincers. Some chelicerae, such as those found on nearly all spiders, are hollow and contain (or are connected to) venom glands, and are used to inject venom into prey or a perceived threat. In ''Pisaurina mira'', also known as the nursery web spider, the chelicerae are utilized to snatch the prey once it becomes within reach, facilitating the "sit-and-wait ambush predator" behavior. Both pseudoscorpions and harvestmen have structures on their chelicerae that are used for grooming (papillae in pseudoscorpions, cheliceral teeth in Opiliones). Types Chelicerae can be divided into three kinds: jackknife chelicerae, scissor chelicerae, and 3-segmented chelate chelicerae. Jackknife chelicerae The jackknife chelicera is subchelate (with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ricinulei From Fernandez & Giribet, Male Ricinoides Karschii From Campo Reserve, Cameroon (2015) (cropped)
Ricinulei is a small order of arachnids. Like most arachnids, they are predatory, eating small arthropods. They occur today in west-central Africa ('' Ricinoides'') and the Neotropics ('' Cryptocellus'' and '' Pseudocellus'') as far north as Texas. As of 2021, 91 extant species of ricinuleids have been described worldwide, all in the single family Ricinoididae. In older works they are sometimes referred to as Podogona. Due to their obscurity they do not have a proper common name, though in academic literature they are occasionally referred to as hooded tickspiders. In addition to the three living genera, there are fossil species from the upper Carboniferous of Euramerica and the Cretaceous Burmese amber. Description The most important general account of ricinuleid anatomy remains the 1904 monograph by Hans Jacob Hansen and William Sørensen. Useful further studies can be found in, e.g., the work of Pittard and Mitchell, Gerald Legg and L. van der Hammen. Body Ricinulei are ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosoma
The cephalothorax, also called prosoma in some groups, is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. (The terms ''prosoma'' and ''opisthosoma'' are equivalent to ''cephalothorax'' and ''abdomen'' in some groups.) The word ''cephalothorax'' is derived from the Greek words for head (, ') and thorax (, '). This fusion of the head and thorax is seen in chelicerates and crustaceans; in other groups, such as the Hexapoda (including insects), the head remains free of the thorax. In horseshoe crabs and many crustaceans, a hard shell called the carapace covers the cephalothorax. Arachnid anatomy Fovea The fovea is the centre of the cephalothorax and is located behind the head (only in spiders).Dalton, Steve (2008). ''Spiders; The Ultimate Predators''. A & C Black, London. P.p. 19. . It is often important in identification. It can be transverse or procurved Smith, A. M. (1990c). Baboon spiders: Tarantulas of Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthosoma
The opisthosoma is the posterior part of the body in some arthropods, behind the prosoma (cephalothorax). It is a distinctive feature of the subphylum Chelicerata (arachnids, horseshoe crabs and others). Although it is similar in most respects to an abdomen (and is often referred to as such), the opisthosoma is differentiated by its inclusion of the respiratory organs (book lungs or book gills) and the heart. Segments The number of segments and appendages on the opisthosoma vary. Scorpions have 13, but the first is only seen during its embryological development. Other arachnids have fewer; harvestmen, for instance, have only ten. In general, appendages are absent or reduced, although in horseshoe crabs they persist as large plate-like limbs, called opercula or branchiophores, bearing the book gills, and that function in locomotion and gas exchange. In most chelicerates the opisthosomal limbs are greatly reduced and persist only as specialized structures, such as the silk-producing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Carboniferous
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) In scheduling, tardiness is a measure of a delay in exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(cropped).jpg)