|
Richter Peaks
Richter Peaks () is a group of peaks rising to about 1,385 m located near the southern extremity of the Walton Mountains, situated in the central portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. The peaks were named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Joseph J. Richter, United States Antarctic Research Program biologist, Palmer Station, 1965–66 and 1966–67. See also * Landers Peaks The Landers Peaks () are a group of peaks east of Mount Braun, rising to about between Palestrina Glacier and Nichols Snowfield in the northern portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. They were named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Na ... * Mussorgsky Peaks * Staccato Peaks Mountains of Alexander Island {{AlexanderIsland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summit (topography)
A summit is a point on a surface that is higher in elevation than all points immediately adjacent to it. The topographic terms acme, apex, peak (mountain peak), and zenith are synonymous. The term (mountain top) is generally used only for a mountain peak that is located at some distance from the nearest point of higher elevation. For example, a big, massive rock next to the main summit of a mountain is not considered a summit. Summits near a higher peak, with some prominence or isolation, but not reaching a certain cutoff value for the quantities, are often considered ''subsummits'' (or ''subpeaks'') of the higher peak, and are considered part of the same mountain. A pyramidal peak is an exaggerated form produced by ice erosion of a mountain top. Summit may also refer to the highest point along a line, trail, or route. The highest summit in the world is Mount Everest with a height of above sea level. The first official ascent was made by Tenzing Norgay and Sir Edmund Hillary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walton Mountains
Walton Mountains is an isolated chain of three predominantly snow-covered mountain masses, rising to about 1,450 m at Mount McArthur, extending south from Schubert Inlet for 25 miles (40 km) in central Alexander Island, Antarctica. The mountains were first sighted from the air by Lincoln Ellsworth on November 23, 1935, and roughly mapped from photos obtained on that flight by W.L.G. Joerg. Resighted from the air by the United States Antarctic Service in 1940, and in 1947 by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition under Ronne. Ronne named the mountains after Lieutenant Colonel R.C. Walton, United States Marine Corps, of the Office of Naval Research, who was instrumental in obtaining the loan of a ship from the Navy and in securing Navy assistance for the Ronne expedition. See also * Havre Mountains * Lassus Mountains * Rouen Mountains The Rouen Mountains () are a prominent mountain range, reaching to about 2,800 m and extending 35 miles (60 km) NW-SE from Mount B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
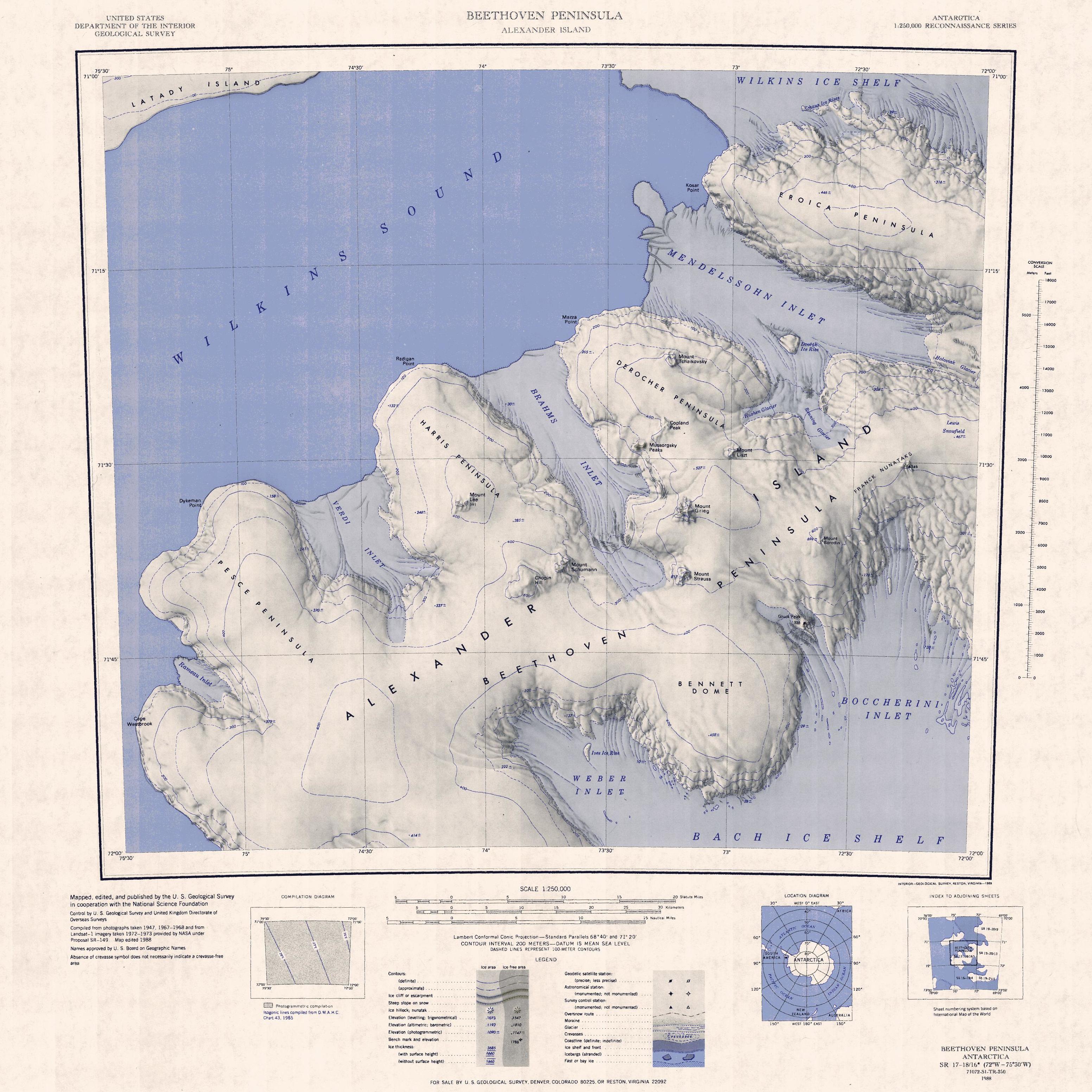
Alexander Island
Alexander Island, which is also known as Alexander I Island, Alexander I Land, Alexander Land, Alexander I Archipelago, and Zemlja Alexandra I, is the largest island of Antarctica. It lies in the Bellingshausen Sea west of Palmer Land, Antarctic Peninsula from which it is separated by Marguerite Bay and George VI Sound. The George VI Ice Shelf entirely fills George VI Sound and connects Alexander Island to Palmer Land. The island partly surrounds Wilkins Sound, which lies to its west.Stewart, J. (2011) ''Antarctic An Encyclopedia'' McFarland & Company Inc, New York. 1776 pp. . Alexander Island is about long in a north–south direction, wide in the north, and wide in the south. Alexander Island is the second-largest uninhabited island in the world, after Devon Island. History Alexander Island was discovered on January 28, 1821, by a Russian expedition under Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen, who named it Alexander I Land for the reigning Tsar Alexander I of Russia. Wha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Antarctic Research Program
The United States Antarctic Program (or USAP; formerly known as the United States Antarctic Research Program or USARP and the United States Antarctic Service or USAS) is an organization of the United States government which has presence in the Antarctica continent. Founded in 1959, the USAP manages all U.S. scientific research and related logistics in Antarctica as well as aboard ships in the Southern Ocean. United States Antarctic Program The United States established the U.S. Antarctic Research Program (USARP) in 1959—the name was later changed to the U.S. Antarctic Program—immediately following the success of the International Geophysical Year (IGY). Today, the National Science Foundation (NSF) has a Presidential Mandate to manage the United States Antarctic Program, through which it operates three year-round research stations and two research vessels, coordinates all U.S. science on the southernmost continent, and works with other federal agencies, the U.S. military, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual cell, a multicellular organism, or a community of interacting populations. They usually specialize in a particular branch (e.g., molecular biology, zoology, and evolutionary biology) of biology and have a specific research focus (e.g., studying malaria or cancer). Biologists who are involved in basic research have the aim of advancing knowledge about the natural world. They conduct their research using the scientific method, which is an empirical method for testing hypotheses. Their discoveries may have applications for some specific purpose such as in biotechnology, which has the goal of developing medically useful products for humans. In modern times, most biologists have one or more academic degrees such as a bachelor's degree plus an advanced degree like a master's degree or a doctorate. Like other scientists, biologists can be fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmer Station
Palmer Station is a United States research station in Antarctica located on Anvers Island, the only US station located north of the Antarctic Circle. Initial construction of the station finished in 1968. The station, like the other U.S. Antarctic stations, is operated by the United States Antarctic Program (USAP) of the National Science Foundation. The base is about as distant from the equator as Fairbanks, Alaska. Description The station is named for Nathaniel B. Palmer, usually recognized as the first American to see Antarctica. The maximum population that Palmer Station can accommodate is 46 people. The normal austral summer contingent varies, but it is generally around 40 people. Palmer is staffed year-round; however, the population drops to 15-20 people for winter maintenance after the conclusion of the summer research season. There are science labs located in the Bio-Lab building (pictured), the other main building is GWR (Garage, Warehouse, and Recreation). Webcam image ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landers Peaks
The Landers Peaks () are a group of peaks east of Mount Braun, rising to about between Palestrina Glacier and Nichols Snowfield in the northern portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. They were named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Commander Robert J. Landers, U.S. Navy, an LC-130 aircraft pilot in Squadron VXE-6 during U.S. Navy Operation Deep Freeze, 1965 and 1966. See also * Lamina Peak * Mimas Peak * Saint George Peak Saint George Peak (Russian: "Gora Svyatogo Georgiya Pobedonostsa") is a peak rising to about 1,500 m in the western part of the Havre Mountains, situated 3 mi northeast of Cape Vostok within the northwest portion of Alexander Island, Antarc ... References Mountains of Alexander Island {{AlexanderIsland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mussorgsky Peaks
Mussorgsky Peaks () are two rocky peaks rising to about 500 m lying northwest of Mount Grieg on the base of the Derocher Peninsula, a minor, ice-covered peninsula that protrudes out from the Beethoven Peninsula into the Wilkins Ice Shelf in the southwest portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. A number of peaks in this vicinity first appear on maps by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48. These peaks, apparently included within that group, were mapped from RARE air photos by Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1960. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) after Modeste Mussorgsky (1839–81), Russian composer. See also * Landers Peaks * Miranda Peaks * Richter Peaks Richter Peaks () is a group of peaks rising to about 1,385 m located near the southern extremity of the Walton Mountains, situated in the central portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. The peaks were named by Advisory Committee on Anta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staccato Peaks
Staccato Peaks () is a series of rock peaks extending 11 miles (18 km) in a north–south direction, rising to about 940 m with Hageman Peak Hageman Peak () is a montane landform pinnacle rising to about at the northwest end of the Staccato Peaks in southern Alexander Island, Antarctica. The peak was photographed from the air by Lincoln Ellsworth in 1935, and was named by the Advisor ... being the highest peak of the Staccato Peaks, rising from the snowfields 20 miles (32 km) south of the Walton Mountains in the south part of Alexander Island, Antarctica. The peaks were first sighted from the air by Lincoln Ellsworth on November 23, 1935, and mapped from photos taken on that flight by W.L.G. Joerg. Remapped from air photos taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in 1947–48, by Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1960. The name, given by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee, refers to the precipitous and abrupt way in which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |