|
Riboviria
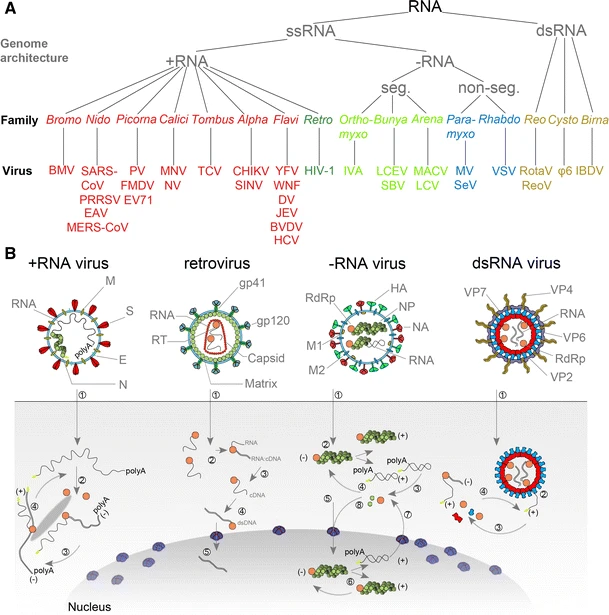
''Riboviria'' is a realm of viruses that includes all viruses that use a homologous RNA-dependent polymerase for replication. It includes RNA viruses that encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, as well as reverse-transcribing viruses (with either RNA or DNA genomes) that encode an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called RNA replicase, produces RNA (ribonucleic acid) from RNA. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (RdDp), also called reverse transcriptase (RT), produces DNA ( deoxyribonucleic acid) from RNA. These enzymes are essential for replicating the viral genome and transcribing viral genes into messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation of viral proteins. ''Riboviria'' was established in 2018 to accommodate all RdRp-encoding RNA viruses and was expanded a year later to also include RdDp-encoding retroviruses. These two groups of viruses are assigned to two separate kingdoms: ''Orthornavirae'' for RdRp-encoding RNA viruses, and ''Pararnavirae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Realm (virology)
In virology, realm is the highest taxonomic rank established for viruses by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), which oversees virus taxonomy. Six virus realms are recognized and united by specific highly conserved traits: * '' Adnaviria'', which contains archaeal filamentous viruses with A-form double-stranded (ds) DNA genomes encoding a unique alpha-helical major capsid protein; * '' Duplodnaviria'', which contains all dsDNA viruses that encode the HK97-fold major capsid protein; * '' Monodnaviria'', which contains all single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses that encode a HUH superfamily endonuclease and their descendants; * ''Riboviria'', which contains all RNA viruses that encode RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and all viruses that encode reverse transcriptase; * '' Ribozyviria'', which contains hepatitis delta-like viruses with circular, negative-sense ssRNA genomes; * and '' Varidnaviria'', which contains all dsDNA viruses that encode a vertical jelly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthornavirae
''Orthornavirae'' is a kingdom of viruses that have genomes made of ribonucleic acid (RNA), those genomes encoding an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). The RdRp is used to transcribe the viral RNA genome into messenger RNA (mRNA) and to replicate the genome. Viruses in this kingdom also share a number of characteristics involving evolution, including high rates of genetic mutations, recombinations, and reassortments. Viruses in ''Orthornavirae'' belong to the realm ''Riboviria''. They are descended from a common ancestor that may have been a non-viral molecule that encoded a reverse transcriptase instead of an RdRp for replication. The kingdom is subdivided into five phyla that separate member viruses based on their genome type, host range, and genetic similarity. Viruses with three genome types are included: positive-strand RNA viruses, negative-strand RNA viruses, and double-stranded RNA viruses. Many of the most widely known viral diseases are caused by RNA viruses in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Virus
An RNA virus is a virusother than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid ( RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza, SARS, MERS, Covid-19, Dengue Virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles. The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) classifies RNA viruses as those that belong to ''Group III'', ''Group IV'' or ''Group V'' of the Baltimore classification system. This category excludes ''Group VI'', viruses with RNA genetic material but which use DNA intermediates in their life cycle: these are called retroviruses, including HIV-1 and HIV-2 which cause AIDS. As of May 2020, all known RNA viruses encoding an RNA-directed RNA polymerase are believed to form a monophyletic group, known as the realm ''Riboviria''. The majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold (which is also caused by other viruses, predominantly rhinoviruses), while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19, which is causing the ongoing pandemic. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis. Coronaviruses constitute the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'', in the family '' Coronaviridae'', order ''Nidovirales'' and realm ''Riboviria''. They are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. The genome size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kilobases, one of the largest among RNA viruses. They have characteristic club-shaped spikes that project from their surface, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pararnavirae
''Revtraviricetes'' is a class of viruses that contains all viruses that encode a reverse transcriptase. The group includes all ssRNA-RT viruses (including the retroviruses) and dsDNA-RT viruses. It is the sole class in the phylum ''Artverviricota'', which is the sole phylum in the kingdom ''Pararnavirae''. The name of the group is a portmanteau of "''rev''erse ''tra''nscriptase" and -''viricetes'' which is the suffix for a virus class. Orders The following orders are recognized: * '' Blubervirales'' (e.g. hepatitis B virus) * '' Ortervirales'' (retrovirus A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptas ...es, '' Caulimoviridae'' and various LTR retrotransposons) References Viruses Virus classes {{Virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Replication
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome and packaging these copies, the virus continues infecting new hosts. Replication between viruses is greatly varied and depends on the type of genes involved in them. Most DNA viruses assemble in the nucleus while most RNA viruses develop solely in cytoplasm. Viral production / replication Viruses multiply only in living cells. The host cell must provide the energy and synthetic machinery and the low- molecular-weight precursors for the synthesis of viral proteins and nucleic acids. The virus replication occurs in seven stages, namely; # Attachment # Entry, # Uncoating, # Transcription / mRNA production, # Synthesis of virus components, # Virion assembly and # Release (Liberation Stage). Attachment It is the first step of viral replicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of transcription, where an enzyme ( RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and, utilising amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA), the ribosome creates the protein. This process is known as translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genetic information in a biological system. As in DNA, gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (biology)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples. Less than 2% of the human genome can be transcribed into mRNA ( Human genome#Coding vs. noncoding DNA), while at least 80% of mammalian genomic DNA can be actively transcribed (in one or more types of cells), with the majority of this 80% considered to be ncRNA. Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. Transcription proceeds in the following general steps: # RNA polymerase, together with one or more general transcription factors, binds to promoter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribonucleic Acid
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, nucleic acids constitute one of the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA, RNA is found in nature as a single strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (''mRNA'') to convey genetic information (using the nitrogenous bases of guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine, denoted by the letters G, U, A, and C) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome. Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation (biology)
In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins after the process of transcription of DNA to RNA in the cell's nucleus. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later folds into an active protein and performs its functions in the cell. The ribosome facilitates decoding by inducing the binding of complementary tRNA anticodon sequences to mRNA codons. The tRNAs carry specific amino acids that are chained together into a polypeptide as the mRNA passes through and is "read" by the ribosome. Translation proceeds in three phases: # Initiation: The ribosome assembles around the target mRNA. The first tRNA is attached at the start codon. # Elongation: The last tRNA validated by the small ribosomal subunit (''acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |