|
Riberalta
Riberalta is a town in the Beni Department in northern Bolivia, situated where the Madre de Dios River joins the Beni River. Riberalta is on the south (south east) bank of the Beni River. As the capital of the province of Vaca Diez, the city has maintained its charm even after the Brazilian nut trade sparked recent development. Bolivia is the dominant producer of the nuts, in the period 2017/2018, the country accounted for 78% of production. Peru producers 16% while Brazil produces a mere 2%. City life in Riberalta Municipality is punctuated by nature thanks to its location on the banks of the Beni and Madre de Dios rivers and its proximity to the Amazon rainforest. Home to the Bolivian Navy flotilla and the 1st Naval District, the city is also called the Bolivian capital of the Amazon. The population wa99,070 in 2018 History Riberalta was originally inhabited by the Chácobo and Pacahuara natives who called it “Pamahuayá”, which means “place of the fruits”. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riberalta Airport
Capitán Av. Selin Zeitun Lopez Airport is an airport serving Riberalta, a port city on the Beni River in the Beni Department of Bolivia. The airport is in the western section of the city, near the confluence of the Beni and Madre de Dios Rivers. The Riberalta non-directional beacon (Ident: REA) is located on the field. Airlines and destinations See also * * *Transport in Bolivia *List of airports in Bolivia References External linksRiberalta Airportat OpenStreetMap OpenStreetMap (OSM) is a free, open geographic database updated and maintained by a community of volunteers via open collaboration. Contributors collect data from surveys, trace from aerial imagery and also import from other freely licensed g ...Riberalta Airportat OurAirports *at FallingRain * * Airports in Bolivia Airports in Beni Department {{bolivia-airport-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
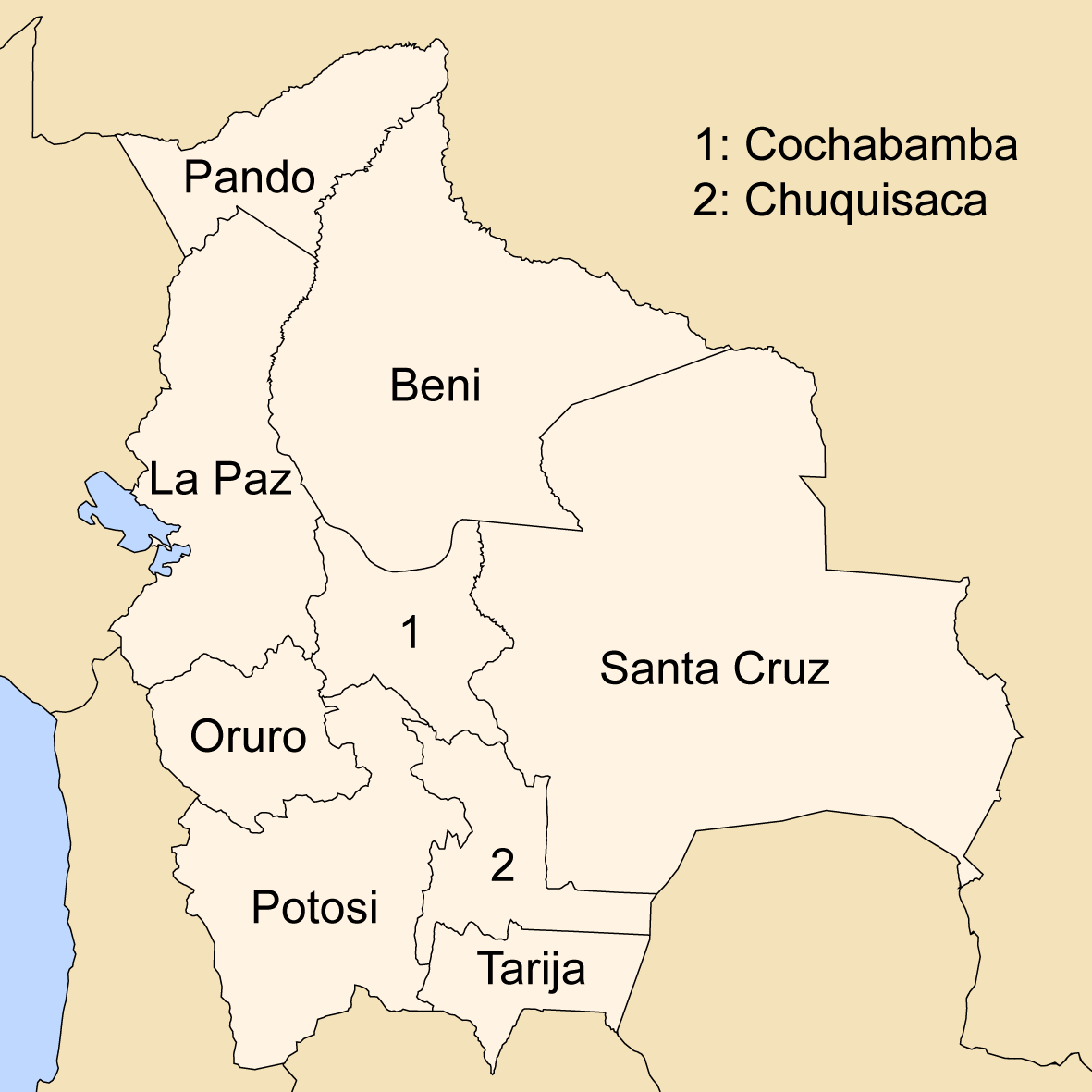
Provinces Of Bolivia
A province is the second largest administrative division in Bolivia, after a department. Each department is divided into provinces. There are 112 provinces. The country's provinces are further divided into 337 municipalities which are administered by an alcalde and municipal council. List of provinces Beni Department Chuquisaca Department Cochabamba Department La Paz Department Oruro Department Pando Department Potosí Department Santa Cruz Department Tarija Department See also * Departments of Bolivia * Municipalities of Bolivia Municipalities in Bolivia are administrative divisions of the entire national territory governed by local elections. Municipalities are the third level of administrative divisions, below departments and provinces. Some of the provinces consist of ... Sources Instituto Nacional de Estadística - Bolivia(Spanish) {{Articles on second-level administrative divisions of South American countries Subd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riberalta Municipality
Riberalta Municipality is a municipality of the Beni Department, Bolivia , image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg , flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center , flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p .... References Instituto Nacional de Estadistica de Bolivia Municipalities of Beni Department {{Beni-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobija
Cobija is a city in Bolivia, capital of the department of Pando, is located about 600 km (373 mi.) north of La Paz in the Amazon Basin on the border with Brazil. Cobija lies on the banks of the Rio Acre across from the Brazilian city of Brasiléia. Cobija lies at an elevation of ca. 280 m (920 ft.) above sea level and has a tropical and rainy climate. Cobija has approximately 80,000 inhabitants, is the seat of a university and capital of the Bolivian Pando Department. Cobija has two airports and is connected by one road to El Choro in the Beni Department, which is not always passable during the rainy season. When the rain allows it, Cobija is connected to the rest of Bolivia also via road. Cobija is connected to Brazil by two bridges. History Cobija was founded in 1906 by Colonel Enrique Cornejo, originally under the name of ''Bahía'' and received its current name in 1908 in commemoration of the former Bolivian seaport Cobija on the Pacific, which has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beni River
The Beni River ( es, Río Beni) is a river in the north of Bolivia. It rises north of La Paz and flows northeast. The Madre de Dios River is where its mouth is at. In the upper portion of its course it flows through highland forest and rainforest, where the rapids of Cachuela Esperanza interrupt the upstream navigability of the river. The middle river runs through dense rainforest where it is joined by the Madidi River and the Tuichi River which flow through Madidi National Park. The Tuichi River joins the Beni River upstream from the town Rurrenabaque. North of Rurrenabaque, the Beni River runs through the Llanos de Moxos also known as the Beni Savanna, which is named from the river. It empties into the larger Madre de Dios at Riberalta. The Beni River has a number of minor tributaries, including intermittent streams such as the Emero River. In 1947, the CIA The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaca Díez Province
Vaca Diéz is a Provinces of Bolivia, province in the Beni Department, Bolivia. The two largest settlements in Vaca Diéz are Guayaramerín with a population of 35,764 in 2012, along with Riberalta with a population of 78,754. Vaca Diéz measures 16,228 km² (10,083 miles) in size. See also *Exaltación, Vaca Diéz References Provinces of Beni Department {{Beni-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg , flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center , flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square patchwork with the (top left to bottom right) diagonals forming colored stripes (green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, white, green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, from top right to bottom left) , other_symbol = , other_symbol_type = Dual flag: , image_coat = Escudo de Bolivia.svg , national_anthem = " National Anthem of Bolivia" , image_map = BOL orthographic.svg , map_width = 220px , alt_map = , image_map2 = , alt_map2 = , map_caption = , capital = La Paz Sucre , largest_city = , official_languages = Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madre De Dios River
The Madre de Dios River () is a river shared by Bolivia and Peru which is homonymous to the Peruvian region it runs through. On Bolivian territory it receives the Beni River, close to the town of Riberalta, which later joins with the Mamore River to become the Madeira River after the confluence. The Madeira is a tributary to the Amazon River. The Madre de Dios is an important waterway for the department of Madre de Dios, particularly Puerto Maldonado, the largest town in the area, and the capital of the department. Mango farming and gold mining are among the many industries on its beaches. Other important industries the Madre de Dios provides are selective logging and farming, both of which are serious environmental problems. Along the length of the river there are several national parks and reserves, notably Tambopata-Candamo National Park, Manú National Park (also known as Manú Biosphere Reserve) and Bahuaja-Sonene National Park. Hydrography The Madre de Dios serves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivian Navy
The Bolivian Navy ( es, Armada Boliviana) is a branch of the Armed Forces of Bolivia. As of 2008, the Bolivian Navy had approximately 5,000 personnel. Although Bolivia has been landlocked since the War of the Pacific and its 1904 peace treaty, Bolivia established a River and Lake Force () in January 1963 under the Ministry of National Defense. It consisted of four boats supplied from the United States and 1,800 personnel recruited largely from the Bolivian Army. The Bolivian Navy was renamed the Bolivian Naval Force () in January 1966, but it has since been called the Bolivian Navy () as well. It became a separate branch of the armed forces in 1963. Bolivia has large rivers which are tributaries to the Amazon which are patrolled to prevent smuggling and drug trafficking. Bolivia also maintains a naval presence on Lake Titicaca, the highest navigable lake in the world, which the country shares with Peru. Landlocked Bolivia has not reconciled with the loss of its coast to Chile, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beni Department
Beni (), sometimes El Beni, is a northeastern department of Bolivia, in the lowlands region of the country. It is the second-largest department in the country (after Santa Cruz), covering 213,564 square kilometers (82,458 sq mi), and it was created by supreme decree on November 18, 1842, during the administration of General José Ballivián. Its capital is Trinidad. Population With a population of 420,000 (2006 census), Beni is the second least-populated of the nine departments of Bolivia, after Pando. Although Beni is rich in natural resources, the poverty level of its inhabitants is high, mainly as a result of centuries of exploitation of native populations by European-descended elites. The main economic activities are agriculture, timber, and cattle. In addition, an underground economy linked to illegal narcotics activities flourished in the area during the last decades of the 20th century, with many cocaine laboratories hidden behind the façade of remote cattle ranches. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of Bolivia
Bolivia is a unitary state consisting of nine departments ( es, departamentos). Departments are the primary subdivisions of Bolivia, and possess certain rights under the Constitution of Bolivia. Each department is represented in the Plurinational Legislative Assembly—a bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. Each department is represented by four Senators, while Deputies are awarded to each department in proportion to their total population. Out of the nine departments, La Paz was originally the most populous, with 2,706,351 inhabitants as of 2012 but the far eastern department of Santa Cruz has since surpassed it by 2020; Santa Cruz also claims the title as the largest, encompassing . Pando is the least populated, with a population of 110,436. The smallest in area is Tarija, encompassing . Departments Former Departments By population Notes See also * ISO 3166-2:BO, the ISO codes for the departments of Bolivia. * Bolivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio José De Sucre
Antonio José de Sucre y Alcalá (; 3 February 1795 – 4 June 1830), known as the "Gran Mariscal de Ayacucho" ( en, "Grand Marshal of Ayacucho"), was a Venezuelan independence leader who served as the president of Peru and as the second president of Bolivia. Sucre was one of Simón Bolívar's closest friends, generals and statesmen. Due to his influence on geopolitical affairs of Latin America, a number of notable localities on the continent now bear Sucre's name. These include the eponymous capital of Bolivia, the Venezuelan state, the department of Colombia and both the old and new airports of Ecuador's capital Quito. Additionally, many schools, streets and districts across the region bear his name as well. Family The aristocratic Sucre family traces its roots back to origins in Flanders. It arrived in Venezuela through Charles de Sucre y Franco Perez, a Flemish nobleman, son of Charles Adrian de Sucre, Marquess of Peru and Buenaventura Carolina Isabel Garrido y Pardo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |