|
Riasg Buidhe Cross
The Riasg Buidhe Cross is a cross standing in the gardens of Colonsay House on the Inner Hebridean island of Colonsay, Scotland. It takes its name from the now abandoned and ruined village of Riasg Buidhe, about southeast of Colonsay House, where it was found in the nineteenth century. History Dating from the 7th or 8th century, the cross stood at Riasg Buidhe in what was recorded as an old burial ground until 1870, when it was taken to Colonsay House close to Kiloran ( gd, Cill Odhráin) which was built in 1722. The cross was placed beside Tobar Oran ( en, The well of St. Oran) and in the vicinity of the now lost Chapel of St. Oran, Colonsay, Chapel of St. Oran. One side of the cross shows a solemn face with distinctive eyebrows and ears, below which extends a long thin neck. The arms of the figure - presumably Christ - are represented by two opposite spirals, and the lower part of the body ends in a fishtail, perhaps referring to the ancient Christian tradition of represent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riasg Buidhe Cross
The Riasg Buidhe Cross is a cross standing in the gardens of Colonsay House on the Inner Hebridean island of Colonsay, Scotland. It takes its name from the now abandoned and ruined village of Riasg Buidhe, about southeast of Colonsay House, where it was found in the nineteenth century. History Dating from the 7th or 8th century, the cross stood at Riasg Buidhe in what was recorded as an old burial ground until 1870, when it was taken to Colonsay House close to Kiloran ( gd, Cill Odhráin) which was built in 1722. The cross was placed beside Tobar Oran ( en, The well of St. Oran) and in the vicinity of the now lost Chapel of St. Oran, Colonsay, Chapel of St. Oran. One side of the cross shows a solemn face with distinctive eyebrows and ears, below which extends a long thin neck. The arms of the figure - presumably Christ - are represented by two opposite spirals, and the lower part of the body ends in a fishtail, perhaps referring to the ancient Christian tradition of represent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonsay House
Colonsay House is a Georgian country house on the island of Colonsay, in the Scottish Inner Hebrides. It is a Category B listed building, and is now in the ownership of the Barons Strathcona. The gardens are open to the public, and are listed on the ''Inventory of Gardens and Designed Landscapes in Scotland'', the national listing of historic gardens. Colonsay House The central part of the house, was first built by the McNeill family in 1722. It is a medium-sized Georgian country house on the island of Colonsay, in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. It is often said in twentieth-century sources to have been built on the site of an earlier abbey, but there is no evidence in any charter or list of Scottish monasteries of any abbey (or any other monastic foundation) having been here. Nor is there any mention in any medieval witness-list of a prior or abbot of Kiloran. We must regard the story as a fable, though the church (and the island as a whole) did belong to the abbey of Iona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Hebridean
The Inner Hebrides (; Scottish Gaelic: ''Na h-Eileanan a-staigh'', "the inner isles") is an archipelago off the west coast of mainland Scotland, to the south east of the Outer Hebrides. Together these two island chains form the Hebrides, which experience a mild oceanic climate. The Inner Hebrides comprise 35 inhabited islands as well as 44 uninhabited islands with an area greater than . Skye, Mull, and Islay are the three largest, and also have the highest populations. The main commercial activities are tourism, crofting, fishing and whisky distilling. In modern times the Inner Hebrides have formed part of two separate local government jurisdictions, one to the north and the other to the south. Together, the islands have an area of about , and had a population of 18,948 in 2011. The population density is therefore about . There are various important prehistoric structures, many of which pre-date the first written references to the islands by Roman and Greek authors. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonsay
Colonsay (; gd, Colbhasa; sco, Colonsay) is an island in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland, located north of Islay and south of Mull. The ancestral home of Clan Macfie and the Colonsay branch of Clan MacNeil, it is in the council area of Argyll and Bute and has an area of . Aligned on a south-west to north-east axis, it measures in length and reaches at its widest point. Geology The Colonsay Group, which takes its name from the island, is an estimated sequence of mildly metamorphosed Neoproterozoic sedimentary rocks that also outcrop on the islands of Islay and Oronsay and the surrounding seabed. The sequence has been correlated with the Grampian Group, the oldest part of the Dalradian Supergroup. It includes the meta wackes of the Oronsay Greywacke Formation, the sandstones of the Dun Gallain Grit Formation, the metasandstones and metamudstones of the Machrins Arkose, Kilchattan and Milbuie formations, the sandstones and phyllites of the Kiloran Flags Formation and the phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapel Of St
A chapel is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. Firstly, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are often called chapels; the Lady chapel is a common type of these. Secondly, a chapel is a place of worship, sometimes non-denominational, that is part of a building or complex with some other main purpose, such as a school, college, hospital, palace or large aristocratic house, castle, barracks, prison, funeral home, cemetery, airport, or a military or commercial ship. Thirdly, chapels are small places of worship, built as satellite sites by a church or monastery, for example in remote areas; these are often called a chapel of ease. A feature of all these types is that often no clergy were permanently resident or specifically attached to the chapel. Finally, for historical reasons, ''chapel'' is also often the term used by independent or nonconformist denominations for their places of worshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In The Southern Inner Hebrides
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Argyll And Bute
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
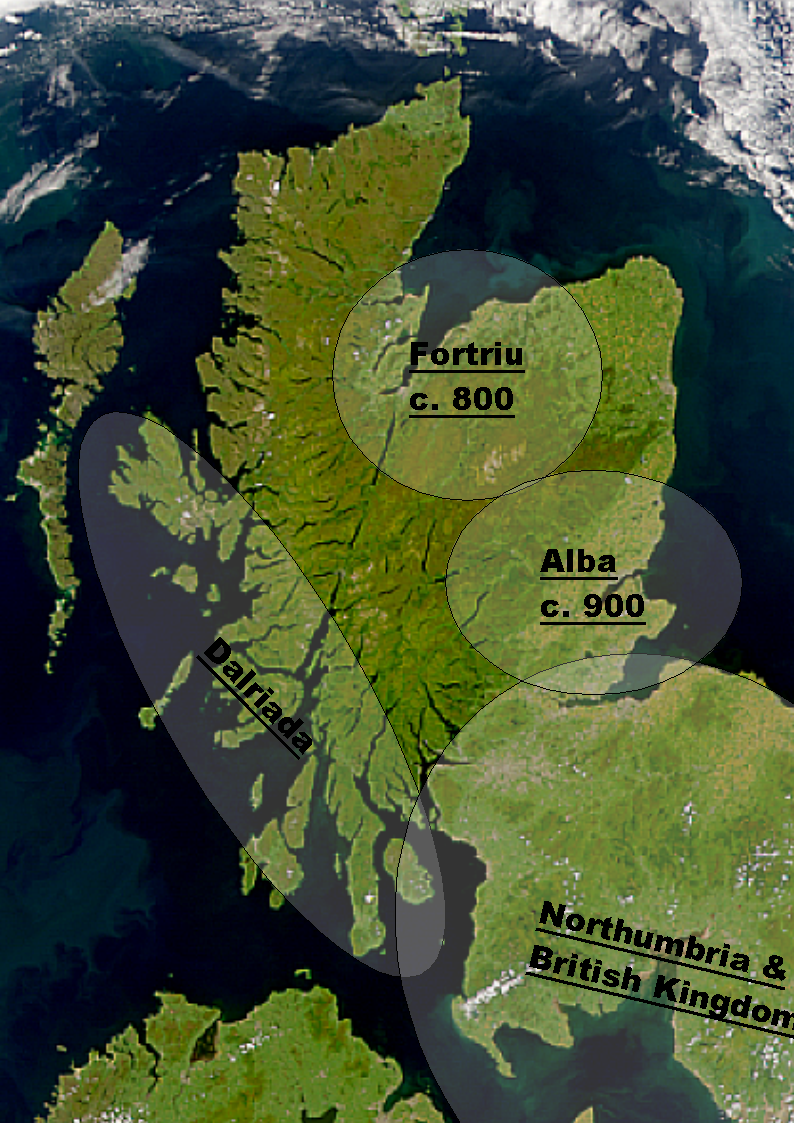
Scotland In The Early Middle Ages
Scotland was divided into a series of kingdoms in the early Middle Ages, i.e. between the end of Roman authority in southern and central Britain from around 400 CE and the rise of the kingdom of Alba in 900 CE. Of these, the four most important to emerge were the Picts, the Gaels of Dál Riata, the Britons of Alt Clut, and the Anglian kingdom of Bernicia. After the arrival of the Vikings in the late 8th century, Scandinavian rulers and colonies were established on the islands and along parts of the coasts. In the 9th century, the House of Alpin combined the lands of the Scots and Picts to form a single kingdom which constituted the basis of the Kingdom of Scotland. Scotland has an extensive coastline and vast areas of difficult terrain and poor agricultural land. In this period, more land became marginal due to climate change, resulting in relatively light human settlement, particularly in the interior and Highlands. Northern Britain lacked urban centres and settlements were bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)