|
Rhynchactis Macrothrix
''Rhynchactis macrothrix'' is a species of whipnose angler found in the Atlantic and western Indian Ocean The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...s where it is found at depths of around . This species grows to a length of SL. References * macrothrix Taxa named by Theodore Wells Pietsch III Fish described in 1998 Taxa named by Erik Bertelsen {{Lophiiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erik Bertelsen
Erik Bertelsen (8 August 1912 – 18 March 1993) was a Danish ichthyologist, who specialised in deep sea fish. The fish, '' Diaphus bertelseni'' is named in his honour. He studied biology at the University of Copenhagen (1930 -) and in 1937 started work on the Dana collection at Charlottenlund Castle and also for the Danish Fisheries Investigation (DFI). He earned a doctorate in 1951 with his dissertation, ''The ceratioid fishes. Ontology, taxonomy, distribution and biology''. He was director of DFI from 1958 to 1971, when he resigned to work at the zoological museum of the University of Copenhagen, where with fewer administrative duties he was able to concentrate on his research on deep sea fish. In 1961 he was made a Knight of the Order of the Dannebrog. Taxon described by him He authored over 50 taxa. His zoological author abbreviation is Bertelsen. Research In 1932 he participated in a fisheries biology research trip to the Faroe Islands and Iceland. In 1933 (as part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Wells Pietsch III
Theodore Wells Pietsch III (born March 6, 1945) is an American systematist and evolutionary biologist especially known for his studies of anglerfishes. Pietsch has described 72 species and 14 genera of fishes and published numerous scientific papers focusing on the relationships, evolutionary history, and functional morphology of teleosts, particularly deep-sea taxa. For this body of work, Pietsch was awarded the Robert H. Gibbs Jr. Memorial Award in Systematic Ichthyology by the American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists in 2005. Pietsch has spent most of his career at the University of Washington in Seattle as a professor mentoring graduate students, teaching ichthyology to undergraduates, and curating the ichthyology collections of the UW Burke Museum of Natural History and Culture. His zoological author abbreviation is Pietsch. Education Pietsch attended John Adams High School in Indiana. After a B.A. in zoology at the University of Michigan he did a M.S. and P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whipnose Angler
The whipnose anglers or whipnose seadevils comprise the family Gigantactinidae, marine ray-finned fishes classified within the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep sea anglerfishes. These fishes are found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans. Etymology The whipnose angler family name, Gigantactinidae, has a name that is derived from ''Giganactis'', its type genus and the only genus in the family when it was proposed by Boulenger. ''Gigantactis'' is a combination of ''gigantos'', meaning "giant", with ''actis'', which means "ray", an allusion to the unusually long illicium of genus's type species, '' G. vanhoeffeni''. Taxonomy Whipnose anglers are classified within the family Gigantactinidae which was proposed as a monotypic family in 1904 by the Belgian-born British ichthyologist George Albert Boulenger for the genus ''Giganactis''. ''Giganactis'' was first proposed as a monospecific genus by the German zoologist August Brauer when he described ''Giganactis vanhoeffeni'' from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for separating the New World of the Americas (North America and South America) from the Old World of Afro-Eurasia (Africa, Asia, and Europe). Through its separation of Afro-Eurasia from the Americas, the Atlantic Ocean has played a central role in the development of human society, globalization, and the histories of many nations. While the Norse colonization of North America, Norse were the first known humans to cross the Atlantic, it was the expedition of Christopher Columbus in 1492 that proved to be the most consequential. Columbus's expedition ushered in an Age of Discovery, age of exploration and colonization of the Americas by European powers, most notably Portuguese Empire, Portugal, Spanish Empire, Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. The Indian Ocean has large marginal or regional seas, including the Andaman Sea, the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Laccadive Sea. Geologically, the Indian Ocean is the youngest of the oceans, and it has distinct features such as narrow continental shelf, continental shelves. Its average depth is 3,741 m. It is the warmest ocean, with a significant impact on global climate due to its interaction with the atmosphere. Its waters are affected by the Indian Ocean Walker circulation, resulting in unique oceanic currents and upwelling patterns. The Indian Ocean is ecologically diverse, with important ecosystems such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
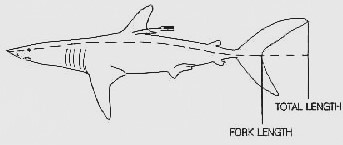
Fish Measurement
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes ( lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchactis
''Rhynchactis'' is a genus of deep-sea anglerfish in the family Gigantactinidae, containing three species found worldwide at depths greater than . Adult female ''Rhynchactis'' reach a standard length (SL) of and have a dark-colored, streamlined body and a relatively small head bearing a very long illicium (the "fishing rod" formed by the first ray of the dorsal fin). Unlike almost all other deep-sea anglerfishes, the illicium bears no bioluminescent esca (the "lure") at the tip. The mouth is almost devoid of teeth, and the inside of both jaws are covered by numerous white glands that are unique to this genus. The lack of an esca, greatly reduced dentition, and glands inside the mouth all point to ''Rhynchactis'' having a highly specialized mode of feeding, the nature of which has yet to be deciphered. As in other deep-sea anglerfishes, there is enormous sexual dimorphism with males being much smaller than females and lacking an illicium, though they do not appear to be parasiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Theodore Wells Pietsch III
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Described In 1998
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fish wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |