|
Rhodope (province)
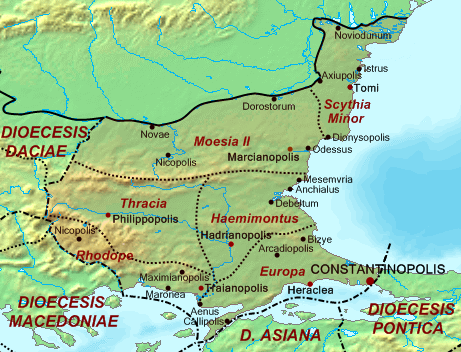
Rhodope ( el, ) was a late Roman and early Byzantine province, situated on the northern Aegean coast. A part of the Diocese of Thrace, it extended along the Rhodope Mountains range, covering parts of modern Western Thrace (in Greece) and south-western Bulgaria. The province was headed by a governor of the rank of ''praeses'', with Trajanopolis as the provincial capital. According to the 6th-century ''Synecdemus'', there were six further cities in the province, Maroneia, Maximianopolis, Nicopolis, Kereopyrgos (unknown location) and Topeiros (mod. Toxotai in Greece). The province survived until the Slavic invasions of the 7th century, although as an ecclesiastic province, it continued in existence at least until the 12th century. The theme of Boleron Boleron ( el, Βολερόν) was the name of a region and a Byzantine province in southwestern Thrace during the Middle Ages. The region is first mentioned in the mid-9th century ''Life of Saint Gregory of Dekapolis'', and desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as governor. For centuries it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the imperial prefectures). Terminology The English word ''province'' comes from the Latin word ''provincia''. In early Republican times, the term was used as a common designation for any task or set of responsibilities assigned by the Roman Senate to an individual who held ''imperium'' (right of command), which was often a military command within a specified theatre of operations. In time, the term became t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praeses
''Praeses'' (Latin ''praesides'') is a Latin word meaning "placed before" or "at the head". In antiquity, notably under the Roman Dominate, it was used to refer to Roman governors; it continues to see some use for various modern positions. Roman governors ''Praeses'' began to be used as a generic description for provincial governors—often through paraphrases, such as ''qui praeest'' ("he who presides")—already since the early Principate, but came in general use under the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. The jurist Aemilius Macer, who wrote at the time of Caracalla (reigned 198–217), insists that the term was applied only to the governors who were also senators—thereby excluding the equestrian '' procuratores''—but, while this may reflect earlier usage, it was certainly no longer the case by the time he wrote. In the usage of the 2nd and 3rd centuries, the term appears originally to have been used as an honorific, affixed to the formal gubernatorial titles (''legatus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of The Byzantine Empire
Subdivisions of the Byzantine Empire were administrative units of the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire (330–1453). The Empire had a developed administrative system, which can be divided into three major periods: the late Roman/early Byzantine, which was a continuation and evolution of the system begun by the emperors Diocletian and Constantine the Great, which gradually evolved into the middle Byzantine, where the theme system predominated alongside a restructured central bureaucracy, and the late Byzantine, where the structure was more varied and decentralized and where feudal elements appeared. Early period: 4th–7th centuries The classical administrative model, as exemplified by the ''Notitia Dignitatum'', divided the late Roman Empire into provinces, which in turn were grouped into dioceses and then into praetorian prefectures. The late Roman administrative system remained intact until the 530s, when Justinian I (r. 527–565) undertook his administrative reforms. He ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece In The Roman Era
Greece in the Roman era describes the Roman conquest of Greece, as well as the period of Greek history when Greece was dominated first by the Roman Republic and then by the Roman Empire. The Roman era of Greek history began with the Corinthian defeat in the Battle of Corinth in 146 BC. However, before the Achaean War, the Roman Republic had been steadily gaining control of mainland Greece by defeating the Kingdom of Macedon in a series of conflicts known as the Macedonian Wars. The Fourth Macedonian War ended at the Battle of Pydna in 148 BC with the defeat of the Macedonian royal pretender Andriscus. The definitive Roman occupation of the Greek world was established after the Battle of Actium (31 BC), in which Augustus defeated Cleopatra VII, the Greek Ptolemaic queen of Egypt, and the Roman general Mark Antony, and afterwards conquered Alexandria (30 BC), the last great city of Hellenistic Egypt. The Roman era of Greek history continued with Emperor Constantine the Great's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Thrace
Thracia or Thrace ( ''Thrakē'') is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical and Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek Diadochi ruler Lysimachus, but became a client state of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire as the Sapaean kingdom. Roman emperor Claudius annexed the kingdom as a Roman province in 46 AD. Confines From the perspective of classical Greece, Thracia included the territory north of Thessaly, with no definite boundaries, sometimes to the inclusion of Macedonia and Scythia Minor. Later, Thracia proper was understood to include the territory bordered by the Danube on the north, by the Black Sea on the east, by Macedonia in the south and by Illyria to the west, roughly equivalent with the territory of the Thracian kingdom as it stood during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. With the annexation of the Thracian kingdom by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Dictionary Of Byzantium
The ''Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium'' (ODB) is a three-volume historical dictionary published by the English Oxford University Press. With more than 5,000 entries, it contains comprehensive information in English on topics relating to the Byzantine Empire. It was edited by Alexander Kazhdan, and was first published in 1991.''The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium'', Oxford University Press, New York and Oxford, 1991. Kazhdan was a professor at Princeton University who became a Senior Research Associate at Dumbarton Oaks, Washington, DC, before his death. He contributed to many of the articles in the Dictionary and always signed his initials ''A.K.'' at the end of the article to indicate his contribution. Description The dictionary is available in printed and e-reference text versions from Oxford Reference Online. It covers the main historical events of Byzantium, as well as important social and religious events. It also includes biographies of eminent political and literary personal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boleron
Boleron ( el, Βολερόν) was the name of a region and a Byzantine province in southwestern Thrace during the Middle Ages. The region is first mentioned in the mid-9th century ''Life of Saint Gregory of Dekapolis'', and designated the area enclosed between the Nestos River in the west, the Rhodope Mountains to the north, the Korpiles defile to the east, and the Aegean Sea to the south. In the early 11th century, it became a distinct administrative unit, but had a chequered history: a '' dioikesis'' (fiscal district) in 1047, it is attested as a separate theme—with at least two known '' banda'', Mosynopolis and Peritheorion—in 1083, but most often it is found as part of a composite province along with the older themes of Thessalonica and Strymon. After the dissolution of the Byzantine Empire following the Fourth Crusade, the region fell to the Kingdom of Thessalonica and followed its fortunes until its conquest by the Empire of Nicaea. In ca. 1246, John III Vatatzes re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theme (Byzantine District)
The themes or ( el, θέματα, , singular: , ) were the main military/administrative divisions of the middle Byzantine Empire. They were established in the mid-7th century in the aftermath of the Slavic invasion of the Balkans and Muslim conquests of parts of Byzantine territory, and replaced the earlier provincial system established by Diocletian and Constantine the Great. In their origin, the first themes were created from the areas of encampment of the field armies of the East Roman army, and their names corresponded to the military units that had existed in those areas. The theme system reached its apogee in the 9th and 10th centuries, as older themes were split up and the conquest of territory resulted in the creation of new ones. The original theme system underwent significant changes in the 11th and 12th centuries, but the term remained in use as a provincial and financial circumscription until the very end of the Empire. History Background During the late 6th and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicopolis Ad Nestum
Nicopolis ad Nestum ( grc, Νικόπολις ἡ περὶ Νέσσον) or Nicopolis ad Mestum is a ruined Roman town in the province of Thracia (Thrace) near to the modern village of Garmen on the left bank of the Mesta river, in Garmen Municipality, Bulgaria. Although "ad Nestum" is the more commonly used alternative, "ad Mestum" (which is what appears, in Greek, on the coins of the city) is the correct form of the name during the Roman period. Nicopolis The town was one of two fortified towns founded to mark Emperor Trajan’s victory in 105-106 AD over the Dacians. The area had been inhabited for about 14 centuries and attained its peak in late antiquity (4th-6th centuries AD). The original town occupied about 25-30 decаres. The Slavs destroyed Nicopolis in the 6th-7th centuries but it re-emerged as a medieval settlement in the late 10th century. Excavations have cleared 280 metres of fortress walls, administrative and religious buildings and tumuli. Several archaeologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximianopolis (Thrace)
Mosynopolis ( el, Μοσυνόπολις), of which only ruins now remain in Greek Thrace, was a city in the Roman province of Rhodope, which was known until the 9th century as Maximianopolis (Μαξιμιανούπολις) or, to distinguish it from other cities of the same name, as Maximianopolis in Rhodope. History The city of Maximianopolis appears in written sources from the 4th century on. Its fortifications were renewed by Byzantine emperor Justinian I, and it was later a base for operations by Emperor Basil II in his wars against the Bulgarians. In the 11th century, the city was the center of a district ('' bandon'') in the theme of Boleron, and Anna Komnene reports in her '' Alexiad'' that there were many Manichaeans living in Mosynopolis in the late 11th/early 12th centuries. The town was captured in 1185 by the Normans, while the monk Ephrem says that the city was captured in 1190 by Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor. The Battle of Messinopolis, in which the Bulgarians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maroneia
Maroneia ( el, Μαρώνεια) is a village and a former municipality in Rhodope regional unit, East Macedonia and Thrace, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Maroneia-Sapes, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 287.155 km2. Population 6,350 (2011). The seat of the municipality was in Xylagani. History In legend, it was said to have been founded by Maron, a son of Dionysus, or even a companion of Osiris. According to Pseudo-Scymnus it was founded by Chios in the fourth year of the fifty-ninth Olympiad (540 BCE). According to Pliny, its ancient name was Ortagures or Ortagurea. It was located on the hill of Agios Charalampos, and archaeological findings date it as a much older and as a pure Thracian city. Herodotus says it belonged to the Cicones. Maroneia was close to the Ismaros mentioned by Homer in the ''Odyssey''. Some scholars identify Maroneia with his Ismaros. Homer has Odysseus plundering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synecdemus
The ''Synecdemus'' or ''Synekdemos'' ( el, Συνέκδημος) is a geographic text, attributed to Hierocles, which contains a table of administrative divisions of the Byzantine Empire and lists of their cities. The work is dated to the reign of Justinian but prior to 535, as it divides the 912 listed cities in the Empire among 64 Eparchies. The ''Synecdemus'', along with the work of Stephanus of Byzantium were the principal sources of Constantine VII's work on the Themes (''De Thematibus''). The ''Synecdemus'' was published in various editions beginning in 1735, notably by Gustav Parthey (''Hieroclis Synecdemus''; Berlin, 1866) and slightly later in a corrected text by A. Burckhardt in the Teubner series. The most recent major publication was by E. Honigmann (Le Synekdèmos d'Hiéroklès et l'opuscule géographique de Georges de Chypre; Brussels, 1939). References Sources * * * * . (''Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium The ''Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium'' (ODB) is a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)

