|
Rhodnius Prolixus
''Rhodnius prolixus'' is the principal triatomine vector of the Chagas parasite due to both its sylvatic and domestic populations in northern South America as well as to its exclusively domestic populations in Central America. It has a wide range of ecotopes, mainly savanna and foothills with an altitude of between above sea level and temperatures of . Sylvatic ''R. prolixus'', as virtually all ''Rhodnius'' spp., is primarily associated with palm tree habitats and has a wide range of hosts including birds, rodents, marsupials, sloths, and reptiles. The insect was used by Sir Vincent Wigglesworth for the detection of insect hormones. It has been implicated in the transmission of transposons between it and some of its vertebrate hosts, squirrel monkeys and opossums. ''Rhodnius prolixus'' is also known as the kissing bug because it tends to feed on the area around victims' mouths. History ''Rhodnius prolixus'' established itself throughout Central America after specimens that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodnius
''Rhodnius'' is a genus of assassin bugs in the subfamily Triatominae (the kissing bugs), and is an important vector in the spread of Chagas disease. The ''Rhodnius'' species were important models for Sir Vincent Wigglesworth's studies of insect physiology, specifically growth and development. Species *''Rhodnius amazonicus'' Almeida, Santos & Sposina, 1973 *''Rhodnius brethesi'' Matta, 1919 (Tc) *''Rhodnius colombiensis'' Moreno Mejía, Galvão & Jurberg, 1999 *''Rhodnius dalessandroi'' Carcavallo & Barreto, 1976 *''Rhodnius domesticus'' Neiva & Pinto, 1923 (Tc) *''Rhodnius ecuadoriensis'' Lent & León, 1958 (Tc) *''Rhodnius milesi'' Carcavallo, Rocha, Galvão, Jurberg, 2001 *'' Rhodnius nasutus'' Stål, 1859 (Tc) *'' Rhodnius neglectus'' Lent, 1954 (Tc) *''Rhodnius neivai'' Lent, 1953 *'' Rhodnius pallescens'' Barber, 1932 (Tc) (principal vector in Panama). *''Rhodnius paraensis'' Sherlock, Guitton & Miles, 1977 (Tc) *''Rhodnius pictipes'' Stål, 1872 (Tc) *''Rhodnius prolixus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Stål
Carl Stål (21 March 1833 – 13 June 1878) was a Swedish entomologist specialising in Hemiptera. He was born at Karlberg Castle, Stockholm on 21 March 1833 and died at Frösundavik near Stockholm on 13 June 1878. He was the son of architect, author and officer Carl Stål then Colonel, Swedish Corps of Engineers. He matriculated at Uppsala University in 1853, studying medicine and passing the medico-philosophical examination in 1857. He then turned to entomology and completed his Ph.D. at the University of Jena in 1859. The same year he became assistant to Carl Henrik Boheman in the Zoological department of the Swedish Museum of Natural History in Stockholm, where, in 1867, he was appointed keeper with the title of professor. He made collecting trips in Sweden and throughout Europe and visited other museums including the collection of Johan Christian Fabricius in Kiel. His study of the Fabrician types resulted in his "Hemiptera Fabriciana". A significant part of Stål's work wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsid, sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, Squamata, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean taxonomy, Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern Cladistics, cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile Order (biology), orders, historically combined with that of modern amphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipocalin
The lipocalins are a family of proteins which transport small hydrophobic molecules such as steroids, bilins, retinoids, and lipids and most lipocalins are also able to bind to complexed iron (via siderophores or flavonoids) as well as heme. They share limited regions of sequence homology and a common tertiary structure architecture. This is an eight stranded antiparallel beta barrel with a repeated + 1 topology enclosing an internal ligand binding site. These proteins are found in gram negative bacteria, vertebrate cells, and invertebrate cells, and in plants. Lipocalins have been associated with many biological processes, among them immune response, pheromone transport, biological prostaglandin synthesis, retinoid binding, and cancer cell interactions. Function Immune response Lipocalin proteins are important key players of nutritional immunity by withholding and sequestering micronutrients. They are thereby able to regulate inflammatory and detoxification processe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juvenile Hormone
Juvenile hormones (JHs) are a group of acyclic sesquiterpenoids that regulate many aspects of insect physiology. The first discovery of a JH was by Vincent Wigglesworth. JHs regulate development, reproduction, diapause, and polyphenisms.The chemical formula for juvenile hormone is C_18H_30O_3. In insects, JH (formerly called neotenin) refers to a group of hormones, which ensure growth of the larva, while preventing metamorphosis. Because of their rigid exoskeleton, insects grow in their development by successively shedding their exoskeleton (a process known as molting). Juvenile hormones are secreted by a pair of endocrine glands behind the brain called the corpora allata. JHs are also important for the production of eggs in female insects. JH was isolated in 1965 by Karel Sláma and Carroll Williams and the first molecular structure of a JH was solved in 1967. Most insect species contain only juvenile growth hormone (JH) III. To date JH 0, JH I, and JH II have been identifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpora Allata
In insect physiology and anatomy, the corpus allatum (plural: corpora allata) is an endocrine gland that generates juvenile hormone; as such, it plays a crucial role in metamorphosis. Surgical removal of the corpora allata (an allatectomy) can cause an immature larva to pupate at its next molt, resulting in a miniature adult. Similarly, transplantation of corpora allata from a young larva to a fully mature larva can greatly extend the larval stage, resulting in an equivalent to gigantism. In many Diptera species, the corpus allatum is fused with the corpus cardiacum, forming a "ring gland", also known as Weismann's ring. In Lepidoptera species, the corpus allatum acts as a release site for prothoracicotropic hormone Prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) was the first insect hormone to be discovered.The chemical symbol for prothoracicotropic hormone is (C64H102N16O19S2). It was originally described simply as "brain hormone" by early workers such as Stefan Kopeć (1 ... which is g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prothoracicotropic Hormone
Prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) was the first insect hormone to be discovered.The chemical symbol for prothoracicotropic hormone is (C64H102N16O19S2). It was originally described simply as "brain hormone" by early workers such as Stefan Kopeć (1922) and Vincent Wigglesworth (1934), who realized that ligation of the head of immature insects could prevent molting or pupation of the body region excluded from the head if the ligation was performed before a critical age in the lifestage was reached. After a certain point the ligation had no effect and both sections of the insect would molt or pupate. However, implantation of a conspecific brain to a sessile ligated abdomen or an abdomen under diapause would induce molting or pupation. Thus, the brain was originally thought to be the source of the hormone that induces molting in insects. Later it was established that the insect brain produces a number of hormones, but the hormone which was the cause of the observations made by Kopeć ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Salvador
San Salvador (; ) is the capital and the largest city of El Salvador and its eponymous department. It is the country's political, cultural, educational and financial center. The Metropolitan Area of San Salvador, which comprises the capital itself and 13 of its municipalities, has a population of 2,404,097. The urban area of San Salvador has a population of 1,600,000 inhabitants. The city is home to the ''Consejo de Ministros de El Salvador'' (Council of Ministries of El Salvador), the Legislative Assembly of El Salvador, the Supreme Court of El Salvador, and other governmental institutions, as well as the official residence of the President of El Salvador. San Salvador is located in the Salvadoran highlands, surrounded by volcanoes and prone to earthquakes. The city is also home to the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of San Salvador, as well as many Protestant branches of Christianity, including Evangelicals, Latter-day Saints, Baptists, and Pentecostals. San Salvador has the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. The Venezuelan government maintains a claim against Guyana to Guayana Esequiba. Venezuela is a federal presidential republic consisting of 23 states, the Capital District and federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
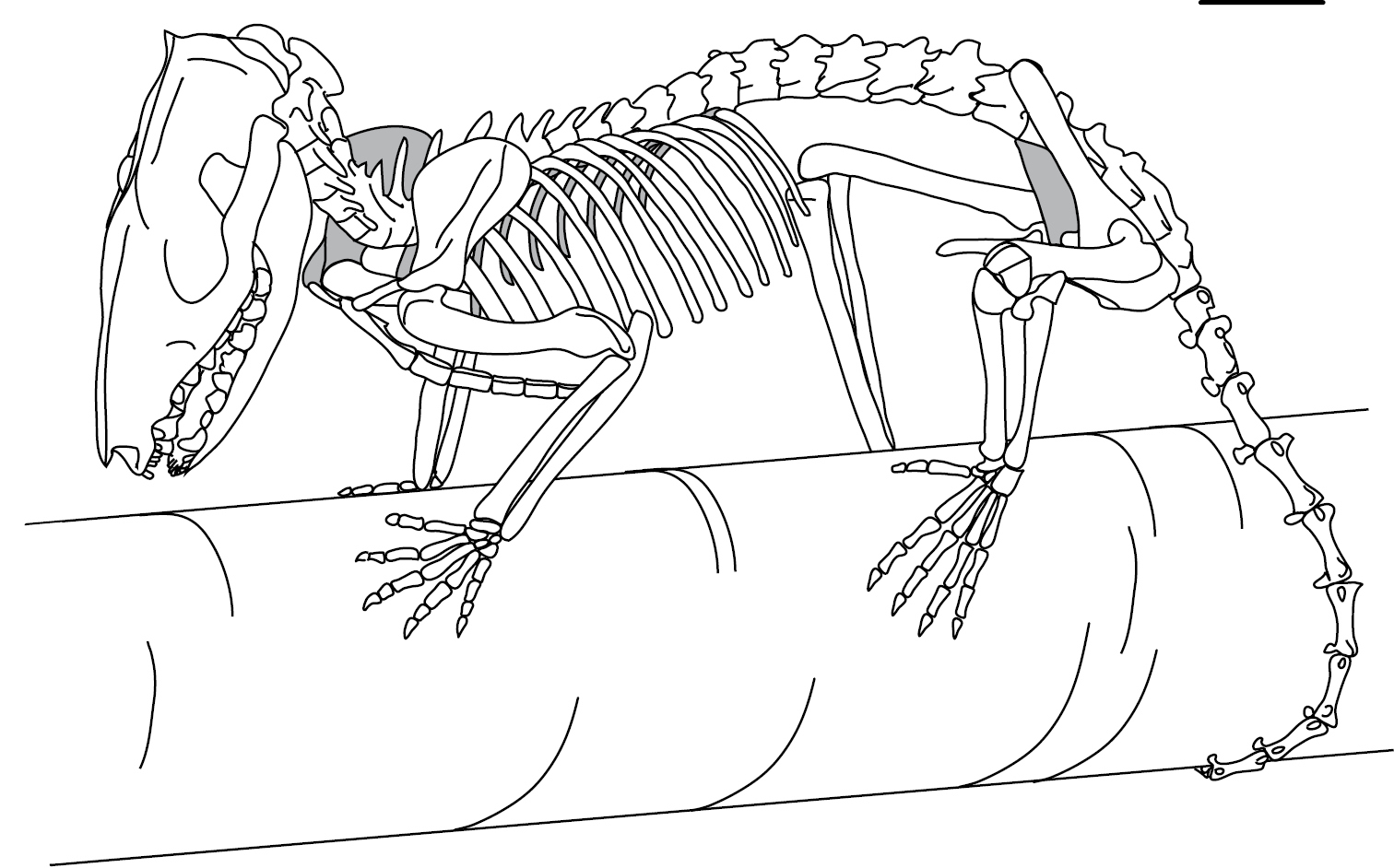
Opossums
Opossums () are members of the marsupial order Didelphimorphia () endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 93 species in 18 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered North America in the Great American Interchange following the connection of North and South America. The Virginia opossum is the only species found in the United States and Canada. It is often simply referred to as an opossum, and in North America it is commonly referred to as a possum (; sometimes rendered as ''possum'' in written form to indicate the dropped "o"). Possums should not be confused with the Australasian arboreal marsupials of suborder Phalangeriformes that are also called possums because of their resemblance to the Didelphimorphia. The opossum is typically a nonaggressive animal. Etymology The word ''opossum'' is borrowed from the Powhatan language and was first recorded between 1607 and 1611 by John Smith (as ''opassom'') an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |