|
Rhinochelys
Rhinochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtles belonging to the family Protostegidae. Fossil records Fossils of ''Rhinochelys'' have been found in Cenomanian-age marine deposits of southern England, Lebanon, and France. Species Three species of ''Rhinochelys'' are recognized:Scavezzoni I, Fischer V. (2018) Rhinochelys amaberti Moret (1935), a protostegid turtle from the Early Cretaceous of France. PeerJ 6:e4594 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4594 * ''Rhinochelys pulchriceps'' (Owen, 1851) * ''Rhinochelys amaberti'' Moret, 1935 * ''Rhinochelys nammourensis'' Tong, Hirayama, Makhoul & Escuillie, 2006Haiyan Tong, Hirayama R., Makhoul, E. & Escuillie F. 2006. Rhinochelys (Chelonioidea : Protostegidae) from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) of Nammoura, Lebanon. Atti della società italiana di scienze naturali e del museo civico di storia naturale di Milano 147 (1) : 113 – 138 ''Rhinochelys cantabrigiensis'' and ''R. elegans'', both named by Richard Lydekker in 1889, are recover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protostegidae
Protostegidae is a family of extinct sea turtle, marine turtles that lived during the Cretaceous period. The family includes some of the largest sea turtles that ever existed. The largest, ''Archelon'', had a head long. Like most sea turtles, they had flattened bodies and flipper (anatomy), flippers for front appendages; protostegids had minimal carapace, shells like Dermochelyidae, leatherback turtles of modern times. Anatomy As some of the first sea turtle, marine turtles, the protostegids set the general body plan for future species of sea turtles. They had a generally depressed turtle body plan, complete with four limbs, a short tail, and a large head at the end of a relatively short neck. Like other sea turtles, they possessed oar-like front appendages especially evolved for swimming in the open ocean. Similar to the still-extant taxon, extant, possibly closely related Dermochelyidae, protostegids possessed extremely reduced carapaces. Some specimens had skeletal protrusio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
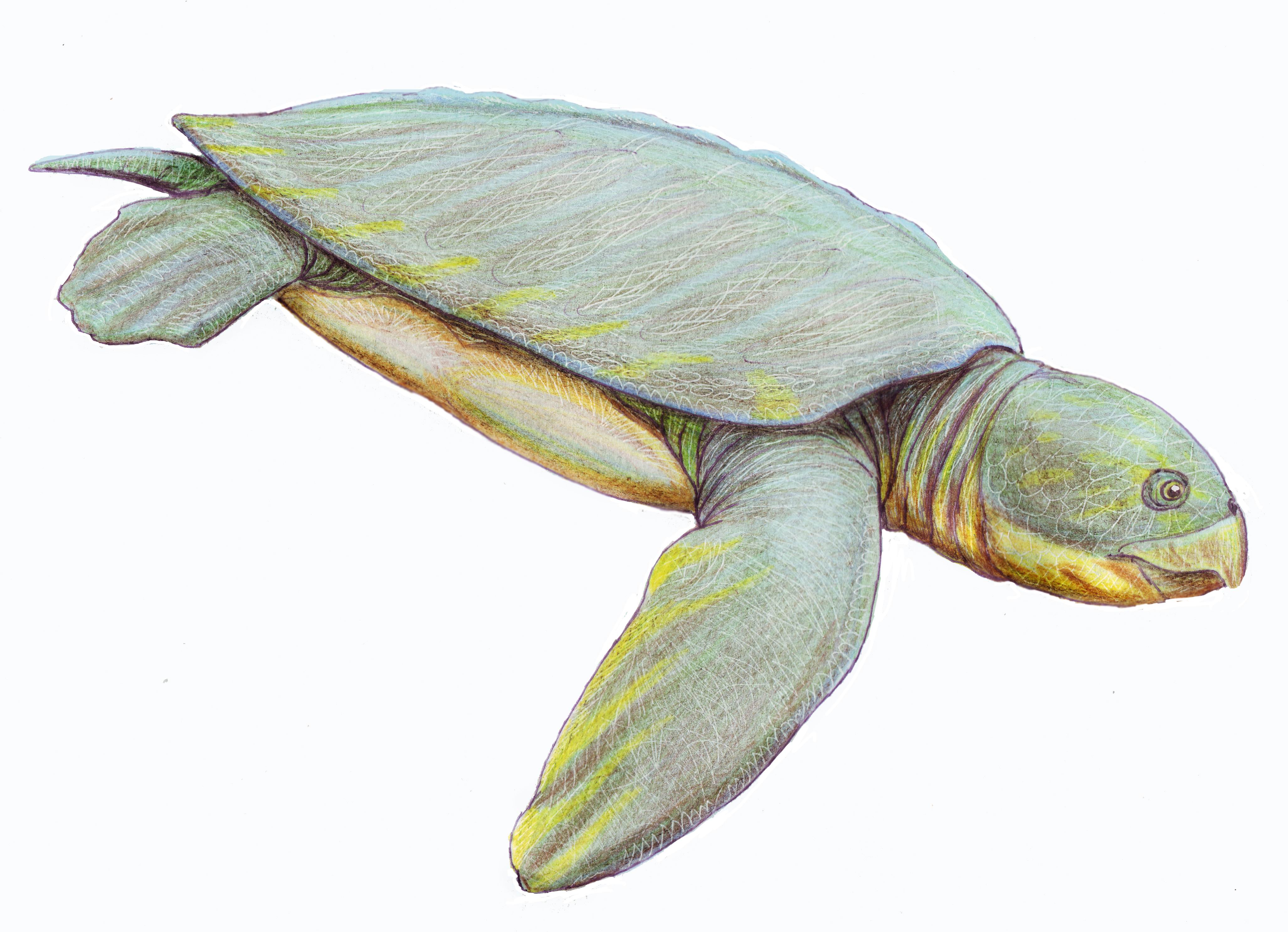
Sea Turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, Kemp's ridley, and olive ridley sea turtles. All six of the sea turtle species present in US waters (all of those listed above except the flatback) are listed as endangered and/or threatened under the Endangered Species Act. The seventh sea turtle species is the flatback, which exists in the waters of Australia, Papua New Guinea and Indonesia. Sea turtles can be separated into the categories of hard-shelled (cheloniid) and leathery-shelled ( dermochelyid).Wyneken, J. 2001. The Anatomy of Sea Turtles. U.S Department of Commerce NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFSC-470, 1-172 pp. There is only one dermochelyid species which is the leatherback sea turtle. Description For each of the seven types of sea turtles, females and males are the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmatochelys
''Desmatochelys'' (from Greek δεσμός ''desmos'' 'link' + χέλῡς ''khelus'' ‘tortoise’) is an extinct genus of sea turtles belonging to the family Protostegidae. This genus contains two known species, ''D. lowii'' and ''D. padillai''. ''D. lowii'' was first discovered in 1895, followed by ''D. padillai'' in 2015. Having been estimated at over 120 million years old, ''D. padillai'' is currently the oldest known species of sea turtle. ''Desmatochelys'' lived during the Cretaceous, and had a wide geographic range, primarily along the Western Interior Seaway. Taxonomy The genus contains two species: * ''Desmatochelys lowi'' * ''Desmatochelys padillai'' Initially, ''Desmatochelys'' formed its own family, Desmatochelydae. Later it was reassigned into the family Protostegidae. There is some debate among the paleontological community over the placement of Protostegidae (and therefore ''Desmatochelys'') within turtle phylogeny. According to Elizabeth L. Nicholls, the gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Seeley
Harry Govier Seeley (18 February 1839 – 8 January 1909) was a British paleontologist. Early life Seeley was born in London on 18 February 1839, the second son of Richard Hovill Seeley, a goldsmith, and his second wife Mary Govier. When his father was declared bankrupt, Seeley was sent to live with a family of piano makers. Between the ages of eleven and fourteen, he went to a day school and then spent the next two years learning to make pianos. He also attended lectures at the Royal School of Mines by Thomas Henry Huxley, Edward Forbes, and other notable scientists. In 1855, with the support of his uncle, Seeley began to study law but shortly gave it up to pursue a career as an actuary. In the late 1850s, he studied English and mathematics at the Working Men's College and served as a secretary for the college's museum. He also worked in the library of the British Museum, where Samuel Pickworth Woodward encouraged him to study geology. In 1859, Seeley began studies at Sidney Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and paleontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkable gift for interpreting fossils. Owen produced a vast array of scientific work, but is probably best remembered today for coining the word '' Dinosauria'' (meaning "Terrible Reptile" or "Fearfully Great Reptile"). An outspoken critic of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection, Owen agreed with Darwin that evolution occurred, but thought it was more complex than outlined in Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species''. Owen's approach to evolution can be considered to have anticipated the issues that have gained greater attention with the recent emergence of evolutionary developmental biology. Owen was the first president of the Microscopical Society of London in 1839 and edited many issues of its journal – then known as ''The Microscopic Journal''. Owen also c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Léon Moret
Léon Marie Louis Moret (4 July 1890 – 22 November 1972) was a French geologist and paleontologist. Initially trained in medicine he became a paleontologist and wrote several books on fossil plants and animals while also examining alpine geology. He supported the view that all rocks and soils were susceptible to flow over geological time. Moret was born in Annecy, Haute-Savoie where his father was a notary. He took an early interest in natural history, and went to study medicine at Lyon as several members of the family were doctors. He studied medicine and was enlisted into World War I in 1914. He received a Croix de Guerre and after being demobilized he received his doctorate in 1919 with a thesis titled ''Contribution à l’étude des exostoses ostéogéniques''. He then decided to study geology and became an assistant to Maurice Gignoux Maurice Irénée Marie Gignoux (19 October 1881 – 20 October 1955) was a French geologist who was a specialist on the stratigraphy of the Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous Turtles
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Turtles Of Europe
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |