|
Revolt Of Horea, Cloșca And Crișan
The Revolt of Horea, Cloșca and Crișan (; 31 October – 14 December, 1784) began in the Metaliferi Mountains, Transylvania, but it soon spread throughout all Transylvania and the Apuseni Mountains. The leaders were Horea (Vasile Ursu Nicola, 1731–1785), Cloșca (, 1747–1785) and Crișan (, 1733–1785). Background The revolt was directly related to the poor conditions of feudal serfs in the Principality of Transylvania. Though Orthodox Romanians lacked political equality with Catholic subjects in Transylvania, the events were not necessarily motivated by religious or ethnic tensions, but by basic human rights. After Holy Roman Emperor Leopold I's incorporation of the principality into the Habsburg domains in 1691, the rights of the Hungarian, Székely, and Saxon nobles were preserved. The peasants however, still had no representation in politics. Especially the Romanian peasantry had no guarantees for their Orthodox church institutions, though they were tolerated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chc Horea
CHC may refer to: Health care * Centro Hospitalar de Coimbra (C.H.C.), a hospital complex in Coimbra, Portugal * Columbia Health Care * Community health center * Community Health Clubs in Africa * Community health council * Continuing healthcare Education * Calvert Hall College, a Catholic preparatory high school in Maryland, USA * Chavakachcheri Hindu College, a famous school in the Thenmarachchi region, Jaffna * Chestnut Hill College - a Catholic college in Philadelphia, PA * College of the Holy Cross, a college in Worcester, Massachusetts * Cornwall Hill College, a college in Pretoria, South Africa * Robert D. Clark Honors College at the University of Oregon in Eugene, Oregon Politics * Cooler Heads Coalition, an organisation of self-described scientists who reject the scientific consensus on climate change * Congressional Hispanic Caucus, in the Congress of the United States * Croatian Helsinki Committee, a human rights group Sports * Colonial Hockey Conference, an NCA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
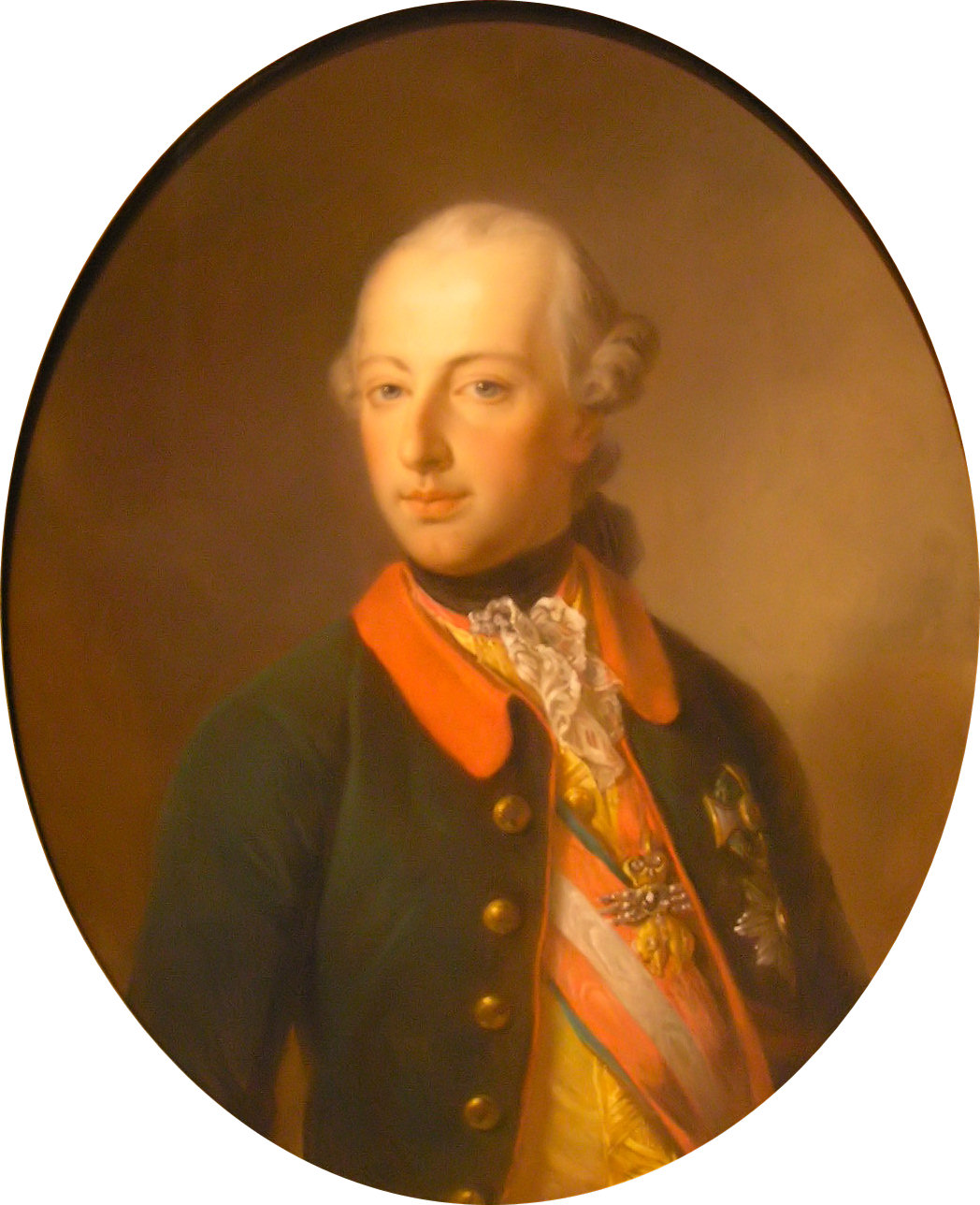
Georg Decker Joseph II
{{disambiguation ...
Georg may refer to: * ''Georg'' (film), 1997 *Georg (musical), Estonian musical * Georg (given name) * Georg (surname) * , a Kriegsmarine coastal tanker See also * George (other) George may refer to: People * George (given name) * George (surname) * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Washington, First President of the United States * George W. Bush, 43rd Preside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Pierre Brissot
Jacques Pierre Brissot (, 15 January 1754 – 31 October 1793), who assumed the name of de Warville (an English version of "d'Ouarville", a hamlet in the village of Lèves where his father owned property), was a leading member of the Girondins during the French Revolution and founder of the abolitionist Society of the Friends of the Blacks. Some sources give his name as Jean Pierre Brissot. Biography Early life and family Brissot was born at Chartres, the 13th child of a tavern keeper. He received an education and worked as a law clerk; first in Chartres then in Paris. He later moved to London because he wanted to pursue a literary career. He published many literary articles throughout his time in the British capital. While there, Brissot founded two periodicals that later did not do well and failed. He married Félicité Dupont (1759–1818), who translated English works, including Oliver Goldsmith and Robert Dodsley. They lived in London and had three children. His first works, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while phrases like ''liberté, égalité, fraternité'' reappeared in other revolts, such as the 1917 Russian Revolution, and inspired campaigns for the abolition of slavery and universal suffrage. The values and institutions it created dominate French politics to this day. Its causes are generally agreed to be a combination of social, political and economic factors, which the ''Ancien Régime'' proved unable to manage. In May 1789, widespread social distress led to the convocation of the Estates General, which was converted into a National Assembly in June. Continuing unrest culminated in the Storming of the Bastille on 14 July, which led to a series of radical measures by the Assembly, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breaking Wheel
The breaking wheel or execution wheel, also known as the Wheel of Catherine or simply the Wheel, was a torture method used for public execution primarily in Europe from antiquity through the Middle Ages into the early modern period by breaking the bones of a criminal or bludgeoning them to death. The practice was abolished in Bavaria in 1813 and in the Electorate of Hesse in 1836: the last known execution by the "Wheel" took place in Prussia in 1841. In the Holy Roman Empire it was a "mirror punishment" for highwaymen and street thieves, and was set out in the ''Sachsenspiegel'' for murder, and arson that resulted in fatalities. Punishment Those convicted as murderers, rapists, traitors and/or robbers to be executed by the wheel, sometimes termed to be "wheeled" or "broken on the wheel", would be taken to a public stage scaffold site and tied to the floor. The execution wheel was typically a large wooden spoked wheel, the same as was used on wooden transport carts and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adevărul
''Adevărul'' (; meaning "The Truth", formerly spelled ''Adevĕrul'') is a Romanian daily newspaper, based in Bucharest. Founded in Iași, in 1871, and reestablished in 1888, in Bucharest, it was the main left-wing press venue to be published during the Romanian Kingdom's existence, adopting an independent pro- democratic position, advocating land reform, and demanding universal suffrage. Under its successive editors Alexandru Beldiman and Constantin Mille, it became noted for its virulent criticism of King Carol I. This stance developed into a republican and socialist agenda, which made ''Adevărul'' clash with the Kingdom's authorities on several occasions. As innovative publications which set up several local and international records during the early 20th century, ''Adevărul'' and its sister daily ''Dimineața'' competed for the top position with the right-wing ''Universul'' before and throughout the interwar period. In 1920, ''Adevărul'' also began publishing its prestigious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Câmpeni
Câmpeni (German: ''Topesdorf''; Hungarian: ''Topánfalva'') is a town in Alba County, Transylvania, Romania. The town administers 21 villages: Boncești, Borlești, Botești (''Botesbánya''), Certege (''Csertés''), Coasta Vâscului, Dănduț, Dealu Bistrii, Dealu Capsei, Dric, Fața Abrudului, Florești, Furduiești, Mihoești, Motorăști, Peste Valea Bistrii, Poduri, Sorlița, Tomușești, Valea Bistrii, Valea Caselor, and Vârși (''Virs''). History The town has historical significance as the capital of the "Țara Moților" region. It is believed to be the site where the Revolt of Horea, Cloșca and Crișan (1784–1785) started. Horea was born near Câmpeni in the village that used to be called Arada (since renamed to Horea). His cellar is a tourist attraction in the town. During the Transylvanian revolution of 1848, Câmpeni was the political and military stronghold of Avram Iancu, a revolutionary leader of the Transylvanian Romanians' national movement. The Avram Ian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deva, Romania
Deva (; Hungarian: ''Déva'', Hungarian pronunciation: ; German: ''Diemrich'', ''Schlossberg'', ''Denburg''; Latin: ''Sargetia''; Turkish: ''Deve'', ''Devevar'') is a city in Romania, in the historical region of Transylvania, on the left bank of the river Mureș. It is the capital of Hunedoara County. Name Its name was first recorded in 1269 as castrum ''Dewa''. The origin of the name gave rise to controversy. It is considered that the name comes from the ancient Dacian word ''dava'', meaning "fortress" (as in ''Pelendava'', ''Piroboridava'', or ''Zargidava''). Other theories trace the name to a Roman Legion, the Legio II Augusta, transferred to Deva from Castrum Deva, now Chester (''Deva Victrix'') in Britain. János András Vistai assume the name is of old Turkic origin from the name Gyeücsa.Tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
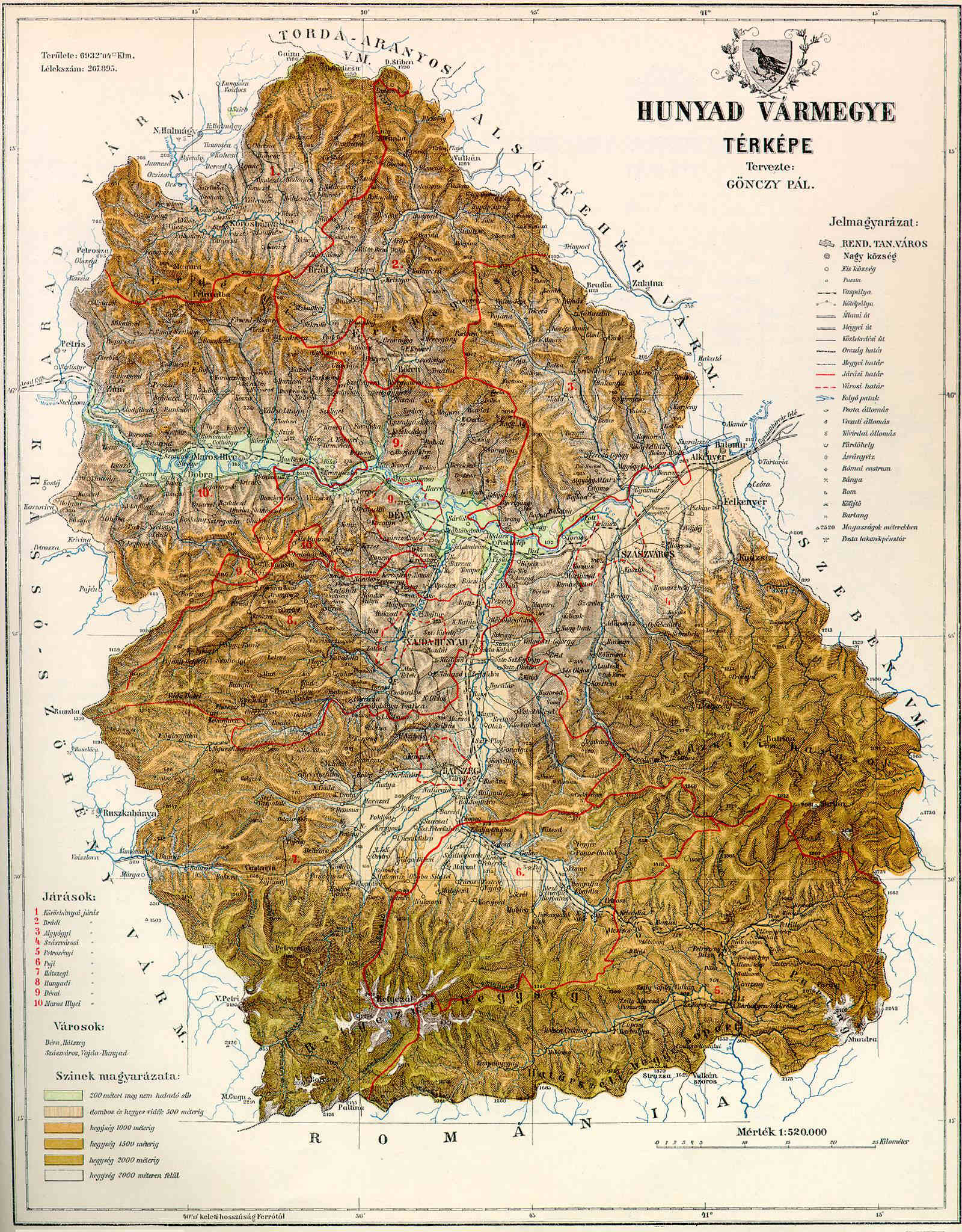
Hunyad County
Hunyad (today mainly Hunedoara) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary, of the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom and of the Principality of Transylvania. Its territory is now in Romania in Transylvania. The capital of the county was Déva (present-day Deva). Geography After 1876, Hunyad county shared borders with Romania and the Hungarian counties Krassó-Szörény, Arad, Torda-Aranyos, Alsó-Fehér and Szeben. Its area was 7,809 km2 around 1910. Etymology The toponym Hunyad most likely comes from the Hungarian verb, meaning 'to close' or 'to die'. According to linguist Géza Kuun, the name may keep the memory of the Huns. History The first known civilization living on the territory were the Scythian Agathyrsi and Sigynnae. Later the Dacians under their leader Burebista established solid control over the territory, but were conquered and massacred by the Roman Empire. Hunyad was part of Roman Dacia for a short time, but by the 3rd century it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaránd County
Zaránd County ( hu, Zaránd vármegye, la, Comitatus Zarandiensis) was an administrative unit of the Kingdom of Hungary and the Principality of Transylvania from the middle ages until 1876. Located mainly in the Fehér-Körös/ Crișul Alb river valley, today its former territory lies mostly in Romania, with a small amount in south-eastern Hungary. In the 16th century Zaránd was part of the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom and later the Partium territories of the Principality of Transylvania. It returned to Habsburg Hungary in 1699. In 1744 most of the western territory of Zaránd County, including its capital Zaránd/ Zărand, was transferred to Arad County; Körösbánya/ Baia de Criș became the capital of the new rump county. During a period of significant administrative reform in the Austrian Empire following the Revolutions of 1848 the traditional counties of Transylvania (including the Partium territories of Zaránd, Kraszna, Közép-Szolnok and Kővár) were abolished and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsó-Fehér County
Alsó-Fehér was an administrative county (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in western Romania (central Transylvania). The latest capital of the county was Nagyenyed (present-day Aiud). Geography Alsó-Fehér county shared borders with Hunyad, Torda-Aranyos, Kis-Küküllő, Nagy-Küküllő and Szeben counties. The rivers Mureș (river), Mureș and Târnava flowed through the county. Its area was 3,576.5 km2 around 1910. History Alsó-Fehér (Lower Fehér) county was formed when Fehér County (former), Fehér county was split in 1744 (the other half, Felső-Fehér county, consisted entirely of enclaves between Székely and Saxon Seat (administrative division), ''seats''). In 1876, when the administrative structure of Transylvania was changed, the territory of Alsó-Fehér was modified and parts of it were annexed to the counties of Torda-Aranyos County, Torda-Aranyos and Szeben County, Seben (during the same administra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |