|
Return Channel
In communications systems, the return channel (also reverse channel or return link) is the transmission link from a user terminal to the central hub. Return links are often, but not always, slower than the corresponding forward links. Examples where this is true include asymmetric digital subscriber line, cable modems, mobile broadband and satellite internet access. The return channel need not use the same medium as the main channel. For example, some hybrid Internet access services use a one-way cable television system for the forward channel and a dial-up modem for the return channel. Even when the return and forward channels use the same medium, their differences often dictate the use of very different data modulation and coding techniques. For example, in a star radio network, only the central hub transmits on the forward link, so channel access method is a consideration only on the return link. The "forward/return" terminology is also used for spacecraft communication lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications System
A communications system or communication system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks, transmission systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. The components of a communications system serve a common purpose, are technically compatible, use common procedures, respond to controls, and operate in union. Telecommunications is a method of communication (e.g., for sports broadcasting, mass media, journalism, etc.). Communication is the act of conveying intended meanings from one entity or group to another through the use of mutually understood signs and semiotic rules. Types By media An optical communication system is any form of telecommunication that uses light as the transmission medium. Equipment consists of a transmitter, which encodes a ''message'' into an optical '' signal'', a ''communication channel'', which carries the signal to its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Communication
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upstream (networking)
In computer networking, upstream refers to the direction in which data can be transferred from the client to the server ( uploading). This differs greatly from downstream not only in theory and usage, but also in that upstream speeds are usually at a premium. Whereas downstream speed is important to the average home user for purposes of downloading content, uploads are used mainly for web server applications and similar processes where the ''sending'' of data is critical. Upstream speeds are also important to users of peer-to-peer software. ADSL and cable modems are asymmetric, with the upstream data rate much lower than that of its downstream. Symmetric connections such as Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL) and T1, however, offer identical upstream and downstream rates. If a node A on the Internet is closer (fewer hops away) to the Internet backbone The Internet backbone may be defined by the principal data routes between large, strategically interconnected comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backward Channel
In a data transmission circuit a backward channel is the channel that passes data in a direction opposite to that of its associated forward channel. The backward channel is usually used for transmission of request, supervisory, acknowledgement, or error-control signals. The direction of flow of these signals is opposite to that in which user information is being transferred. The backward-channel bandwidth is usually less than that of the primary channel, that is, the forward ( user information) channel. For example, ADSL's upstream channel, considered a backward channel for some types of analysis, typically has a bandwidth less than one-fourth of the downstream channel. In data transmission, it is a secondary channel in which the direction of transmission is constrained to be opposite to that of the primary, ''i.e.'', the forward (user-information) channel. The direction of transmission in the backward channel is restricted by the control interchange circuit that controls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bent-pipe Transponder
A communications satellite's transponder is the series of interconnected units that form a communications channel between the receiving and the transmitting antennas. It is mainly used in satellite communication to transfer the received signals. A transponder is typically composed of: * an input band-limiting device (an input band-pass filter), * an input low-noise amplifier (LNA), designed to amplify the signals received from the Earth station (normally very weak, because of the large distances involved), * a frequency translator (normally composed of an oscillator and a frequency mixer) used to convert the frequency of the received signal to the frequency required for the transmitted signal, * an output band-pass filter, * a power amplifier (this can be a traveling-wave tube or a solid-state amplifier). Most communication satellites are radio relay stations in orbit and carry dozens of transponders, each with a bandwidth of tens of megahertz. Most transponders operate on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Communication
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The high frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications satell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downlink
In a telecommunications network, a link is a communication channel that connects two or more devices for the purpose of data transmission. The link may be a dedicated physical link or a virtual circuit that uses one or more physical links or shares a physical link with other telecommunications links. A telecommunications link is generally based on one of several types of information transmission paths such as those provided by communication satellites, terrestrial radio communications infrastructure and computer networks to connect two or more points. The term ''link'' is widely used in computer networking to refer to the communications facilities that connect nodes of a network. Sometimes the communications facilities that provide the communication channel that constitutes a link are also included in the definition of ''link''. Types Point-to-point A point-to-point link is a dedicated link that connects exactly two communication facilities (e.g., two nodes of a network, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', "remote", and ''metron'', "measure". Systems that need external instructions and data to operate require the counterpart of telemetry, telecommand. Although the term commonly refers to wireless data transfer mechanisms (e.g., using radio, ultrasonic, or infrared systems), it also encompasses data transferred over other media such as a telephone or computer network, optical link or other wired communications like power line carriers. Many modern telemetry systems take advantage of the low cost and ubiquity of GSM networks by using SMS to receive and transmit telemetry data. A ''telemeter'' is a physical device used in telemetry. It consists of a sensor, a transmission path, and a display, recording, or control device. Electronic devices are widely used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Access Method
In telecommunications and computer networks, a channel access method or multiple access method allows more than two terminals connected to the same transmission medium to transmit over it and to share its capacity. Examples of shared physical media are wireless networks, bus networks, ring networks and point-to-point links operating in half-duplex mode. A channel access method is based on multiplexing, that allows several data streams or signals to share the same communication channel or transmission medium. In this context, multiplexing is provided by the physical layer. A channel access method may also be a part of the multiple access protocol and control mechanism, also known as medium access control (MAC). Medium access control deals with issues such as addressing, assigning multiplex channels to different users and avoiding collisions. Media access control is a sub-layer in the data link layer of the OSI model and a component of the link layer of the TCP/IP model. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forward Link
In a telecommunications network, a link is a communication channel that connects two or more devices for the purpose of data transmission. The link may be a dedicated physical link or a virtual circuit that uses one or more physical links or shares a physical link with other telecommunications links. A telecommunications link is generally based on one of several types of information transmission paths such as those provided by communication satellites, terrestrial radio communications infrastructure and computer networks to connect two or more points. The term ''link'' is widely used in computer networking to refer to the communications facilities that connect nodes of a network. Sometimes the communications facilities that provide the communication channel that constitutes a link are also included in the definition of ''link''. Types Point-to-point A point-to-point link is a dedicated link that connects exactly two communication facilities (e.g., two nodes of a network, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
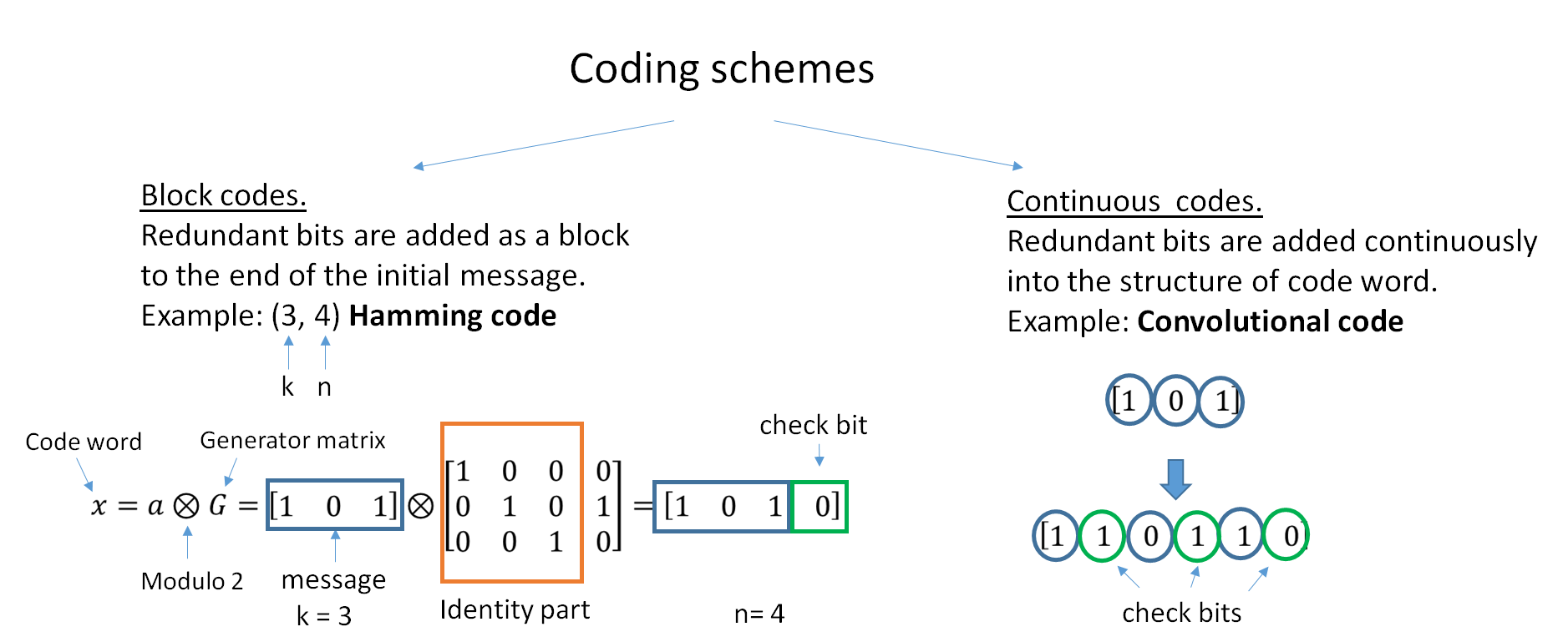
Channel Coding
In computing, telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, an error correction code, sometimes error correcting code, (ECC) is used for controlling errors in data over unreliable or noisy communication channels. The central idea is the sender encodes the message with redundant information in the form of an ECC. The redundancy allows the receiver to detect a limited number of errors that may occur anywhere in the message, and often to correct these errors without retransmission. The American mathematician Richard Hamming pioneered this field in the 1940s and invented the first error-correcting code in 1950: the Hamming (7,4) code. ECC contrasts with error detection in that errors that are encountered can be corrected, not simply detected. The advantage is that a system using ECC does not require a reverse channel to request retransmission of data when an error occurs. The downside is that there is a fixed overhead that is added to the message, thereby requiring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |