|
Retronectidae
Catenulida is an order of flatworms in the classical classification, or a class of flatworms in a phylogenetic approach. They are relatively small free-living flatworms, inhabiting freshwater and marine environments. There are about 100 species described worldwide, but the simple anatomy makes species distinction problematic. Description The anatomy of catenulids is simple and lacks hard parts. The mouth is located anteriorly and connects to a simple pharynx and a simple intestine that forms a ciliated sac. They possess two pairs of nerve cords and often a statocyst, as well as a single protonephridium. The gonads are unpaired. Unusually, the male gonopore opens on the dorsal surface of the animal, above the pharynx, while the female reproductive system lacks any of the usual ducts and related structures found in other flatworms. The sperm is nonmobile and lacks flagella or cilia. Asexual reproduction by paratomy is common, and it usually leads to a chain of organisms (zooids), h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracatenula
''Paracatenula'' is a genus of millimeter sized free-living marine gutless catenulid flatworms. ''Paracatenula'' is found worldwide in warm temperate to tropical subtidal sediments. They are part of the interstitial meiofauna of sandy sediments. Adult ''Paracatenula'' lack a mouth and a gut and are associated with intracellular symbiotic alphaproteobacteria of the genus ''Candidatus''. Riegeria. The symbionts are housed in bacteriocytes in a specialized organ, the trophosome (Greek ‘food’). ''Ca.'' Riegeria can make up half of the worms' biomass. The beneficial symbiosis with the carbon dioxide fixing and sulfur-oxidizing endosymbionts allows the marine flatworm to live in nutrient poor environments. The symbionts ''not only'' provide the nutrition but also maintain the primary energy reserves in the symbiosis. Diversity Five species of ''Paracatenula'' have been described - ''P. erato'', ''P. kalliope'', ''P. polyhymnia'', ''P. urania'' and ''P. galateia'', named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catenulida
Catenulida is an order of flatworms in the classical classification, or a class of flatworms in a phylogenetic approach. They are relatively small free-living flatworms, inhabiting freshwater and marine environments. There are about 100 species described worldwide, but the simple anatomy makes species distinction problematic. Description The anatomy of catenulids is simple and lacks hard parts. The mouth is located anteriorly and connects to a simple pharynx and a simple intestine that forms a ciliated sac. They possess two pairs of nerve cords and often a statocyst, as well as a single protonephridium. The gonads are unpaired. Unusually, the male gonopore opens on the dorsal surface of the animal, above the pharynx, while the female reproductive system lacks any of the usual ducts and related structures found in other flatworms. The sperm is nonmobile and lacks flagella or cilia. Asexual reproduction by paratomy is common, and it usually leads to a chain of organisms (zooids), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordariidae
Catenulida is an order of flatworms in the classical classification, or a class of flatworms in a phylogenetic approach. They are relatively small free-living flatworms, inhabiting freshwater and marine environments. There are about 100 species described worldwide, but the simple anatomy makes species distinction problematic. Description The anatomy of catenulids is simple and lacks hard parts. The mouth is located anteriorly and connects to a simple pharynx and a simple intestine that forms a ciliated sac. They possess two pairs of nerve cords and often a statocyst, as well as a single protonephridium. The gonads are unpaired. Unusually, the male gonopore opens on the dorsal surface of the animal, above the pharynx, while the female reproductive system lacks any of the usual ducts and related structures found in other flatworms. The sperm is nonmobile and lacks flagella or cilia. Asexual reproduction by paratomy is common, and it usually leads to a chain of organisms (zooid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retronectidae
Catenulida is an order of flatworms in the classical classification, or a class of flatworms in a phylogenetic approach. They are relatively small free-living flatworms, inhabiting freshwater and marine environments. There are about 100 species described worldwide, but the simple anatomy makes species distinction problematic. Description The anatomy of catenulids is simple and lacks hard parts. The mouth is located anteriorly and connects to a simple pharynx and a simple intestine that forms a ciliated sac. They possess two pairs of nerve cords and often a statocyst, as well as a single protonephridium. The gonads are unpaired. Unusually, the male gonopore opens on the dorsal surface of the animal, above the pharynx, while the female reproductive system lacks any of the usual ducts and related structures found in other flatworms. The sperm is nonmobile and lacks flagella or cilia. Asexual reproduction by paratomy is common, and it usually leads to a chain of organisms (zooids), h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrrheniellidae
Catenulida is an order of flatworms in the classical classification, or a class of flatworms in a phylogenetic approach. They are relatively small free-living flatworms, inhabiting freshwater and marine environments. There are about 100 species described worldwide, but the simple anatomy makes species distinction problematic. Description The anatomy of catenulids is simple and lacks hard parts. The mouth is located anteriorly and connects to a simple pharynx and a simple intestine that forms a ciliated sac. They possess two pairs of nerve cords and often a statocyst, as well as a single protonephridium. The gonads are unpaired. Unusually, the male gonopore opens on the dorsal surface of the animal, above the pharynx, while the female reproductive system lacks any of the usual ducts and related structures found in other flatworms. The sperm is nonmobile and lacks flagella or cilia. Asexual reproduction by paratomy is common, and it usually leads to a chain of organisms (zooids), h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catenula Lemnae
Catenulidae is a family of freshwater catenulid flatworms. Catenulids are characterized by an ovoid brain A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ... located in the preoral region. The brain lacks a distinct division into anterior and posterior lobes, although a constriction may occur. References Catenulida Platyhelminthes families {{flatworm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooid
A zooid or zoöid is a single animal that is part of a colonial animal. This lifestyle has been adopted by animals from separate unrelated taxa. Zooids are multicellular; their structure is similar to that of other solitary animals. The zooids can either be directly connected by tissue (e.g. corals, Catenulida, Siphonophorae, Pyrosome or Ectoprocta) or share a common exoskeleton (e.g. Bryozoa or Pterobranchia). The colonial organism as a whole is called a ''zoon'' , plural ''zoa'' (from Ancient Greek meaning animal; plural , ). Zooids can exhibit polymorphism. For instance, extant bryozoans may have zooids adapted for different functions, such as feeding, anchoring the colony to the substratum and for brooding embryos. However, fossil bryozoans are only known by the colony structures that the zooids formed during life. There are correlations between the size of some zooids and temperature. Variations in zooid size within colonies of fossils can be used as an indicator of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Fertilization
Internal fertilization is the union of an egg and sperm cell during sexual reproduction inside the female body. Internal fertilization, unlike its counterpart, external fertilization, brings more control to the female with reproduction. For internal fertilization to happen there needs to be a method for the male to introduce the sperm into the female's reproductive tract. Most taxa that reproduce by internal fertilization are gonochoric. In mammals, reptiles, and certain other groups of animals, this is done by copulation, an intromittent organ being introduced into the vagina or cloaca. In most birds, the cloacal kiss is used, the two animals pressing their cloacas together while transferring sperm. Salamanders, spiders, some insects and some molluscs undertake internal fertilization by transferring a spermatophore, a bundle of sperm, from the male to the female. Following fertilization, the embryos are laid as eggs in oviparous organisms, or continue to develop inside the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhabditophora
Rhabditophora (from ''rhabdito''-, rhabdite + Greek -φορος ''phoros'' bearer, i.e., "rhabdite bearers") is a class of flatworms. It includes all parasitic flatworms (clade Neodermata) and most free-living species that were previously grouped in the now obsolete class Turbellaria. Therefore, it contains the majority of the species in the phylum Platyhelminthes, excluding only the catenulids, to which they appear to be the sister group. The clade Rhabditophora was originally erected by Ulrich Ehlers in 1985Ehlers, U. (1985) ''Phylogenetic relationships within the Platyhelminthes''. ''In'' S. Conway Morris; J. D. George; R. Gibson; H. M. Platt (Eds.), ''The origins and relationships of lower invertebrates''. Oxford, Clarendon Press, p. 143-158. based on morphological analyses and its monophyly was later confirmed by molecular studies. Description Rhabditophorans are characterized by the presence of lamellated rhabdites, rodlike granules secreted in the cells of the epidermis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyly
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic groups are typically characterised by shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies), which distinguish organisms in the clade from other organisms. An equivalent term is holophyly. The word "mono-phyly" means "one-tribe" in Greek. Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic group'' consists of all of the descendants of a common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups. A '' polyphyletic group'' is characterized by convergent features or habits of scientific interest (for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, aquatic insects). The features by which a polyphyletic group is differentiated from others are not inherited from a common ancestor. These definitions have taken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotroph
A Chemotroph is an organism that obtains energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments. These molecules can be organic ( chemoorganotrophs) or inorganic (chemolithotrophs). The chemotroph designation is in contrast to phototrophs, which use photons. Chemotrophs can be either autotrophic or heterotrophic. Chemotrophs can be found in areas where electron donors are present in high concentration, for instance around hydrothermal vents. Chemoautotroph Chemoautotrophs, in addition to deriving energy from chemical reactions, synthesize all necessary organic compounds from carbon dioxide. Chemoautotrophs can use inorganic energy sources such as hydrogen sulfide, elemental sulfur, ferrous iron, molecular hydrogen, and ammonia or organic sources to produce energy. Most chemoautotrophs are extremophiles, bacteria or archaea that live in hostile environments (such as deep sea vents) and are the primary producers in such ecosystems. Chemoautotrophs generally fall into s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
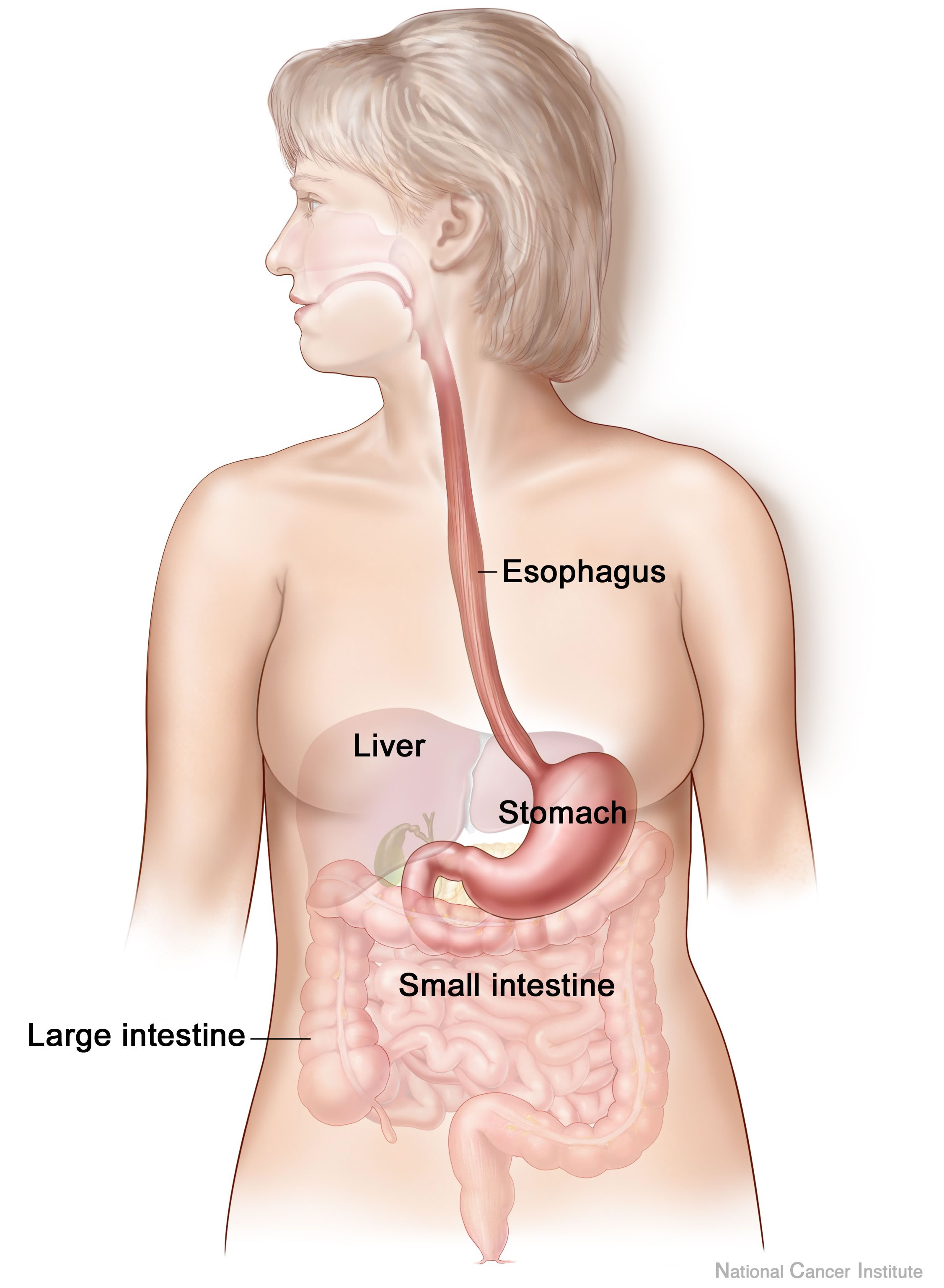
Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to enter the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |