|
Restalrig
Restalrig () is a small residential suburb of Edinburgh, Scotland (historically, an estate and independent parish). It is located east of the city centre, west of Craigentinny and to the east of Lochend, both of which it overlaps. Restalrig Road is the main route through the area, running from London Road, at Jock's Lodge, to Leith Links. It is in the ward of Lochend. History and buildings The place name ''Restalrig'' means ''ridge of the miry land'' (from ''lestal'', a northern dialect term meaning ''mire'' and ''rig'', Scots and northern English meaning a linear field or land-holding). It is first mentioned as Lestalric in 1165, when Edward de Lestalric built a church on the site. The church was completed in 1210 by his grandson, Sir Thomas de Lestalric. The area, over the following centuries, is variously named as Lestalryk, Restalric or Rastalrig. The Norman noble family the de Lestalrics were the ancient landowners in the area (including nearby South Leith). Sir Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan Logan
Clan Logan is a Scottish clan. Two distinct branches of Clan Logan exist: the Highland branch; and the Lowland branch (which descends from Sir Robert Logan of Restalrig who married Katherine Stewart, a daughter of the future Robert II () and, in 1400, became Lord High Admiral of Scotland). The clan does not have a chief recognised by Lord Lyon King of Arms, and therefore can be considered an armigerous clan. Today, some regard Clan MacLennan as a variant of the Highland Logan clan. History The surname ''Logan'' is a territorial name, likely derived from the lands of Logan in present Ayrshire, Scotland. The earliest record of the surname is of Robert Logan who is recorded as witnessing the resignation of the lands of Ingilbristoun in 1204. The name is variously recorded throughout the 13th century. Several Logans are recorded as paying homage to Edward I of England within the Ragman Rolls of 1296. These are Phelippe de Logyn (burgess from Montrose), Thurbrandus de Logyn (from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calton Hill
Calton Hill () is a hill in central Edinburgh, Scotland, situated beyond the east end of Princes Street and included in the city's UNESCO World Heritage Site. Views of, and from, the hill are often used in photographs and paintings of the city. Calton Hill is the headquarters of the Scottish Government, which is based at St Andrew's House,Youngson, A.J. (2001): "The Companion Guide to Edinburgh and the borders", Chapter 9 (Calton Hill), Polygon Books, Edinburgh, UK, on the steep southern slope of the hill. The Scottish Parliament Building and other prominent buildings such as Holyrood Palace lie near the foot of the hill. Calton Hill is also the location of several monuments and buildings: the National Monument,The Calton Hill |
Siege Of Leith
The siege of Leith ended a twelve-year encampment of French troops at Leith, the port near Edinburgh, Scotland. The French troops arrived by invitation in 1548 and left in 1560 after an English force arrived to attempt to assist in removing them from Scotland. The town was not taken by force and the French troops finally left peacefully under the terms of a treaty signed by Scotland, England and France.Knight, p. 120 Background The Auld Alliance and Reformation of religion Scotland and France had long been allies under the "Auld Alliance", first established in the 13th century. However, during the 16th century, divisions appeared between a pro-French faction at Court and Protestant reformers. The Protestants saw the French as a Catholic influence and, when conflict broke out between the two factions, called on English Protestants for assistance in expelling the French from Scotland. In 1542, King James V of Scotland died, leaving only a week-old daughter who was proclaimed Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lochend Castle
Lochend House, also known as Restalrig Castle Coventry, Martin (2001) ''The Castles of Scotland''. Goblinshead. p.300 and Lochend Castle, is an occupied house, incorporating the remains of a 16th-century L-plan tower house, in Edinburgh, Scotland. It is located in the Lochend area, about east of Edinburgh Castle. The house is protected as a category B listed building. History The original castle was built on lands originally belonging to the Lestalric family, but which had passed to the Logan family of Restalrig early in the 14th century. That family retained possession until forfeited for their part in the Gowrie conspiracy against King James VI. The castle was burned by William Gilmour of the Inch at that time. Sir Robert Logan was the last member of the family to own the property. Thereafter the property was in the hands of Arthur Elphinstone, 6th Lord Balmerino, from 1704. He was executed in London for his part in the Jacobite rising of 1745, having been captured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marian Civil War
The Marian civil war in Scotland (1568–1573) was a period of conflict which followed the abdication of Mary, Queen of Scots, and her escape from Lochleven Castle in May 1568. Those who ruled in the name of her infant son James VI fought against the supporters of the Queen, who was exiled in England. Edinburgh Castle, which was garrisoned in her name, became the focus of the conflict and surrendered only after an English intervention in May 1573. The conflict in 1570 was called an "intestine war in the bowels of this commonwealth", and the period was called soon after an "intestine war driven by questions against authority." Queen's men and King's men The supporters of Queen Mary had popular international support for what was seen as the legitimate cause of supporters of an unjustly deposed monarch. The King's party claimed that their cause was a war of religion, like that in France, and that they were fighting for the Protestant cause. Mary had escaped from her imprisonment in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Craigentinny
Craigentinny ( gd, Creag an t-Sionnaich) is a suburb in the north-east of Edinburgh, Scotland, east of Restalrig and close to Portobello. Its name is a corruption of the Scottish Gaelic ''Creag an t-Sionnaich'' meaning "Foxrock" but more likely ''Creag an teine'' meaning "Fire Crag" or a beacon which is similar to Ardentinny in Argyll. History Previously moorland, the first major house was built in 1604. This house, Craigentinny Castle (later renamed Craigentinny House), gives its name to the wider area. It was built by James Nisbet of the Nisbet family associated more strongly with the Dean area of the city, as the occupants of Dean House. The land was bought from the Logan family of Restalrig. Through the Nisbet family it passed to John Nisbet, Lord Dirleton around 1680. Through Lord Dirleton it passed to the Scott-Nisbes. After the death of John Scott-Nisbet in 1765 it was bought by a William Miller, a wealthy seedsman and Quaker, living on the Canongate, who already own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
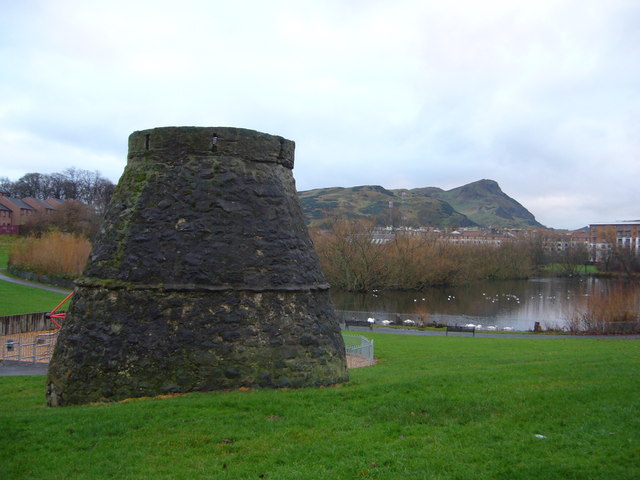
Lochend, Edinburgh
Lochend is a mainly residential suburb of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It is named after Lochend Castle and the adjacent Lochend Loch, located in the western part of Restalrig on the boundary between Leith and The Canongate, approximately two miles from Edinburgh city centre. The suburb consists largely of a 1930s public housing estate, and is bounded on the west by Easter Road. Lochend Loch is fed from underground springs. With no outlet stream, it was once used for a piped water supply to Leith but was partially filled in the 1960s to reduce water depth for safety reasons, and is now fenced and partly overgrown, providing a wildlife area. It forms a central feature of Lochend Park. Nearby, Lochend Castle was largely demolished in the 16th century, but surviving elements of it form part of the 19th century Lochend House. A 16th century beehive doocot, associated with the castle, stands in Lochend Park. James IV of Scotland James IV (17 March 1473 – 9 Septembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jock's Lodge
Jock's Lodge is an area of Edinburgh, Scotland. It centres on the junction of London Road and Willowbrae Road (part of the A1 trunk route to London), Portobello Road and Restalrig Road South (Smokey Brae) and is an alternative name for the Meadowbank / Piershill area. Restalrig village lies to its north. The name is mentioned, as ''Jokis Ludge'', in John Nicoll's diary in 1650. A sasine in 1736 refers to "the Bleugowns Lodge commonly called Jocks Lodge". It is recorded that the Bluegowns, the king's bedesmen, were called by themselves and others ''Jockies''. Thus the name of their house was ''Jockies Lodge''. The area is dominated by civil service office blocks, St Margaret's House and Meadowbank House, which were constructed in the early-1970s on the site of the St Margaret's railway locomotive depot, which was primarily for steam locomotives. From 2008, St Margaret's House has been leased to Edinburgh Palette, a registered charity which provides some 200 affordable stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capture Of Berwick (1482)
In July 1482 an English army invaded Scotland during the Anglo-Scottish Wars. The town of Berwick-upon-Tweed and its castle were captured and the English army briefly occupied Edinburgh. These events followed the signing of the Treaty of Fotheringhay, 11 June 1482, in which Alexander Stewart, Duke of Albany, the brother of James III of Scotland declared himself King of Scotland and swore loyalty to Edward IV of England. The follow-up invasion of Scotland under the command of Edward's brother, Richard, Duke of Gloucester failed to install Albany on the throne, but Berwick has remained English ever since the castle surrendered on 24 August. The English army left Edinburgh with a promise for the repayment of the dowry paid for the marriage of Princess Cecily of England to the Scottish Prince. Treaty of Fotheringhay Edward IV was disappointed by the failure of his 1474 treaty with James III who had promised that his son, Prince James would marry Cecily of York. The betrothal wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh East (UK Parliament Constituency)
Edinburgh East is a burgh constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It elects one Member of Parliament (MP) by the first past the post system of election. In present form, the constituency was first used at the 2005 general election, but there was also an Edinburgh East constituency in existence from 1885 to 1997. Boundaries Edinburgh East is now one of five constituencies covering the City of Edinburgh council area. All are entirely within the city council area. Prior to the 2005 general election, the city area was covered by six constituencies, with one straddling a boundary with another council area. The Redistribution of Seats Act 1885 provided that the constituency was to consist of the Municipal Wards of Broughton, Calton, and Canongate, and so much of St. Leonard's Ward as lies to the north of a line drawn along the centres of East and West Richmond Streets. In 1918 the constituency consisted of the "Burgh of Musselburgh and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Drury
Sir William Drury (2 October 152713 October 1579) was an English statesman and soldier. Family William Drury, born at Hawstead in Suffolk on 2 October 1527, was the third son of Sir Robert Drury (c. 1503–1577) of Hedgerley, Buckinghamshire, and Elizabeth Brudenell, the daughter of Edmund Brudenell of Chalfont St Peter, Buckinghamshire. He was the grandson of another Sir Robert Drury (c. 1456–2 March 1535), Speaker of the House of Commons in 1495. He was a brother of Sir Robert Drury (1525–1593) and Sir Drue Drury (1531/2–1617). Career Drury was educated at Gonville College, Cambridge. Fighting in France, Drury was taken prisoner in 1544; then after his release, he helped Lord Russell, afterwards Earl of Bedford, to quell a rising in Devonshire in 1549, but he did not come to the front until the reign of Elizabeth I. In 1554 he sat as Member of Parliament for Chipping Wycombe. In 1559, he was sent to Edinburgh to report on the condition of Scottish politics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by ''Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world. The earliest surviving historical references are in the royal charter authorising the construction of Holyrood Abbey in 1128 in which it is termed ''Inverlet'' (Inverleith). After centuries of control by Edinburgh, Leith was made a separate burgh in 1833 only to be merged into Edinburgh in 1920. Leith is located on the southern coast of the Firth of Forth and lies within the City of Edinburgh Council area; since 2007 it has formed one of 17 multi-member wards of the city. History As the major port serving Edinburgh, Leith has seen many significant events in Scottish history. First settlement The earliest evidence of settlement in Leith comes from several archaeological digs undertaken in The Shore area in the late 20th century. Amongst the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
.jpg)