|
Reserves Act 1977
The Reserves Act 1977 is an Act of Parliament passed in New Zealand. It is administered by the Department of Conservation It contains provisions for the acquisition, control, management, maintenance, development and use of public reserves. Types of reserves The law defines particular types of reserves, which are all managed by the department: * National reserves are areas that have been designated as having national importance due to their historical or ecological value. * Recreation reserves have been established for recreation and sporting activities, to promote physical welfare and enjoyment and protect the natural environment and beauty. * Historic reserves have been established to protect and preserve places, objects and natural features that are of historic, archaeological, cultural, educational and other special interest. * Scenic reserves are reserves protected because of their scenic interest, beauty or natural features. These are the most common type of protecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Parliament
The New Zealand Parliament ( mi, Pāremata Aotearoa) is the unicameral legislature of New Zealand, consisting of the King of New Zealand ( King-in-Parliament) and the New Zealand House of Representatives. The King is usually represented by his governor-general. Before 1951, there was an upper chamber, the New Zealand Legislative Council. The New Zealand Parliament was established in 1854 and is one of the oldest continuously functioning legislatures in the world. It has met in Wellington, the capital of New Zealand, since 1865. The House of Representatives normally consists of 120 members of Parliament (MPs), though sometimes more due to overhang seats. There are 72 MPs elected directly in electorates while the remainder of seats are assigned to list MPs based on each party's share of the total party vote. Māori were represented in Parliament from 1867, and in 1893 women gained the vote. Although elections can be called early, each three years Parliament is dissolved and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Purpose Reserves
A government purpose reserve is a type of Protected areas of New Zealand, New Zealand protected area. There are currently 215 recognised government purpose reserves in New Zealand. Some of these reserves are important wetlands. Others are small pockets of land around lighthouses. North Island Northland Region * Awakino Government Purpose Wildlife Management Reserve * Coates Memorial Church Reserve * Hewlett Point Sand Islands Government Purpose Reserve * Lake Taeore Wildlife Management Reserve * Manganui River Government Purpose Wildlife Management Reserve * Mangawhai Government Purpose Wildlife Refuge Reserve * Mangonuiowae Government Purpose Wildlife Management Reserve * Marsden Spit Government Purpose Wildlife Management Reserve * Matapouri Estuary Government Purpose Wildlife Management Reserve * Ngunguru Government Purpose Wildlife Management Reserve * Omamari Government Purpose Wildlife Management Reserve * Omatai Government Purpose Wildlife Management Reserve * Opuawhanga G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Law In New Zealand
Environmental law in New Zealand is an increasingly well defined body of national law that has a specialist court, The Environment Court of New Zealand (Māori: Te Kooti Taiao o Aotearoa), to decide related issues. History The roots of New Zealand environmental law can be traced to the common law of Australia. The increasing environmental awareness of the 1960s led to a specific body of environmental law that developed in many Western countries including New Zealand. Environmental law became more integrated in the 1980s with the passing of the Environment Act 1986 and the Conservation Act 1987. These Acts set up the Ministry for the Environment, Parliamentary Commissioner for the Environment and the Department of Conservation. The most significant Act of Parliament concerning environmental law was the passing of Resource Management Act 1991. Issues under the Act are adjudicated by the Environment Court of New Zealand. Timeline This timeline outlines the more significant envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statutes Of New Zealand
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by legislative bodies; they are distinguished from case law or precedent, which is decided by courts, and regulations issued by government agencies. Publication and organization In virtually all countries, newly enacted statutes are published and distributed so that everyone can look up the statutory law. This can be done in the form of a government gazette which may include other kinds of legal notices released by the government, or in the form of a series of books whose content is limited to legislative acts. In either form, statutes are traditionally published in chronological order based on date of enactment. A universal problem encountered by lawmakers throughout human history is how to organize published statutes. Such publications ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Areas Of New Zealand
Protected areas of New Zealand are areas that are in some way protected to preserve their environmental, scientific, scenic, historical, cultural or recreational value. There are about 10,000 protected areas covering about a third of the country. The method and aims of protection vary according to the importance of the resource and whether it is publicly or privately owned. Nearly 30 percent of New Zealand's land mass is publicly owned with some degree of protection. Most of this land – about – is administered by the Department of Conservation. There are 13 national parks, thousands of reserves, 54 conservation parks, and a range of other conservation areas. The department also manages 44 offshore and coastal marine reserves. Any development in Coastal Marine Areas, which extend up to the mean high water spring mark and up to a kilometre up rivers, require a resource consent under the Resource Management Act. History The history of New Zealand's protected areas dates back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Of New Zealand
The environment of New Zealand is characterised by an endemic flora and fauna which has evolved in near isolation from the rest of the world. The main islands of New Zealand span two biomes, temperate and subtropical, complicated by large mountainous areas above the tree line.Walter, H. & Breckle, S-W. (2002). ''Walter's Vegetation of the Earth: The Ecological Systems of the Geo-Biosphere''. New York: Springer-Verlag, p. 86 There are also New Zealand Subantarctic Islands, numerous smaller islands which extend into the subantarctic. The prevailing weather systems bring significantly more rain to the west of the country. New Zealand's territorial waters cover a much larger area than its landmass and extend over the continental shelf and abyssal plateau in the South Pacific Ocean, Tasman Sea and Southern ocean. Historically having an isolated and endemic ecosystem far into modernity, the arrival of Polynesians about 1300 AD and then later European settlers began to have significa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation In New Zealand
Conservation in New Zealand has a history associated with both Māori and Europeans. Both groups of people caused a loss of species and both altered their behaviour to a degree after realising their effect on indigenous flora and fauna. Protected areas New Zealand has thirteen national parks, forty four marine reserves and many other protected areas for the conservation of biodiversity. The introduction of many invasive species is threatening the indigenous biodiversity, since the geographical isolation of New Zealand led to the evolution of plants and animals that did not have traits to protect against predation. New Zealand has a high proportion of endemic species, so pest control is generally regarded as a high priority. The New Zealand Department of Conservation administers approximately 30% of New Zealand's land, along with less than 1% of the country's marine environment, for conservation and recreational purposes. It has published lists, under the New Zealand Threat C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Land Court
The Māori Land Court (Māori: Te Kōti Whenua Māori) is the specialist court of record in New Zealand that hears matters relating to Māori land. Māori Land Court history The Māori Land Court was established in 1865 as the Native Land Court of New Zealand under the Native Lands Act. The court was established to facilitate the purchase of Māori land by the Crown by converting collectively owned Māori customary land into Māori freehold land. The Act created the Native Land Court to identify ownership interests in Māori land and to create individual titles (in place of customary communal title) that were recognisable in English law. Under the Native Lands Act 1865 only ten owners could be listed on land titles issued by the court. As outlined by Williams, "government policy from 1858 onwards ... sought to introduce a rapid individualisation of ancestral Māori land in order to ensure the availability of most of that land for settlement by Pakeha settlers". A continuatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilderness Areas Of New Zealand
Wilderness or wildlands (usually in the plural), are natural environments on Earth that have not been significantly modified by human activity or any nonurbanized land not under extensive agricultural cultivation. The term has traditionally referred to terrestrial environments, though growing attention is being placed on marine wilderness. Recent maps of wilderness suggest it covers roughly one quarter of Earth's terrestrial surface, but is being rapidly degraded by human activity. Even less wilderness remains in the ocean, with only 13.2% free from intense human activity. Some governments establish protection for wilderness areas by law to not only preserve what already exists, but also to promote and advance a natural expression and development. These can be set up in preserves, conservation preserves, national forests, national parks and even in urban areas along rivers, gulches or otherwise undeveloped areas. Often these areas are considered important for the survival of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Purpose Reserves
Local purpose reserves are a type of New Zealand protected area established under the Reserves Act 1977. Unlike other forms of reserve established under the act, they do not need to have a specific conservation purpose. Many are owned by councils. Under the legislation, local purpose reserves can be created for a "utility, road, street, access way, esplanade, service lane, playcentre, kindergarten, plunket room, or other like purpose". They include quarry reserves, pilot reserves, aerodrome reserves, and water reserves to protect reservoir catchments. Esplanade reserves Esplanade reserves are strips of land beside the sea, rivers and lakes. Historically, many esplanade reserves were wide when they were created, often known as the ' Queen's Chain'. Under the Resource Management Act 1991 The Resource Management Act (RMA) passed in 1991 in New Zealand is a significant, and at times, controversial Act of Parliament. The RMA promotes the sustainable management of natural and ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Reserves Of New Zealand
A scientific reserve is a type of New Zealand protected area owned by the New Zealand Government and administered by the Department of Conservation as an area for scientific research and education. Scientific reserves are established under the Reserves Act 1977 " for the purpose of protecting and preserving in perpetuity for scientific study, research, education, and the benefit of the country, ecological associations, plant or animal communities, types of soil, geomorphological phenomena, and like matters of special interest.". Land Information New Zealand Toitū Te Whenua Land Information New Zealand (LINZ) is the public service department of New Zealand charged with geographical information and surveying functions as well as handling land titles, and managing Crown land and property. The minist ... lists 51 recreation reserves on its website. Entry to part of all of these reserves is limited to those with specific permits. References Protected areas of New Zealand Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
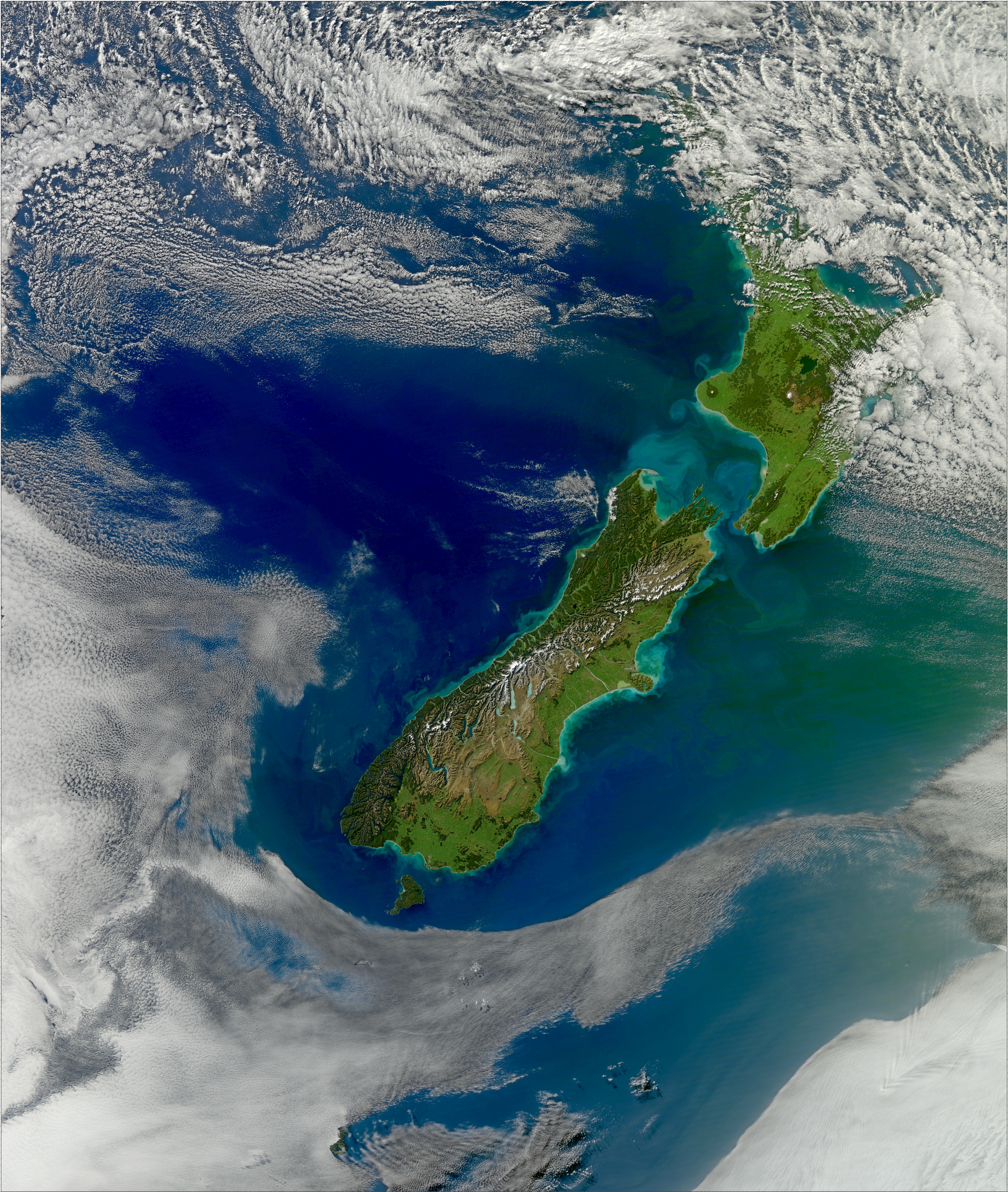
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |