|
Research And Development In Pakistan
Science and technology is a growing field in Pakistan and has played an important role in the country's development since its founding. Pakistan has a large pool of scientists, engineers, doctors, and technicians assuming an active role in science and technology. The real growth in science in Pakistan occurred after the establishment of the Higher education Commission in 2002 which supported science in a big way and also became the major sponsor of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences under the leadership of Prof. Atta-ur-Rahman. The emphasis was placed on quality rather than numbers during this period. The quality measures introduced by Prof. Atta-ur-Rahman as Founding Chairman HEC included:1) All Ph.D. thesis were evaluated by eminent foreign scientists,2) All PhD theses and research papers were checked for plagiarism 3) Some 11,000 students were sent abroad to leading universities for PhD level training and absorbed on their return, 4) Appointments at faculty positions were lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdus Salam 1987
Abdul (also Romanization of Arabic, transliterated as Abdal, Abdel, Abdil, Abdol, Abdool, or Abdoul; ar, عبد ال, ) is the most frequent transliteration of the combination of the Arabic word ''Abd (Arabic), Abd'' (, meaning "Servant") and the definite prefix ''Al-, al / el'' (, meaning "the"). It is the initial component of many compound (linguistics), compound names, names made of two words. For example, , ', usually spelled ''Abdel Hamid'', ''Abdelhamid'', ''Abd El Hamid'' or ''Abdul Hamid'', which means "servant of The Praised" (God). The most common use for ''Abdul'' by far, is as part of a male #Theophoric naming, given name, written in English. When written in English language, English, ''Abdul'' is subject to variable spacing, spelling, and hyphenation. The meaning of ''Abdul'' literally and normally means "Slave of the", but English translations also often translate it to "Servant of the". Spelling variations Variations in spelling are primarily because of the va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
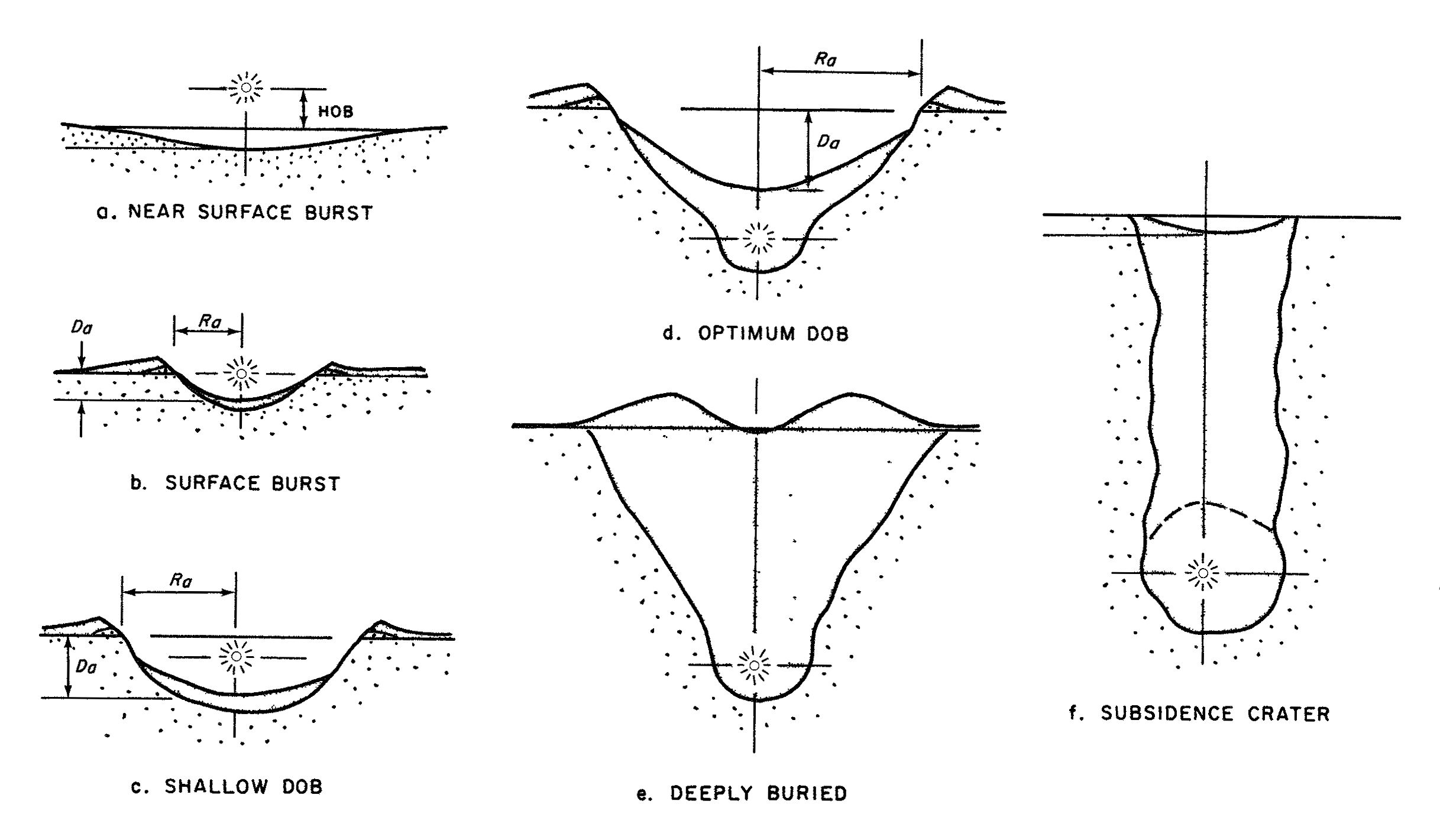
Pokhran-II
The Pokhran-II tests were a series of five nuclear bomb test explosions conducted by India at the Indian Army's Pokhran Test Range in May 1998. It was the second instance of nuclear testing conducted by India; the first test, code-named ''Smiling Buddha'', was conducted in May 1974. The tests achieved their main objective of giving India the capability to build fission and thermonuclear weapons with yields up to 200 kilotons. The then-Chairman of the Indian Atomic Energy Commission described each one of the explosions of ''Pokhran-II'' to be "equivalent to several tests carried out by other nuclear weapon states over decades". Subsequently, India established computer simulation capability to predict the yields of nuclear explosives whose designs are related to the designs of explosives used in this test. ''Pokhran-II'' consisted of five detonations, the first of which was a fusion bomb while the remaining four were fission bombs. The tests were initiated on 11 May 1998, und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chagai-II
Chagai-II is the codename assigned to the second atomic test conducted by Pakistan, carried out on 30 May 1998 in the Kharan Desert in Balochistan Province of Pakistan. ''Chagai-II'' took place two days after Pakistan's first successful test, ''Chagai-I'', which was carried out on 28 May 1998 in the Ras Koh Hills, Ras Koh area in Chagai District, Balochistan, Pakistan. The initial goals were to test the new designs of the weapon rather than studying the effects, and were different from the first tests in that they were primarily conducted by the Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission (PAEC), with the Pakistan Armed Forces Military engineering, engineering formations having only a supporting role. The tests detonated Implosion-type nuclear weapon, implosion-type Boosted fission weapon, boosted-fission Weapon-grade#plutonium, military-grade plutonium devices, contrary to the Chagai-I tests that were weapons-grade uranium devices. The performance of these tests made it a total of six t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chagai-I
Chagai-I is the code name of five simultaneous underground nuclear tests conducted by Pakistan at 15:15 hrs PKT on 28 May 1998. The tests were performed at Ras Koh Hills in the Chagai District of Balochistan Province. Chagai-I was Pakistan's first public test of nuclear weapons. Its timing was a direct response to India's second nuclear test Pokhran-II, on 11 and 13 May 1998. These tests by Pakistan and India resulted in United Nations Security Council Resolution 1172 and economic sanctions on both states by a number of major powers, particularly the United States and Japan. By testing nuclear devices, Pakistan became the seventh country to publicly test nuclear weapons. Pakistan's second nuclear test, Chagai-II, followed on 30 May 1998. Background Several historical and political events and personalities in the 1960s and early 1970s led Pakistan to gradually transition to a program of nuclear weapons development, that began in 1972. Plans for nuclear weapons testing start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pokhran-I
Operation Smiling BuddhaThis test has many code names. Civilian scientists called it "Operation Smiling Buddha" and the Indian Army referred to it as ''Operation Happy Krishna''. According to United States Military Intelligence, ''Operation Happy Krishna'' was the code name for the Indian Army's construction of the underground site in which the tests were conducted. The Ministry of External Affairs designated the test as ''Pokhran-I''. ( MEA designation: Pokhran-I) was the assigned code name of India's first successful nuclear bomb test on 18 May 1974. The bomb was detonated on the army base Pokhran Test Range (PTR), in Rajasthan, by the Indian Army under the supervision of several key Indian generals. ''Pokhran-I'' was also the first confirmed nuclear weapons test by a nation outside the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council. Officially, the Indian Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) characterised this test as a "peaceful nuclear explosion". Indira G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirana-I
The Kirana Hills is a small and extensive rocky mountain range located in Rabwah and Sargodha, Pakistan. It is also a place of tourist attraction in Sargodha City. Locally known as "Black Mountains" due to its brownish landscape, its highest peak is about . Known for its extreme weather conditions, its maximum temperature reaches to in the summer while the minimum temperature recorded is as low as freezing point in the winter. Due to its rocky landscape and minerals, a volcanic and geophysical survey was conducted by the Geological Survey of Pakistan. Its environs are heavily infested with wild boars. Nuclear weapons tests Kirana-I was the assigned codename of the 24 subcritical ' cold tests' conducted by Pakistan from 1983–90. The Pakistan Army Corps of Engineers led the civil engineering of potential sites for the tests to be conducted. The Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission (PAEC) carried out several tests of the feasibility of weapon designs; all tests were subcriti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan And Weapons Of Mass Destruction
Pakistan is one of nine states to possess nuclear weapons. Pakistan began development of nuclear weapons in January 1972 under Prime Minister Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, who delegated the program to the Chairman of the Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission (PAEC) Munir Ahmad Khan with a commitment to having the device ready by the end of 1976. Since PAEC, which consisted of over twenty laboratories and projects under reactor physicist Munir Ahmad Khan, was falling behind schedule and having considerable difficulty producing fissile material, Abdul Qadeer Khan, a metallurgist working on centrifuge enrichment for Urenco, joined the program at the behest of the Bhutto administration by the end of 1974. As pointed out by Houston Wood, "The most difficult step in building a nuclear weapon is the production of fissile material"; as such, this work in producing fissile material as head of the Kahuta Project was pivotal to Pakistan developing the capability to detonate a nuclear weapon by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission
Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission (PAEC) (Urdu: ) is a federally funded independent governmental agency, concerned with research and development of nuclear power, promotion of nuclear science, energy conservation and the peaceful usage of nuclear technology. Since its establishment in 1956, the PAEC has overseen the extensive development of nuclear infrastructure to support the economical uplift of Pakistan by founding institutions that focus on development on food irradiation and on nuclear medicine radiation therapy for cancer treatment. The PAEC organizes conferences and directs research at the country's leading universities. Since the 1960s, the PAEC is also a scientific research partner and sponsor of the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), where Pakistani scientists have contributed to developing particle accelerators and research on high-energy physics. PAEC scientists regularly pay visits to CERN while taking part in projects led by CERN. Until 2001, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munir Ahmad Khan
Munir Ahmad Khan ( ur, ; 20 May 1926 – 22 April 1999), , was a Pakistani nuclear reactor physicist who is credited, among others, with being the "father of the atomic bomb program" of Pakistan for their leading role in developing their nation's nuclear weapons during the successive years after the war with India in 1971. From 1972 to 1991, Khan served as the chairman of the Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission (PAEC) who directed and oversaw the completion of the clandestine bomb program from its earliest efforts to develop the atomic weapons to their ultimate nuclear testings in May 1998. His early career was mostly spent in the International Atomic Energy Agency and he used his position to help establish the International Centre for Theoretical Physics in Italy and an annual conference on physics in Pakistan. As chair of PAEC, Khan was a proponent of the nuclear arms race with India whose efforts were directed towards concentrated production of reactor-grade to weapon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosives Engineering
Explosives engineering is the field of science and engineering which is related to examining the behavior and usage of explosive materials. Topics Some of the topics that explosives engineers study, research, and work on include: * Development and characterization of new explosive materials in various forms * Analysis of the physical process of detonation * Explosive generated shock waves and their effects on materials * Safety testing of explosives * Analysis and engineering of rock blasting for mining * Design and analysis of shaped charges and reactive armor * Design and analysis of military explosives such as shells, aerial bombs, missile warheads, etc. * Bomb disposal *Drilling and Blasting *Explosive Manufacturing *Explosives Safety Education and Certification *Drilling Safety Education and Certification *Blasting Safety Education and Certification Organizations Listed in Alphabetical Order: * Explosives Academy * International Society of Explosives Engineers (ISE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Verlag
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |