|
Republic Of Gersau
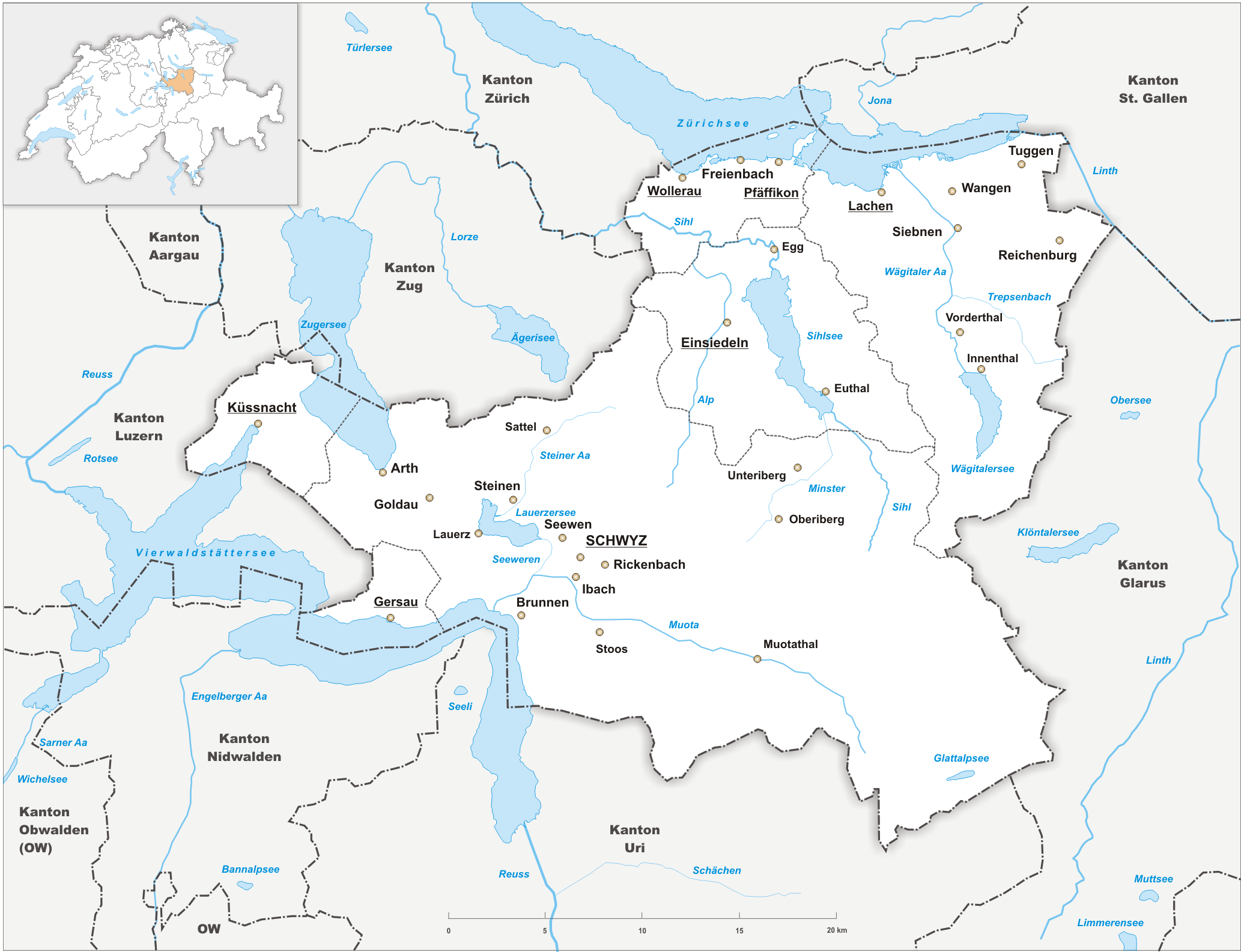
Gersau is a municipality and district in the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland, sitting on the shores of Lake Lucerne. Gersau was for many centuries an independent micro-state in permanent alliance with the Swiss Confederation. History Gersau is first mentioned in 1064 as ''Gersouwe''. The estates of Gersau gradually came into the hands of the Habsburgs, but in 1333, under dukes Albert II and Otto IV ''the Merry'' of Austria, the jurisdiction and rights over Gersau fell into the hands of Lucerne nobility. On 1359, Gersau allied with the Old Swiss Confederacy as a protectorate of the Confederacy, for its protection and to gain arms from the confederates. On 9 July 1386, the citizens of Gersau fought with the Swiss for the first time, on the battlefield of Sempach, where the banner of Count Rudolf of Hohenzollern was captured. Republic of Gersau The Republic of Gersau (called "altfrye Republik Gersau", literal "old-free Republik Gersau", in early modern times) was an inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gersau (district)
Gersau is a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality and Districts of Switzerland#Schwyz, district in the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland, sitting on the shores of Lake Lucerne. Gersau was for many centuries an independent micro-state in permanent alliance with the Swiss Confederation. History Gersau is first mentioned in 1064 as ''Gersouwe''. The estates of Gersau gradually came into the hands of the Habsburgs, but in 1333, under dukes Albert II of Austria, Albert II and Otto, Duke of Austria, Otto IV ''the Merry'' of Austria, the jurisdiction and rights over Gersau fell into the hands of Lucerne nobility. On 1359, Gersau allied with the Old Swiss Confederacy as a protectorate of the Confederacy, for its protection and to gain arms from the confederates. On 9 July 1386, the citizens of Gersau fought with the Swiss for the first time, on the battle of Sempach, battlefield of Sempach, where the banner of Count Rudolf of Hohenzollern was captured. Republic of Gersau The Repub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helvetic Republic
The Helvetic Republic (, , ) was a sister republic of France that existed between 1798 and 1803, during the French Revolutionary Wars. It was created following the French invasion and the consequent dissolution of the Old Swiss Confederacy, marking the end of the ''ancien régime'' in Switzerland. Throughout its existence, the republic incorporated most of the territory of modern Switzerland, excluding the cantons of Geneva and Neuchâtel and the old Prince-Bishopric of Basel. The Swiss Confederacy, which until then had consisted of self-governing cantons united by a loose military alliance (and ruling over subject territories such as Vaud), was invaded by the French Revolutionary Army and turned into an ally known as the "Helvetic Republic". The interference with localism and traditional liberties was deeply resented, although some modernizing reforms took place. Resistance was strongest in the more traditional Catholic cantons, with armed uprisings breaking out in spring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfund (born 1943), Swiss graphic artist
{{surname ...
Pfund is German for " pound weight" and is also a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * August Herman Pfund (1879–1949), American physicist and spectroscopist * Guillermo Pfund (born 1989), Argentine footballer * Jessica Pfund (born 1998), American skater * Lee Pfund (born 1919), Major League Baseball pitcher * Nicola Pfund (born 1960), Swiss-Italian writer * Randy Pfund, NBA head coach & executive *Roger Pfund Roger Pfund (born 1943) is a Swiss graphic artist. In 1970–1971, Pfund won the currency design contest, hosted by the Swiss National Bank, for the design of a new series of bank notes. However another design was printed. He is also credited w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Sempach
The Battle of Sempach was fought on 9 July 1386, between Leopold III, Duke of Austria and the Old Swiss Confederacy. The battle was a decisive Swiss victory in which Duke Leopold and numerous Austrian nobles died. The victory helped turn the loosely allied Swiss Confederation into a more unified nation and is seen as a turning point in the growth of Switzerland. Background During 1383 and 1384, the expansion of the Old Swiss Confederacy collided with Austrian interests. The interests of Austria were further undermined in the Pact of Constance, a union of Zürich, Zug, Solothurn and 51 cities of Swabia. In 1385, there were various attacks, without formal declaration of war or central organization, by forces of Zürich, Zug and Lucerne on the Austrian strongholds of Rapperswil, Rothenburg, Cham and Wolhusen. In 1384 the people of Entlebuch receive the Lucerne citizenry and on Epiphany on the 6 January 1386, Lucerne expanded its sphere of influence by providing the same righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto, Duke Of Austria
Otto, ''the Merry'' (german: der Fröhliche; 23 July 1301 – 17 February 1339), a member of the House of Habsburg, was Duke of Austria and Styria from 1330, as well as Duke of Carinthia from 1335 until his death. He ruled jointly with his elder brother Duke Albert II. Biography Otto was born in the Austrian capital Vienna, the youngest son of King Albert I of Germany and Elizabeth of Carinthia, a member of the House of Gorizia-Tyrol (''Meinhardiner''). His elder brothers were Rudolf III, who became King of Bohemia in 1306, Frederick the Fair, elected King of the Romans in opposition to Louis the Bavarian in 1314, the Austrian dukes Leopold I and Albert II as well as Henry the Friendly. After the murder of King Albert I in 1308, the Habsburgs lost out in the struggle around the German throne, when Frederick the Fair was defeated by his Wittelsbach rival Louis in the 1322 Battle of Mühldorf. In the course of a rapprochement of both dynasties, Otto married Elizabeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert II Of Austria
Albert II (12 December 1298 – 16 August 1358), known as ''the Wise'' or ''the Lame'', a member of the House of Habsburg, was duke of Austria and Styria from 1330, as well as duke of Carinthia and margrave of Carniola from 1335 until his death. Biography Albert II was born at Habsburg Castle in Swabia, a younger son of King Albert I of Germany and his wife Elizabeth of Carinthia, a member of the House of Gorizia (''Meinhardiner''). He initially prepared for an ecclesiastical career and, though still a minor, was elected Bishop of Passau in 1313. However, he had to rival with an opposing candidate and finally renounced the office in 1317. After the death of their elder brother Frederick the Fair in 1330, the surviving sons Albert II and Otto the Merry became joint rulers of all Habsburg dominions in Austria and Styria. Albert was able to further increase his possessions by the inheritance of his wife Joanna of Pfirt, which was made up of the Alsatian county of Pfirt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micro-state
A microstate or ministate is a sovereign state having a very small population or very small land area, usually both. However, the meanings of "state" and "very small" are not well-defined in international law.Warrington, E. (1994). "Lilliputs Revisited". ''Asian Journal of Public Administration'', 16(1). Some recent attempts to define microstates have focused on identifying qualitative features that are linked to their size and population, such as partial delegation of their sovereignty to larger states, such as for international defense. Commonly accepted examples of microstates include Andorra, Liechtenstein, Monaco, Nauru, Palau, San Marino and Tuvalu. The smallest political entity recognized as a sovereign state is Vatican City, with fewer than 1,000 residents and an area of only . Some microstates – such as Monaco and Vatican City – are city-states consisting of a single municipality. Definitions Quantitative Most scholars identify microstates by using a quanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Lucerne
__NOTOC__ Lake Lucerne (german: Vierwaldstättersee, literally "Lake of the four forested settlements" (in English usually translated as ''forest cantons''), french: lac des Quatre-Cantons, it, lago dei Quattro Cantoni) is a lake in central Switzerland and the fourth largest in the country. Geography The lake has a complicated shape, with several sharp bends and four arms. It starts in the south–north bound Reuss Valley between steep cliffs above the ''Urnersee'' from Flüelen towards Brunnen to the north before it makes a sharp bend to the west where it continues into the ''Gersauer Becken''. Here is also the deepest point of the lake with . Even further west of it is the ''Buochser Bucht'', but the lake sharply turns north again through the narrow opening between the ''Unter Nas'' (lower nose) of the Bürgenstock to the west and the ''Ober Nas'' (upper nose) of the Rigi to the east to reach the ''Vitznauer Bucht''. In front of Vitznau below the Rigi the lake turns s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canton Of Schwyz
The canton of Schwyz (german: Kanton Schwyz rm, Chantun Sviz; french: Canton de Schwytz; it, Canton Svitto) is a canton in central Switzerland between the Alps in the south, Lake Lucerne to the west and Lake Zürich in the north, centred on and named after the town of Schwyz. It is one of the founding cantons of Switzerland; Switzerland's name is derived from the name of the canton, and the flag of Switzerland from its coat of arms. For the history of the name, see Schwyz. The Swiss Federal Charter is on display in Schwyz. Northeast of the town of Schwyz is Einsiedeln Abbey. History Prehistory to the Roman era The earliest traces of humans in Schwyz are from the Upper Paleolithic and Early Mesolithic, or about 12,500 BC. An excavation of the karst caves in the valley of the Muota river (''Muotatal'') revealed numerous sites, some dating to the Younger Dryas period (c. 10,000 BC). The alpine meadows at Bödmeren, Twärenen and Silberen were Stone Age hunter-gather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Switzerland
Districts of Switzerland are a political subdivision for cantons. In the federally constituted Switzerland, each canton is completely free to decide its own internal organisation. Therefore, there exists a variety of structures and terminology for the subnational entities between canton and municipality, loosely termed districts. Most cantons are divided into ''Bezirke'' (German for districts, singular ''Bezirk''). They are also termed ''Ämter'' ( Lucerne, singular ''Amt''), ''Amtsbezirke'' ( Bern, ''Amtsbezirk''), ''district'' (in French) or ''distretto'' (Ticino and part of Graubünden). The ''Bezirke'' generally provide only administration and court organization. However, for historical reasons districts in cantons Graubünden and Schwyz are their own legal entities with jurisdiction over tax and often have their own Landsgemeinde. Seven of the 26 cantons – Uri, Obwalden, Nidwalden, Glarus, Zug, Basel-City and Geneva – have always existed without the distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Switzerland
Municipalities (german: Gemeinden, ' or '; french: communes; it , comuni; rm, vischnancas) are the lowest level of administrative division in Switzerland. Each municipality is part of one of the Swiss cantons, which form the Swiss Confederation. In most cantons, municipalities are also part of districts or other sub-cantonal administrative divisions. There are 2,136 municipalities . Their populations range between several hundred thousand (Zürich), and a few dozen people ( Kammersrohr, Bister), and their territory between 0.32 km² (Rivaz) and 439 km² ( Scuol). History The beginnings of the modern municipality system date back to the Helvetic Republic. Under the Old Swiss Confederacy, citizenship was granted by each town and village to only residents. These citizens enjoyed access to community property and in some cases additional protection under the law. Additionally, the urban towns and the rural villages had differing rights and laws. The creation of a uniform S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |