|
Reperfusion Injury
Reperfusion injury, sometimes called ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) or reoxygenation injury, is the tissue damage caused when blood supply returns to tissue ('' re-'' + ''perfusion'') after a period of ischemia or lack of oxygen (anoxia or hypoxia). The absence of oxygen and nutrients from blood during the ischemic period creates a condition in which the restoration of circulation results in inflammation and oxidative damage through the induction of oxidative stress rather than (or along with) restoration of normal function. Reperfusion injury is distinct from cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome (sometimes called "Reperfusion syndrome"), a state of abnormal cerebral vasodilation. Mechanisms Reperfusion of ischemic tissues is often associated with microvascular injury, particularly due to increased permeability of capillaries and arterioles that lead to an increase of diffusion and fluid filtration across the tissues. Activated endothelial cells produce more reactive oxygen sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langendorff Heart
The Langendorff heart or isolated perfused heart assay is an ''ex vivo'' technique used in pharmacological and physiological research using animals and also humans. Named after the German physiologist Oskar Langendorff, this technique allows the examination of cardiac contractile strength and heart rate without the complications of an intact animal or human. After more than 100 years, this method is still being used. Method In the Langendorff preparation, the heart is removed from the animal's or human's body, severing the blood vessels; it is then perfused in a reverse fashion ( retrograde perfusion) via the aorta, usually with a nutrient rich, oxygenated solution (e.g. Krebs–Henseleit solution or Tyrode's solution). The backwards pressure causes the aortic valve The aortic valve is a valve in the heart of humans and most other animals, located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Blood Cell
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are generally larger than red blood cells. They include three main subtypes: granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage ( myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Wound
A chronic wound is a wound A wound is any disruption of or damage to living tissue, such as skin, mucous membranes, or organs. Wounds can either be the sudden result of direct trauma (mechanical, thermal, chemical), or can develop slowly over time due to underlying diseas ... that does not progress through the normal stages of wound healing—haemostasis, inflammation, Cell proliferation, proliferation, and Tissue remodeling, remodeling—in a predictable and timely manner. Typically, wounds that do not heal within three months are classified as chronic. Chronic wounds may remain in the inflammatory phase due to factors like infection or bacterial burden, Ischemia, ischaemia, presence of necrotic tissue, improper moisture balance of wound site, or underlying diseases such as diabetes mellitus. In acute wounds, a regulated balance of Proinflammatory cytokines, pro-inflammatory cytokines (signalling molecules) and Protease, proteases (enzymes) prevent the degradation of the extra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wound Healing
Wound healing refers to a living organism's replacement of destroyed or damaged tissue by newly produced tissue. In undamaged skin, the epidermis (surface, epithelial layer) and dermis (deeper, connective layer) form a protective barrier against the external environment. When the barrier is broken, a regulated sequence of biochemical events is set into motion to repair the damage. This process is divided into predictable phases: blood clotting (hemostasis), inflammation, tissue growth ( cell proliferation), and tissue remodeling (maturation and cell differentiation). Blood clotting may be considered to be part of the inflammation stage instead of a separate stage. The wound-healing process is not only complex but fragile, and it is susceptible to interruption or failure leading to the formation of non-healing chronic wounds. Factors that contribute to non-healing chronic wounds are diabetes, venous or arterial disease, infection, and metabolic deficiencies of old age.Enoch, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest [SCA]) is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly Circulatory system, circulate around the body and the blood flow to the brain and other organs is decreased. When the brain does not receive enough blood, this can cause a person to lose consciousness and brain cells can start to die due to lack of oxygen. Coma and persistent vegetative state may result from cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest is also identified by a lack of Pulse, central pulses and respiratory arrest, abnormal or absent breathing. Cardiac arrest and resultant hemodynamic collapse often occur due to arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms). Ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia are most commonly recorded. However, as many incidents of cardiac arrest occur out-of-hospital or when a person is not having their cardiac activity monitored, it is difficult to identify the specific mechanism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischemic Cascade
The ischemic (ischaemic) cascade is a series of biochemical reactions that are initiated in the brain and other aerobic tissues after seconds to minutes of ischemia (inadequate blood supply). This is typically secondary to stroke, injury, or cardiac arrest due to heart attack. Most ischemic neurons that die do so due to the activation of chemicals produced during and after ischemia.Stroke Center of the Washington University School of Medicine. The ischemic cascade usually goes on for two to three hours but can last for days, even after normal blood flow returns. __TOC__ Mechanism A is a series of events in which one event triggers the next, in a ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
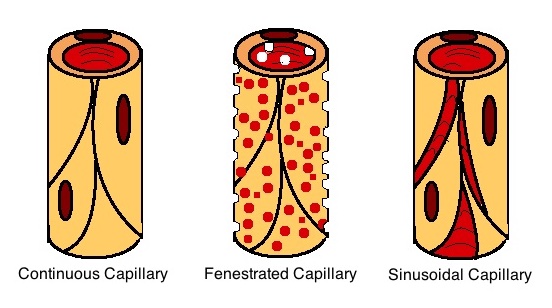
Capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelium
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. Endothelial cells in direct contact with blood are called vascular endothelial cells whereas those in direct contact with lymph are known as lymphatic endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillaries. These cells have unique functions that include fluid filtration, such as in the glomerulus of the kidney, blood vessel tone, hemostasis, neutrophil recruitment, and hormone trafficking. Endothelium of the interior surfaces of the heart chambers is called endocardium. An impaired function can lead to serious health issues throughout the body. Structure The endothelium is a thin layer of single flat (squamous) cells that line the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biology), morphology) and death. These changes include Bleb (cell biology), blebbing, Plasmolysis, cell shrinkage, Karyorrhexis, nuclear fragmentation, Pyknosis, chromatin condensation, Apoptotic DNA fragmentation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses 50 to 70 1,000,000,000, billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For the average human child between 8 and 14 years old, each day the approximate loss is 20 to 30 billion cells. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox Signaling
''Antioxidants & Redox Signaling '' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering reduction–oxidation (redox) signaling and antioxidant research. It covers topics such as reactive oxygen species/reactive nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) as messengers Gaseous signaling molecules, gaseous signal transducers, Hypoxia (medical), hypoxia and Oxygen saturation (medicine), tissue oxygenation, microRNA, prokaryotic systems, and lessons from plant biology. Abstracting and indexing This journal is indexed by the following services: According to ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor of 7.407. References [Baidu] |
Plasma Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic molecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |