|
Relationship Between The Romanian Orthodox Church And The Iron Guard
The relationship between the Romanian Orthodox Church and the Iron Guard was one of ambivalence. The Romanian Orthodox Church promoted its own version of nationalism which highlighted the role of Orthodoxy in preserving the Romanian identity. Starting with the 1920s, the Church became entangled with fascist politics and antisemitism. In this context, the Iron Guard, also known as the Legion of the Archangel Michael, a fascist movement founded in 1927, became very influential with church grassroots. Numerous rank-and-file priests joined the Iron Guard ranks and actively supported its policies; so did a minority of influential high-ranking clergymen such as Nicolae Bălan or Vartolomeu Stănescu. Patriarch Miron Cristea, on the other hand, felt threatened by the Iron Guard's anti-establishment rhetoric and so did his successor Nicodim Munteanu. Thus, when the National Legionary State was proclaimed in 1940, Munteanu showed little enthusiasm. The insurrection of 1941 ended with Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Orthodox Church
The Romanian Orthodox Church (ROC; ro, Biserica Ortodoxă Română, ), or Patriarchate of Romania, is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox church in full communion with other Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, Christian churches, and one of the nine patriarchates in the Eastern Orthodox Church organization, Eastern Orthodox Church. Since 1925, the church's Primate (bishop), Primate bears the title of Patriarch. Its jurisdiction covers the territories of Romania and Moldova, with additional dioceses for Romanians living in nearby Serbia and Hungary, as well as for diaspora communities in Central Europe, Central and Western Europe, North America and Oceania. It is the only autocephalous church within Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy to have a Romance languages, Romance language for liturgical use. The majority of Romania's population (16,367,267, or 85.9% of those for whom data were available, according to the 2011 census data), as well as some 720,000 Moldovans, belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National-Christian Defense League
The National-Christian Defense League ( ro, Liga Apărării Național Creștine, LANC) was a Far-right politics, far-right political party of Romania formed by A. C. Cuza. Origins The LANC had its roots in the National Christian Union, formed in 1922 by Cuza and the famed physiologist Nicolae Paulescu. This group morphed in to the LANC in 1923. Much of LANC's ideas were framed within theology, theological arguments which were created by Nichifor Crainic, who served as Secretary General of LANC. The swastika became the symbol of Cuza's movement and appeared in its publications, booklets and electoral programs. Cuza claimed that the symbol was purely Romanian in character and denied that LANC had copied the Nazi party's symbol. By 1927, the party banner became the flag of Romania with a swastika in the centre. The LANC became associated with extreme anti-semitism, calling for a gradual withdrawal of rights for Jews which would include the withdrawal of political rights for all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sfarmă-Piatră
(; literally "Stone-Crusher" or "Rock-Breaker", named after one of the ''Uriași'' characters in Romanian folklore) was an antisemitic daily, monthly and later weekly newspaper, published in Romania during the late 1930s and early 1940s. One in a series of publications founded by Nichifor Crainic (better known as the head of ''Gândirea'' magazine), with support from ''Universul'' editor-in-chief Stelian Popescu, it attempted to regroup the various fascist and pro-fascist movements around Crainic's " ethnocratic" principle. The editorial staff comprised a group of far right intellectuals; alongside the editor-in-chief Alexandru Gregorian, they included Ovidiu Papadima, Vintilă Horia, Dan Botta, Dragoș Protopopescu, Toma Vlădescu, and Pan M. Vizirescu. It notably hosted contributions by writers Ioan Alexandru Brătescu-Voinești, Radu Gyr and Ștefan Baciu. Noted for its contemptuous style of journalism and its recourse to violent language, ''Sfarmă-Piatră'' launche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuvântul
''Cuvântul'' (, meaning "The Word") was a daily newspaper, published by philosopher Nae Ionescu in Bucharest, Romania Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ..., from 1926 to 1934, and again in 1938. It was primarily noted for progressively adopting a far right and fascist agenda, and for supporting, during the 1930s, the revolutionary fascist Iron Guard. References Newspapers published in Bucharest Romanian-language newspapers Fascist newspapers and magazines Iron Guard Publications established in 1926 Publications disestablished in 1938 {{Romania-newspaper-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Greek Catholic Church
The Romanian Greek Catholic Church or Romanian Church United with Rome, Greek-Catholic ( la, Ecclesia Graeco-Catholica Romaniae; ro, Biserica Română Unită cu Roma, Greco-Catolică), sometimes called, in reference to its Byzantine Rite, the Romanian Byzantine Catholic Church is a ''sui iuris'' Eastern Catholic Church, in full union with the Catholic Church. It has the rank of a Major Archiepiscopal Church and it uses the Byzantine liturgical rite in the Romanian language. It is part of the Major Archiepiscopal Churches of the Catholic Church that are not distinguished with a patriarchal title. Cardinal Lucian Mureșan, Archbishop of Făgăraș and Alba Iulia, has served as the head of the Romanian Greek-Catholic Church since 1994. On December 16, 2005, as the ''Romanian Church United with Rome'', the Greek-Catholic church was elevated to the rank of a Major Archiepiscopal Church by Pope Benedict XVI, with Lucian Mureșan becoming its first major archbishop. Mureşan was e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Peasants' Party
The National Peasants' Party (also known as the National Peasant Party or National Farmers' Party; ro, Partidul Național Țărănesc, or ''Partidul Național-Țărănist'', PNȚ) was an agrarian political party in the Kingdom of Romania. It was formed in 1926 through the fusion of the Romanian National Party (PNR), a conservative-regionalist group centred on Transylvania, and the Peasants' Party (PȚ), which had coalesced the left-leaning agrarian movement in the Old Kingdom and Bessarabia. The definitive PNR–PȚ merger came after a decade-long rapprochement, producing a credible contender to the dominant National Liberal Party (PNL). National Peasantists agreed on the concept of a "peasant state", which defended smallholding against state capitalism or state socialism, proposing voluntary cooperative farming as the basis for economic policy. Peasants were seen as the first defence of Romanian nationalism and of the country's monarchic regime, sometimes within a system of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdiocese ( with some exceptions), or are otherwise granted a titular archbishopric. In others, such as the Lutheran Church of Sweden and the Church of England, the title is borne by the leader of the denomination. Etymology The word archbishop () comes via the Latin ''archiepiscopus.'' This in turn comes from the Greek , which has as components the etymons -, meaning 'chief', , 'over', and , 'seer'. Early history The earliest appearance of neither the title nor the role can be traced. The title of "metropolitan" was apparently well known by the 4th century, when there are references in the canons of the First Council of Nicæa of 325 and Council of Antioch of 341, though the term seems to be used generally for all higher ranks of bishop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Bishop
In Christian churches with episcopal polity, the rank of metropolitan bishop, or simply metropolitan (alternative obsolete form: metropolite), pertains to the diocesan bishop or archbishop of a metropolis. Originally, the term referred to the bishop of the chief city of a historical Roman province, whose authority in relation to the other bishops of the province was recognized by the First Council of Nicaea (AD 325). The bishop of the provincial capital, the metropolitan, enjoyed certain rights over other bishops in the province, later called " suffragan bishops". The term ''metropolitan'' may refer in a similar sense to the bishop of the chief episcopal see (the "metropolitan see") of an ecclesiastical province. The head of such a metropolitan see has the rank of archbishop and is therefore called the metropolitan archbishop of the ecclesiastical province. Metropolitan (arch)bishops preside over synods of the bishops of their ecclesiastical province, and canon law and traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patriarch Of All Romania
The Patriarch of All Romania ( ro, Patriarh al Întregii Românii; ) is the title of the head of the Romanian Orthodox Church. The Patriarch is officially styled as ''Archbishop of Bucharest, Metropolitan of Muntenia and Dobrogea, Locum tenens of the throne of Caesarea Cappadociae and Patriarch of the Romanian Orthodox Church''. Patriarch Daniel acceded to this position on 12 September 2007. in , 14 September 2007 Metropolitans of All Romania Patriarchs of All Romania See also * |
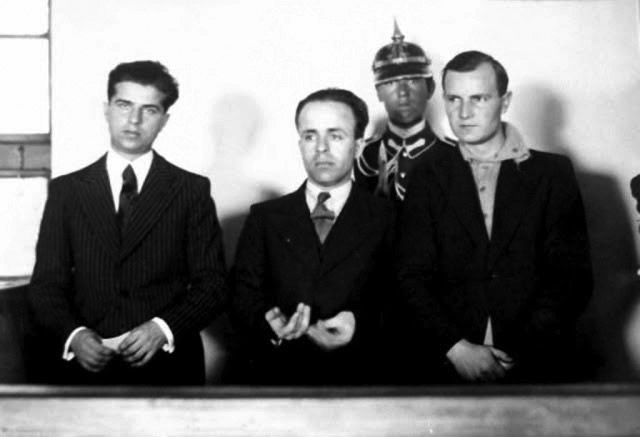
Iron Guard Death Squads
During the 1930s, three notable death squads emerged from Romania's Iron Guard: the ''Nicadori'', the ''Decemviri'' and the ''Răzbunători''. Motivated by a combination of fascist political ideology and religious-nationalist mysticism, they carried out several high-level political assassinations in the inter-war period. Theoretical background Death was a central part of the Iron Guard's ideology. Its members, known as "Legionnaires", were officially asked "to embrace death" if needed; in practice, they were supposed to be ready to both ''give'' and ''embrace'' death—in other words, to be willing to assassinate their political enemies at the risk of their own lives. This "Legionnaire's death" was widely celebrated. For instance, the second verse of the hymn used by the Guard's youth wing is: The Guard aligned itself with the Romanian Orthodox Church, which prohibits murder. However, it had ways of justifying the notion of "giving death" (a notion its founder, Corneliu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galați
Galați (, , ; also known by other alternative names) is the capital city of Galați County in the historical region of Western Moldavia, in eastern Romania. Galați is a port town on the Danube River. It has been the only port for the most part of Moldavia's existence. In 2011, the Romanian census recorded 249,432 residents, making it the 8th most populous city in Romania. Galați is an economic centre based around the port of Galați, the naval shipyard, and the largest steel factory in Romania, Galați steel works. Etymology and names The name ''Galați'' is derived from the Cuman word . This word is ultimately borrowed from the Persian word , "fortress". Other etymologies have been suggested, such as the Serbian . However, the ''galat'' root appears in nearby toponyms, some of which show clearly a Cuman origin, for example Gălățui Lake, which has the typical Cuman -''ui'' suffix for "water". Another toponym in the region is Galicia, with its town of Halych, locally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |