|
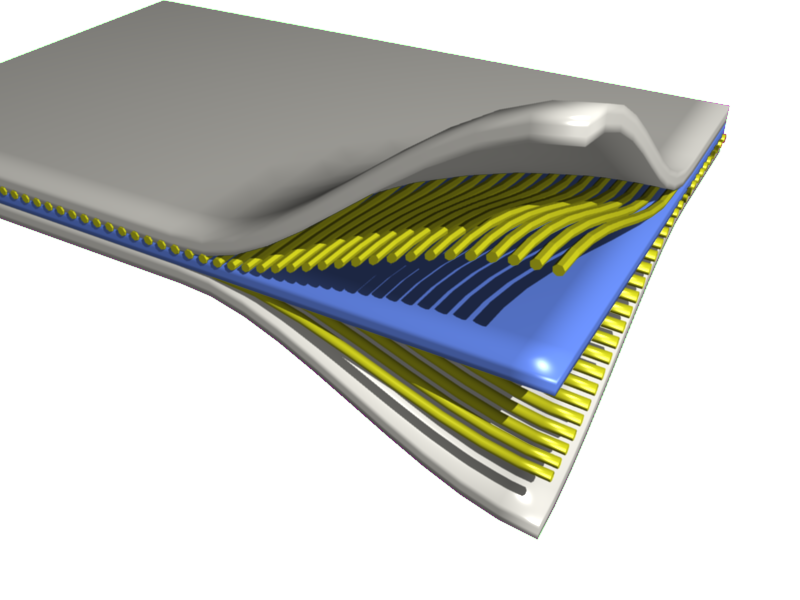
Reinforced Rubber
Reinforced rubber products are one of the largest groups of composite materials, though rarely referred to as composite materials. Familiar examples are automobile tyres, hoses, and conveyor belts. Composite reinforced structure Reinforced rubber products combine a rubber matrix and a reinforcing material so that high strength to flexibility ratios can be achieved. The reinforcing material, usually a kind of fibre, provides the strength and stiffness. The rubber matrix, with low strength and stiffness, provides air-fluid tightness and supports the reinforcing materials to maintain their relative positions. These positions are of great importance because they influence the resulting mechanical properties. A composite structure in which all fibres are loaded equally everywhere when pressurized, is called an isotropic structure, and the type of loading is named an isotensoidal loading. To meet the isotensoidal concept the structure geometry must have an isotensoid meridian profile a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Materials
A composite or composite material (also composition material) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions. Composite materials with more than one distinct layer are called ''composite laminates''. Typical engineered composite materials are made up of a binding agent forming the ''matrix'' and a Filler (materials), filler material (particulates or fibres) giving ''substance'', e.g.: * Concrete, reinforced concrete and masonry with cement, lime or Mortar (masonry), mortar (which is itself a composite material) as a binder * Composite wood such as glulam and plywood with wood glue as a binder * Reinforced plastics, such as fiberglass and fibre-rein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
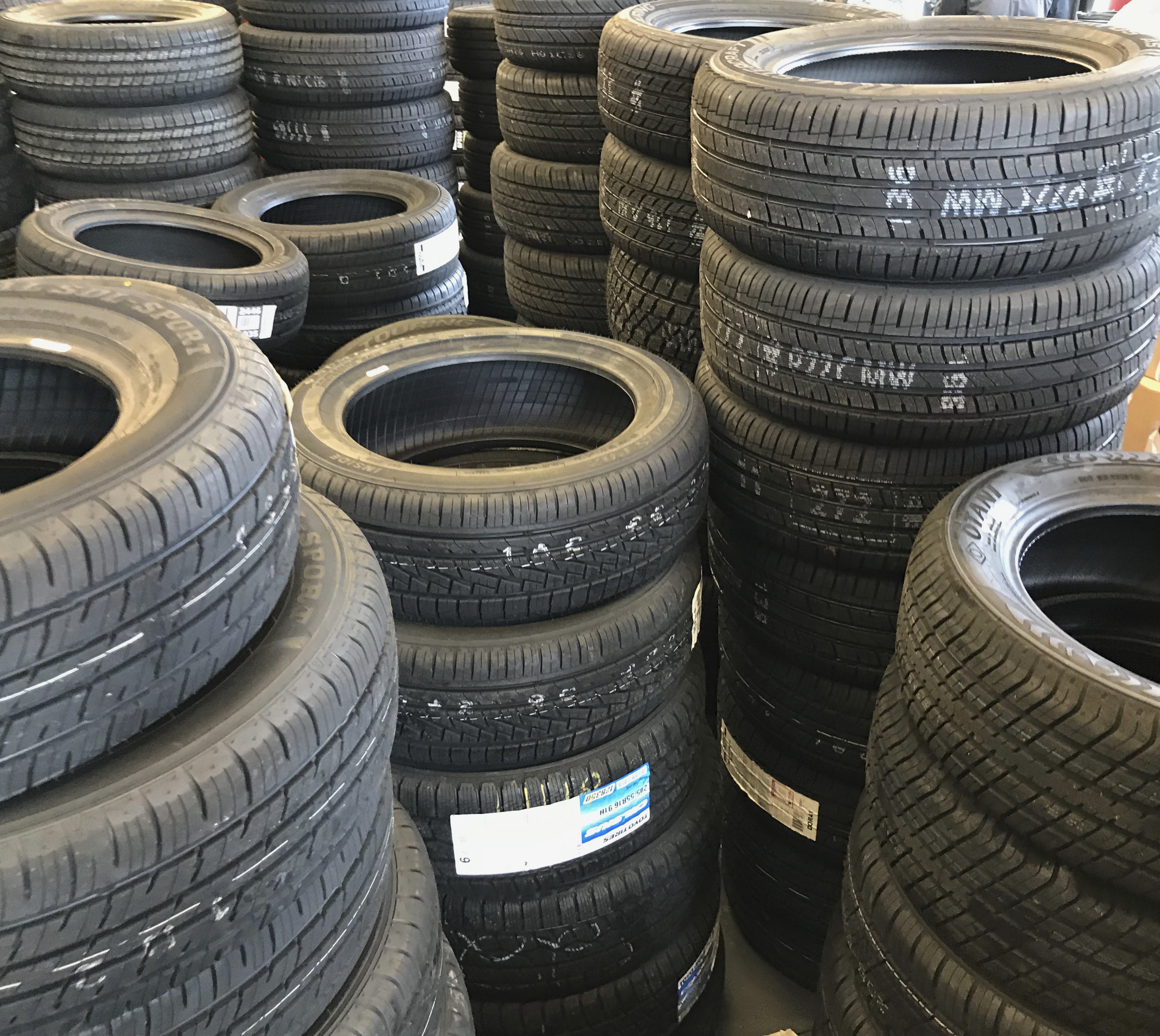
Tyres
A tire (North American English) or tyre (Commonwealth English) is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide traction on the surface over which the wheel travels. Most tires, such as those for automobiles and bicycles, are pneumatically inflated structures, providing a flexible cushion that absorbs shock as the tire rolls over rough features on the surface. Tires provide a footprint, called a contact patch, designed to match the vehicle's weight and the bearing on the surface that it rolls over by exerting a pressure that will avoid deforming the surface. The materials of modern pneumatic tires are synthetic rubber, natural rubber, fabric, and wire, along with carbon black and other chemical compounds. They consist of a tread and a body. The tread provides traction while the body provides containment for a quantity of compressed air. Before rubber was developed, tires were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conveyor Belts
A conveyor belt is the carrying medium of a belt conveyor system (often shortened to a belt conveyor). A belt conveyor system consists of two or more pulleys (sometimes referred to as drums), with a closed loop of carrying medium—the conveyor belt—that rotates about them. One or both of the pulleys are powered, moving the belt and the material on the belt forward. The powered pulley is called the drive pulley, while the unpowered pulley is called the idler pulley. There are two main industrial classes of belt conveyors; Those in general material handling such as those moving boxes along inside a factory and bulk material handling such as those used to transport large volumes of resources and agricultural materials, such as grain, salt, coal, ore, sand, overburden and more. Overview Conveyors are durable and reliable components used in automated distribution and warehousing, as well as manufacturing and production facilities. In combination with computer-controlled pallet ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Types of polyisoprene that are used as natural rubbers are classified as elastomers. Currently, rubber is harvested mainly in the form of the latex from the Hevea brasiliensis, Pará rubber tree (''Hevea brasiliensis'') or others. The latex is a sticky, milky and white colloid drawn off by making incisions in the bark and collecting the fluid in vessels in a process called "tapping". Manufacturers refine this latex into the rubber that is ready for commercial processing. Natural rubber is used extensively in many applications and products, either alone or in combination with other materials. In most of its useful forms, it has a large stretch ratio and high resilience and also is buoyant and water-proof. Industrial demand for rubber-like materials began to out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibre
Fiber (spelled fibre in British English; from ) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate fibers, for example carbon fiber and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene. Synthetic fibers can often be produced very cheaply and in large amounts compared to natural fibers, but for clothing natural fibers have some benefits, such as comfort, over their synthetic counterparts. Natural fibers Natural fibers develop or occur in the fiber shape, and include those produced by plants, animals, and geological processes. They can be classified according to their origin: * Vegetable fibers are generally based on arrangements of cellulose, often with lignin: examples include cotton, hemp, jute, flax, abaca, piña, ramie, sisal, bagasse, and banana. Plant fibers are employed in the manufacture of paper and textile (cloth), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesic
In geometry, a geodesic () is a curve representing in some sense the locally shortest path ( arc) between two points in a surface, or more generally in a Riemannian manifold. The term also has meaning in any differentiable manifold with a connection. It is a generalization of the notion of a " straight line". The noun '' geodesic'' and the adjective '' geodetic'' come from ''geodesy'', the science of measuring the size and shape of Earth, though many of the underlying principles can be applied to any ellipsoidal geometry. In the original sense, a geodesic was the shortest route between two points on the Earth's surface. For a spherical Earth, it is a segment of a great circle (see also great-circle distance). The term has since been generalized to more abstract mathematical spaces; for example, in graph theory, one might consider a geodesic between two vertices/nodes of a graph. In a Riemannian manifold or submanifold, geodesics are characterised by the property of havi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Angle
The magic angle is a precisely defined angle, the value of which is approximately 54.7356°. The magic angle is a root of a second-order Legendre polynomial, , and so any interaction which depends on this second-order Legendre polynomial vanishes at the magic angle. This property makes the magic angle of particular importance in magic angle spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy. In magnetic resonance imaging, structures with ordered collagen, such as tendons and ligaments, oriented at the magic angle may appear hyperintense in some sequences; this is called the magic angle artifact or effect. Mathematical definition The magic angle ''θ''m is \theta_\mathrm = \arccos \frac = \arctan \sqrt \approx 0.955\,32\ \text \approx 54.7^\circ \! , where arccos and arctan are the inverse cosine and tangent functions respectively. is the angle between the space diagonal of a cube and any of its three connecting edges, see image. Another representation of the magic angle is half of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Series Of Tubes
"A series of tubes" is a phrase used originally as an analogy by then-United States Senator Ted Stevens ( R-Alaska) to describe the Internet in the context of opposing net neutrality. On June 28, 2006, he used this metaphor to criticize a proposed amendment to a committee bill. The amendment would have prohibited Internet service providers such as AT&T, Comcast, Time Warner Cable and Verizon Communications from charging fees to give some companies' data a higher priority in relation to other traffic. The metaphor was widely ridiculed, because Stevens was perceived to have displayed an extremely limited understanding of the Internet, despite his leading the Senate committee responsible for regulating it. Partial text of Stevens's comments Media commentary On June 28, 2006, Public Knowledge government affairs manager Alex Curtis wrote a brief blog entry introducing the senator's speech and posted an MP3 recording. The next day, the ''Wired'' magazine blog ''27B Stroke 6'' fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hose
A hose is a flexible hollow tube or pipe designed to carry fluids from one location to another, often from a faucet or hydrant. Early hoses were made of leather, although modern hoses are typically made of rubber, canvas, and helically wound wire. Hoses may also be made from plastics such as polyvinyl chloride, polytetrafluoroethylene, and polyethylene terephthalate, or from metals such as stainless steel. See also * *Heated hose Heated hoses are hoses used for transporting liquids or molten materials where integral heat is needed for temperature control. Heated hoses are suitable for environments from -40°C to 80°C and can be used in explosion proof, explosion-proof zo ... References Further reading * Hydraulics {{tool-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Angle
The magic angle is a precisely defined angle, the value of which is approximately 54.7356°. The magic angle is a root of a second-order Legendre polynomial, , and so any interaction which depends on this second-order Legendre polynomial vanishes at the magic angle. This property makes the magic angle of particular importance in magic angle spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy. In magnetic resonance imaging, structures with ordered collagen, such as tendons and ligaments, oriented at the magic angle may appear hyperintense in some sequences; this is called the magic angle artifact or effect. Mathematical definition The magic angle ''θ''m is \theta_\mathrm = \arccos \frac = \arctan \sqrt \approx 0.955\,32\ \text \approx 54.7^\circ \! , where arccos and arctan are the inverse cosine and tangent functions respectively. is the angle between the space diagonal of a cube and any of its three connecting edges, see image. Another representation of the magic angle is half of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flanged Rubber Bellows
A flange is a protruded ridge, lip or rim (wheel), rim, either external or internal, that serves to increase shear strength, strength (as the flange of a steel beam (structure), beam such as an I-beam or a T-beam); for easy attachment/transfer of contact force with another object (as the flange on the end of a pipe (fluid conveyance), pipe, steam cylinder, etc., or on the lens mount of a camera); or for stabilizing and guiding the movements of a machine or its parts (as the inside flange of a railroad car, rail car or tram train wheel, wheel, which keep the wheels from derailment, running off the rail profile, rails). Flanges are often attached using bolts in the pattern of a bolt circle. Flanges play a pivotal role in piping systems by allowing easy access for maintenance, inspection, and modification. They provide a means to connect or disconnect Pipe (fluid conveyance), pipes and equipment without the need for welding, which simplifies installation and reduces downtime during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |