|
Reichsannalen
The ''Reichsannalen'' are a class of annals composed anonymously in the Carolingian Empire throughout the 9th century. They first appeared under Pepin the Short in 741 and became ubiquitous at monasteries throughout the empire in the following decades. They were not official court annals, but they often bear the bias of having been written in one '' regnum'' or another. The Reichsannalen are distinguished from earlier and later classes of annals by their coverage of supranational and not just local events; they covered the entire empire. Though usually composed at monasteries, they are contrasted with monastic annals which emphasise ecclesiastical and especially local happenings over those of the larger ''Reich''. Some historians, such as Ranke (''Zur Kritik fränkisch-deutscher Reichsannalisten''. Berlin, 1854) have seen a sheen of officiality in the various annals for the kings whose reigns they cover. The authors of the Reichsannalen show a greater awareness of external affairs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Frankish Annals
The ''Royal Frankish Annals'' (Latin: ''Annales regni Francorum''), also called the ''Annales Laurissenses maiores'' ('Greater Lorsch Annals'), are a series of annals composed in Latin in the Carolingian Francia, recording year-by-year the state of the monarchy from 741 (the death of Charles Martel) to 829 (the beginning of the crisis of Louis the Pious). Their authorship is unknown, though Wilhelm von Giesebrecht suggested that Arno of Salzburg was the author of an early section surviving in the copy at Lorsch Abbey. The Annals are believed to have been composed in successive sections by different authors, and then compiled. The depth of knowledge regarding court affairs suggests that the annals were written by persons close to the king, and their initial reluctance to comment on Frankish defeats betrays an official design for use as Carolingian propaganda. Though the information contained within is heavily influenced by authorial intent in favor of the Franks, the annals remai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annales Vedastini
{{italic title The ''Annales Vedastini'' or ''Annals of St-Vaast'' are a series of annals written in the early tenth century at the Abbey of St. Vaast in Arras. They are an important source for the ninth century. The years from 874 to 900 are covered with a strong bias for Lotharingian and West Frankish affairs. Like the ''Annales Fuldenses'' and ''Annales Bertiniani'', the AV, as it is often abbreviated, was combined with the other ''Reichsannalen'' in the so-called ''Chronicon Vedastinum'', a general chronicle covering the history of the Carolingian Empire up until 899. See also * Reichsannalen References * Reuter, Timothy Timothy Alan Reuter (25 January 1947 – 14 October 2002), grandson of the former mayor of Berlin Ernst Reuter, was a German-British historian who specialized in the study of medieval Germany, particularly the social, military and ecclesiastical i ... (trans.) The Annals of Fulda'. (Manchester Medieval series, Ninth-Century Histories, Volume II.) Manchester: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicon Universale Usque Ad Annum 741
The ''Chronicon universale usque ad annum 741'' () is an anonymous Latin chronicle from the creation of the world to AD 741. It was written in Francia, probably in Burgundy, between 741 and 775. It survives wholly or partially in at least six manuscripts. Date and author Nothing is known about the compiler of the ''Chronicon universale'', his place of activity (other than Francia) or his motivation. It has been suggested that he worked in Burgundy. The manuscript tradition is associated with the monasteries of that region and the text includes a Burgundian origin myth. There is a consensus that the ''Chronicon'' was written during the reign of the Byzantine emperor Constantine V (741–775). More precise—and speculative—datings include: shortly after 741, in 741–761, in 751–761, in 768–775 and shortly after 774. There are dissenters who place is composition later, either in 775–778 or around 801. It has been suggested that the ''Chronicon'' was composed at the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annales Fuldenses
The ''Annales Fuldenses'' or ''Annals of Fulda'' are East Frankish chronicles that cover independently the period from the last years of Louis the Pious (died 840) to shortly after the end of effective Carolingian rule in East Francia with the accession of the child-king, Louis III, in 900. Throughout this period they are a near contemporary record of the events they describe and a primary source for Carolingian historiography. They are usually read as a counterpart to the narrative found in the West Frankish ''Annales Bertiniani''. Authorship and manuscripts The ''Annals'' were composed at the Abbey of Fulda in Hesse. A note in one manuscript has been taken to prove that the entries down to 838 were composed by Einhard (''Enhard'' in the MS), yet it has been convincingly argued that this might only have been a copyist's colophon that has abusively entered the manuscript tradition, a sort of accident far from uncommon in medieval ''scriptoria''. Be that as it may, a second note s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals
Annals ( la, annāles, from , "year") are a concise historical record in which events are arranged chronologically, year by year, although the term is also used loosely for any historical record. Scope The nature of the distinction between annals and history is a subject based on divisions established by the ancient Romans. Verrius Flaccus is quoted by Aulus Gellius as stating that the etymology of ''history'' (from Greek , , equated with Latin , "to inquire in person") properly restricts it to primary sources such as Thucydides's which have come from the author's own observations, while annals record the events of earlier times arranged according to years. White distinguishes annals from chronicles, which organize their events by topics such as the reigns of kings, and from histories, which aim to present and conclude a narrative implying the moral importance of the events recorded. Generally speaking, annalists record events drily, leaving the entries unexplained and equally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annales Maximiani
Annals are a concise form of historical writing which record events chronologically, year by year. The equivalent word in Latin and French is ''annales'', which is used untranslated in English in various contexts. List of works with titles containing the word "Annales" * ''Annales'' (Ennius), an epic poem by Quintus Ennius covering Roman history from the fall of Troy down to the censorship of Cato the Elder * Annals (Tacitus) ''Ab excessu divi Augusti'' "Following the death of the divine Augustus" * Annales Alamannici, ed. W. Lendi, Untersuchungen zur frühalemannischen Annalistik. Die Murbacher Annalen, mit Edition (Freiburg, 1971) * Annales Bertiniani, eds. F. , J. Vielliard, S. Clemencet and L. Levillain, Annales de Saint-Bertin (Paris, 1964) * Annales du Muséum national d'histoire naturelle, Paris, France. Published 1802 to 1813, then became the Mémoires then the Nouvelles Annales * Annales Fuldenses, ed. F. Kurze, ''Monumenta Germaniae Historica'' SRG (Hanover, 1891) * ''Ann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicon Vedastinum
In historiography, a ''chronicon'' is a type of chronicle or annals. Examples are: * ''Chronicon'' (Eusebius) * ''Chronicon'' (Jerome) *''Chronicon Abbatiae de Evesham'' *''Chronicon Burgense'' *''Chronicon Ambrosianum'' *''Chronicon Compostellanum'' *''Chronicon Gothanum'' *''Chronicon Helveticum'' *''Chronicon Holtzatiae'' *''Chronicon Iriense'' *''Chronicon Lethrense'' *''Chronicon Lusitanum'' *''Chronicon Paschale'' *''Chronicon Pictum'' *''Chronicon Roskildense'' *''Chronicon Salernitanum'' *''Chronicon Scotorum'' *''Chronicon complutense'' *''Chronicon terrae Prussiae ''Chronicon terræ Prussiæ'' (Latin for "The Chronicle of the Prussian Land") is a chronicle of the Teutonic Knights, by Peter of Dusburg, finished in 1326. The manuscript is the first major chronicle of the Teutonic Order in Prussia and the Gra ...'' Chronicles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
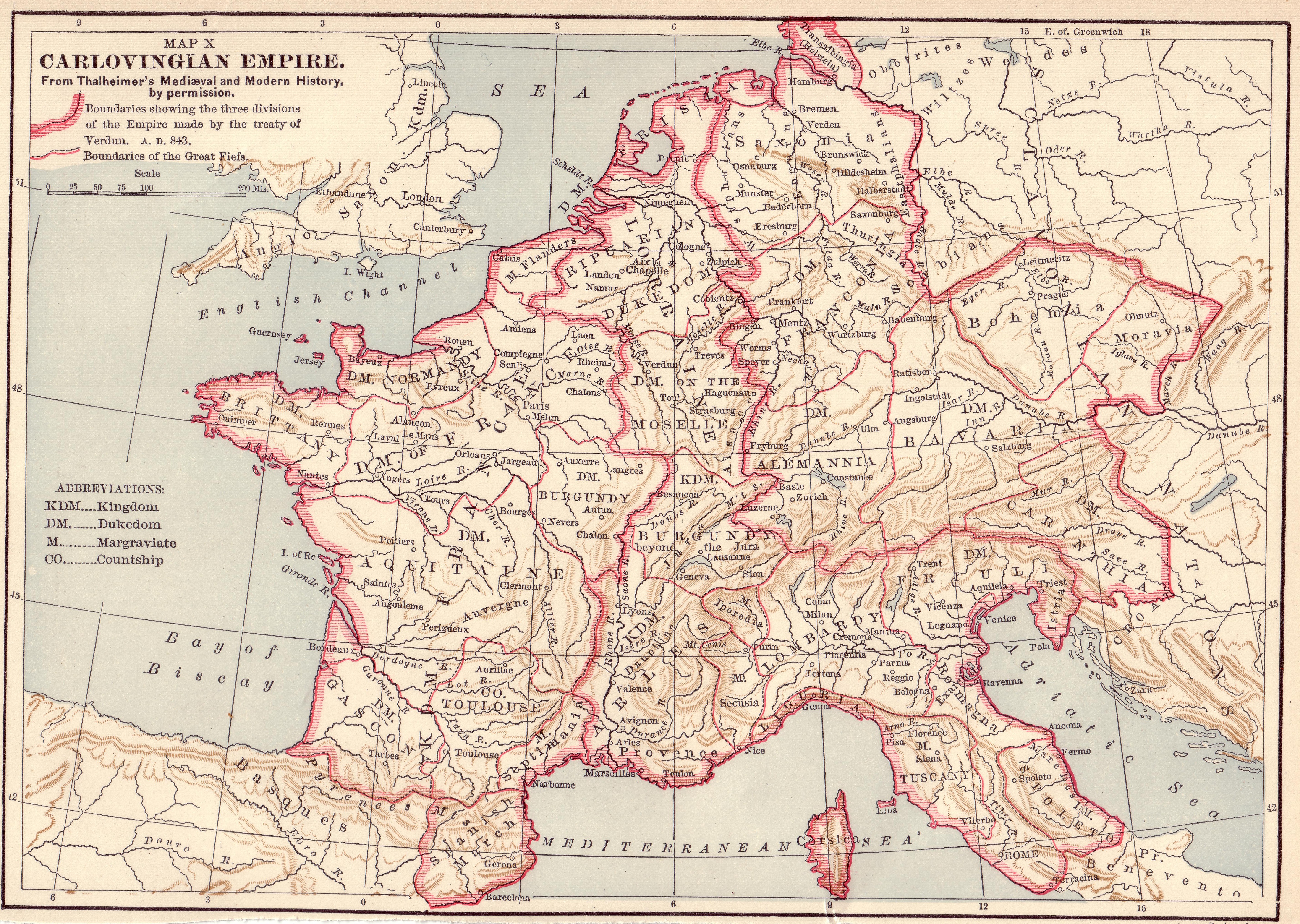
Lotharingia
Lotharingia ( la, regnum Lotharii regnum Lothariense Lotharingia; french: Lotharingie; german: Reich des Lothar Lotharingien Mittelreich; nl, Lotharingen) was a short-lived medieval successor kingdom of the Carolingian Empire. As a more durable later duchy of the Ottonian Empire, it comprised present-day Lorraine (France), Luxembourg, Saarland (Germany), Netherlands, and the eastern half of Belgium, along with parts of today's North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany), Rhineland-Palatinate (Germany) and Nord (France). It was named after King Lothair II, who received this territory after his father Lothair I's kingdom of Middle Francia was divided among his three sons in 855. Lotharingia resulted from the tripartite division in 855 of the kingdom of Middle Francia, which itself was formed after the threefold division of the Carolingian Empire by the Treaty of Verdun of 843. Conflict between East and West Francia over Lotharingia was based on the fact that these were the old Frankish hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicon De Gestis Normannorum In Francia
In historiography, a ''chronicon'' is a type of chronicle or annals. Examples are: * ''Chronicon'' (Eusebius) * ''Chronicon'' (Jerome) *''Chronicon Abbatiae de Evesham'' *''Chronicon Burgense'' *''Chronicon Ambrosianum'' *''Chronicon Compostellanum'' *''Chronicon Gothanum'' *''Chronicon Helveticum'' *''Chronicon Holtzatiae'' *''Chronicon Iriense'' *''Chronicon Lethrense'' *''Chronicon Lusitanum'' *''Chronicon Paschale'' *''Chronicon Pictum'' *''Chronicon Roskildense'' *''Chronicon Salernitanum'' *''Chronicon Scotorum'' *''Chronicon complutense'' *''Chronicon terrae Prussiae ''Chronicon terræ Prussiæ'' (Latin for "The Chronicle of the Prussian Land") is a chronicle of the Teutonic Knights, by Peter of Dusburg, finished in 1326. The manuscript is the first major chronicle of the Teutonic Order in Prussia and the Gra ...'' Chronicles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from about 840 until 987. West Francia emerged from the partition of the Carolingian Empire in 843 under the Treaty of Verdun following the death of Charlemagne's son, Louis the Pious. It is considered the first polity in French history. West Francia extended further north and south than modern metropolitan France, but it did not extend as far east. It did not include such future French holdings as Lorraine, the County and Kingdom of Burgundy (the duchy was already a part of West Francia), Alsace and Provence in the east and southeast for example. It also did not include the Brittany peninsula in the west. In addition, by the 10th century the authority of the West Frankish monarchs was greatly reduced. This was contrasted by the evergrowing power of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annales Bertiniani
''Annales Bertiniani'' (''Annals of Saint Bertin'') are late Carolingian, Frankish annals that were found in the Abbey of Saint Bertin, Saint-Omer, France, after which they are named. Their account is taken to cover the period 830-82, thus continuing the Royal Frankish Annals (741–829), from which, however, it has circulated independently in only one manuscript. They are available in the ''Monumenta Germaniæ Historica'' and in a later French edition taking into account a newly discovered manuscript . The ''Annals of St. Bertin'' are one of the principal sources of ninth-century Francia, and are particularly well-informed on events in the West Frankish sphere of Charles the Bald. The ''Annales Fuldenses'' are usually read as an East Frankish counterpart to their narrative. Authorship and manuscripts It has been suggested that the annals were first written by scribes in the court of Louis the Pious. There is no doubt that they were later continued as an independent narrative, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annales Lithienses
Annals are a concise form of historical writing which record events chronologically, year by year. The equivalent word in Latin and French is ''annales'', which is used untranslated in English in various contexts. List of works with titles containing the word "Annales" * ''Annales'' (Ennius), an epic poem by Quintus Ennius covering Roman history from the fall of Troy down to the censorship of Cato the Elder * Annals (Tacitus) ''Ab excessu divi Augusti'' "Following the death of the divine Augustus" * Annales Alamannici, ed. W. Lendi, Untersuchungen zur frühalemannischen Annalistik. Die Murbacher Annalen, mit Edition (Freiburg, 1971) * Annales Bertiniani, eds. F. , J. Vielliard, S. Clemencet and L. Levillain, Annales de Saint-Bertin (Paris, 1964) * Annales du Muséum national d'histoire naturelle, Paris, France. Published 1802 to 1813, then became the Mémoires then the Nouvelles Annales * Annales Fuldenses, ed. F. Kurze, ''Monumenta Germaniae Historica'' SRG (Hanover, 1891) * ''Ann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |