|
Regola - S
Regola is the 7th ''rione'' of Rome, Italy, identified by the initials R. VII, and belongs to the Municipio I. The name comes from ''Arenula'' (the name is recognizable in the modern ''Via Arenula''), which was the name of the soft sand (''rena'' in Italian) that the river Tiber left after the floods, and that built strands on the left bank. The inhabitants of the ''rione'' are called ''Regolanti''. They were nicknamed ''mangiacode'' ('tail-eaters'), after the typical dish ''coda alla vaccinara'', which was a specialty of the many ''vaccinari'' ('butchers') of the ''rione''. The seal of the ''rione'' represents a rampant deer with a turquoise background. History During the Roman empire, the area belonged to the ''Campus Martius''. In particular, in the modern Regola there was the Trigarium, the stadium where the riders of the ''triga'' (a cart with three horses) used to train. When Emperor Augustus divided Rome into 14 regions, the modern Regola belonged was included in the I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palazzo Farnese
Palazzo Farnese () or Farnese Palace is one of the most important High Renaissance List of palaces in Italy#Rome, palaces in Rome. Owned by the Italian Republic, it was given to the French government in 1936 for a period of 99 years, and currently serves as the French embassy in Italy. First designed in 1517 for the House of Farnese, Farnese family, the building expanded in size and conception when Alessandro Farnese became Pope Paul III in 1534, to designs by Antonio da Sangallo the Younger. Its building history involved some of the most prominent Italian architects of the 16th century, including Michelangelo, Jacopo Barozzi da Vignola and Giacomo della Porta. At the end of the 16th century, the important fresco cycle of The Loves of the Gods (Carracci), ''The Loves of the Gods'' in the Farnese Gallery was carried out by the Bolognese painter Annibale Carracci, marking the beginning of two divergent trends in painting during the 17th century, the Roman High Baroque and Clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campus Martius
The Campus Martius (Latin for the "Field of Mars", Italian ''Campo Marzio'') was a publicly owned area of ancient Rome about in extent. In the Middle Ages, it was the most populous area of Rome. The IV rione of Rome, Campo Marzio, which covers a smaller section of the original area, bears the same name. Antiquity According to Rome's foundation myth, prior to the founding of the city, Rhea Silvia had her twin sons, Romulus and Remus, taken by the King of Alba Longa. The boys were later discarded in the swelling Tiber River, which would later run along the Campus' western boundary. Washing ashore further downriver, the brothers would return decades later to found a new city. Romulus, who became Rome's sole king (after killing his brother Remus), ruled for many years until sometime in the seventh century B.C. As he came to the end of his life, a storm cloud descended upon the center of the open field outside the city's pomerium in order to lift the elderly king to heaven.Jacobs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedetto Cairoli
Benedetto Cairoli (28 January 1825 – 8 August 1889) was an Italian politician. Biography Cairoli was born at Pavia, Lombardy. From 1848 until the completion of Italian unity in 1870, his whole activity was devoted to the ''Risorgimento'', as Garibaldian officer, political refugee, anti-Austrian conspirator and deputy to parliament. He commanded a volunteer company under Garibaldi in 1859 and 1860, being wounded slightly at Calatafimi and severely at Palermo in the latter year. In 1866, with the rank of colonel, he assisted Garibaldi in the campaign in the County of Tyrol, in 1867 fought at Mentana, and in 1870 conducted the negotiations with Bismarck, during which the German chancellor is alleged to have promised Italy possession of Rome and of her natural frontiers if the Democratic party could prevent an alliance between Victor Emmanuel and Napoleon. The prestige personally acquired by Benedetto Cairoli was augmented by that of his four brothers, who fell during the wars o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sant'Eustachio (rione Of Rome)
Sant'Eustachio is the 8th ''rione'' of Rome, identified by the initials R. VIII. It is named after the eponymous church and is located within the Municipio I. Its coat of arms depicts the head of a stag with a cross between the antlers, symbol of Saint Eustace: the figure is golden on a red background. Geography Northward, Sant'Eustachio borders with Campo Marzio (R. IV), whose boundary is defined by Piazza in Campo Marzio, Via della Stelletta and Via dei Portoghesi. It also borders with Ponte, from which is separated by Via dei Pianellari, Piazza di Sant'Agostino, Via di Sant'Agostino and Piazza delle Cinque Lune. To the west, the ''rione'' borders with Parione (R. VI), from which is separated by Piazza delle Cinque Lune, Corso del Rinascimento, Corso Vittorio Emanuele II, Largo dei Chiavari and Via dei Chiavari. Southward, Sant'Eustachio borders with Regola (R. VII), the boundary being outlined by Via dei Giubbonari, Piazza Benedetto Cairoli, Via Arenula and Via di Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campo De' Fiori
Campo de' Fiori (, literally "field of flowers") is a rectangular square south of Piazza Navona in Rome, Italy, at the border between rione Parione and rione Regola. It is diagonally southeast of the Palazzo della Cancelleria and one block northeast of the Palazzo Farnese. ''Campo de' Fiori'', translated literally from Italian, means "field of flowers". The name dates to the Middle Ages when the area was a meadow. History In Ancient Rome, the area was unused space between Pompey's Theatre and the flood-prone Tiber. Though the Orsini established themselves on the south flank of the space in the 13th century, until the 15th century, the square remained undeveloped. The first church in the immediate vicinity was built during the pontificate of Boniface IX (1389–1404), Santa Brigida a Campo de' Fiori; with the building-up of the ''rione'', the church has now come to face that part of the former square that is now Piazza Farnese. In 1456, under Pope Callixtus III, Ludovico Cardin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parione
Parione is the 6th ''rione'' of Rome, identified by the initials R. VI, and belongs to the Municipio I. Its name comes from the fact that in the area there was a huge ancient wall, maybe belonging to the stadium of Domitianus; the nickname people gave to this wall was ''Parietone'' ("big wall" in ancient Italian), from which the name "Parione". The coat of arms of the ''rione'' depicts a rampant griffon, a Greek mythological creature with the head of an eagle and the body of a lion. It was chosen as a symbol of pride and nobility. History During Antiquity, it belonged to the IX Augustan region called ''Circus Flaminius''. In this area Domitianus built his stadium and an ''Odeon'' (''Odeum'' in Latin), for musical and poetic competitions. Pompey too built there his ''curia''. Around the 1200 the area was called ''Parione e S. Lorenzo in Damaso'' and the population kept on increasing until the 15th century, when the borough obtained a great importance thanks to the pavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponte (rione Of Rome)
Ponte is the 5th ''rione'' of Rome, identified by the initials R. V, and is located in Municipio I. Its name (meaning "bridge" in Italian) comes from Ponte Sant'Angelo, which connects Ponte with the rione of Borgo. This bridge was built by Emperor Hadrian (and originally was named after him ''Pons Aelius'') in 134 AD to connect his mausoleum to the rest of the city. Though Pope Sixtus V changed the ''rione'' limits, so that the bridge belongs now to Borgo, not to Ponte anymore, the area has kept its name and a bridge as its coat of arms. History In ancient Rome, the area belonged to the IX Augustan region called ''Circus Flaminius'', that was a part of the Campus Martius. Nero built another bridge, that was called '' Neronianus'' or ''triumphalis'' because the Via Triumphalis, the Triumphal Way, passed over it: starting with Titus, the victorious Emperors celebrating their Triumphs entered Rome marching through it. Nero's bridge was also called ''Pons Vaticanus'' (meaning "V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1875
Events January–March * January 1 – The Midland Railway of England abolishes the Second Class passenger category, leaving First Class and Third Class. Other British railway companies follow Midland's lead during the rest of the year (Third Class is renamed Second Class in 1956). * January 5 – The Palais Garnier, one of the most famous opera houses in the world, is inaugurated in Paris. * January 12 – Guangxu becomes the 11th Qing Dynasty Emperor of China at the age of 3, in succession to his cousin. * January 14 – The newly proclaimed King Alfonso XII of Spain (Queen Isabella II's son) arrives in Spain to restore the monarchy during the Third Carlist War. * February 3 – Third Carlist War – Battle of Lácar: Carlist commander Torcuato Mendíri secures a brilliant victory, when he surprises and routs a Government force under General Enrique Bargés at Lácar, east of Estella, nearly capturing newly crowned King Alfonso XII. The Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borgo (rione Of Rome)
Borgo (sometimes called also I Borghi) is the 14th ''Rioni of Rome, rione'' of Rome, Italy. It is identified by the initials R. XIV and is included within Municipio I. Its coat of arms shows a lion (after the name "Leonine City", which was also given to the district), lying in front of three mounts and a star. These – together with a Heraldry, lion rampant – are also part of the coat of arms of Pope Sixtus V, who annexed Borgo as the 14th rione of Rome. History Roman Age: ''Ager Vaticanus'' During the Roman age, the Borgo district was part of the 14th 14 regions of the Augustan Rome, Regio (Regio XIV Transtiberim) and was named ''Ager Vaticanus'', after the auguries (''vaticinii'') performed there by the Etruscan civilisation, Etruscan ''Augurs''. Since it lay outside the Pomerium (the religious city border inside which burial was forbidden) and was plagued by malaria, this territory was used as a burial place. Some tombs reached notable proportions, including the ''Terebinth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1586
Events * January 18 – The 7.9 Tenshō earthquake strikes the Chubu region of Japan, triggering a tsunami and causing at least 8,000 deaths. * June 16 – The deposed and imprisoned Mary, Queen of Scots, recognizes Philip II of Spain as her heir. * July 6 – The Treaty of Berwick is signed between Queen Elizabeth I of England and King James VI of Scotland. * July 21 – English explorer Thomas Cavendish begins the first deliberately planned circumnavigation of the globe. * September 20– 21 – Execution of the Babington Plotters: The 14 men convicted of a plot (uncovered on July 17) to murder Queen Elizabeth and replace her with Mary, Queen of Scots, are hanged, drawn and quartered (the first seven being disembowelled before death) in St Giles Field, London. * September 22 – Battle of Zutphen: Spanish troops defeat the Dutch rebels and their English allies. English poet and courtier Sir Philip Sidney is mortally wounded. * October 15&nda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
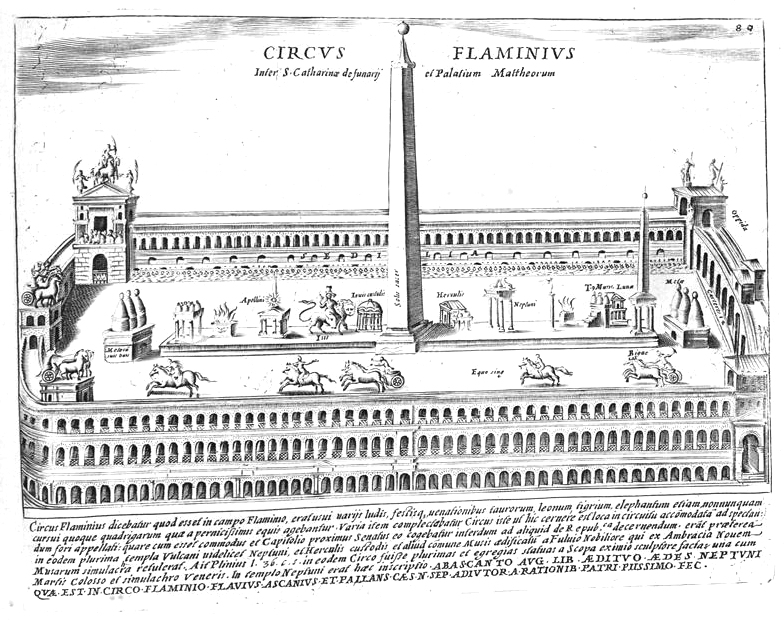
Circus Flaminius
The Circus Flaminius was a large, circular area in ancient Rome, located in the southern end of the Campus Martius near the Tiber River. It contained a small race-track used for obscure games, and various other buildings and monuments. It was "built", or sectioned off, by Gaius Flaminius in 221 BC. After Augustus divided the city into 14 administrative regions, the Circus Flaminius gave its name to Regio IX, which encompassed the Circus and all of the Campus Martius west of the Via Lata. Topography and structures In its early existence, the Circus was a loop, approximately 500 meters in length stretching across the Flaminian Fields (''Prata Flaminia''). Varro states that the actual Circus was built around the Fields, which were already a hallowed site for games by the time the Circus was laid in 220 BC. The '' ludi Taurei'' were hosted in the Fields since they were inaugurated by Rome's last king Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (d. 495 BC). During the 2nd century BC, this broad spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_-_Old_sign.jpg)