|
Regius Professor Of Civil Law (Oxford)
The Regius Chair of Civil Law, founded in the 1540s, is one of the oldest professorships at the University of Oxford. Foundation The Regius Chair of Civil Law at Oxford was founded by King Henry VIII, who established five such Regius Professorships in the University, the others being the chairs of Divinity, Physic (Old English for Medicine), Hebrew and Greek.New Regius Professor of Civil Law Appointed – news release dated 1 December 2005 online at ox.ac.uk (accessed 23 February 2008) The attached to the position was then forty [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberico Gentili
Alberico Gentili (14 January 155219 June 1608) was an Italian-English jurist, a tutor of Queen Elizabeth I, and a standing advocate to the Spanish Embassy in London, who served as the Regius professor of civil law at the University of Oxford for 21 years. He is heralded as the founder of the science of international law alongside Francisco de Vitoria and Hugo Grotius, and thus known as the "Father of international law". Gentili has been the earliest writer on public international law. In 1587, he became the first non-English person to be a Regius Professor. Gentili authored several books, which are recognized to be among the most essential for international legal doctrines, yet that also include theological and literary subjects. Early life and family He was born into a noble family in the town of San Ginesio, Macerata, Italy. It has been conjectured that Gentili's mother might have been the source of his early love for jurisprudence, but it was his father, Matteo Gent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Story (martyr)
John Story (or Storey) (1504 – 1 June 1571) was an English Roman Catholic martyr and Member of Parliament. Story escaped to Flanders in 1563, but seven years later he was lured aboard a boat in Antwerp and abducted to England, where he was imprisoned in the Tower of London, and subsequently executed at Tyburn on a charge of treason. Life He was born in 1504, the son of Nicholas and Joan Story of Salisbury. He became a Franciscan tertiary. Story was educated at Hinxsey Hall, University of Oxford, where he became lecturer on civil law in 1535, and two years later became principal of Broadgates Hall, afterwards Pembroke College. He received his D.C.L. in 1538, and the following year resigned his position at Broadgates and was admitted as an advocate at Doctors' Commons. He married Joan Watts. He appears to have temporarily abjured his Roman Catholic beliefs and took the Oath of Supremacy. In 1544, in recognition of legal services performed in Boulogne for the crown, King Henr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Member Of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members often have a different title. The terms Member of Congress, congressman/congresswoman or Deputy (legislator), deputy are equivalent terms used in other jurisdictions. The term parliamentarian (other), parliamentarian is also sometimes used for members of parliament, but this may also be used to refer to unelected government officials with specific roles in a parliament and other expert advisers on parliamentary procedure such as the Senate Parliamentarian in the United States. The term is also used to the characteristic of performing the duties of a member of a legislature, for example: "The two party leaders often disagreed on issues, but both were excellent parliamentarians and cooperated to get many good things done." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
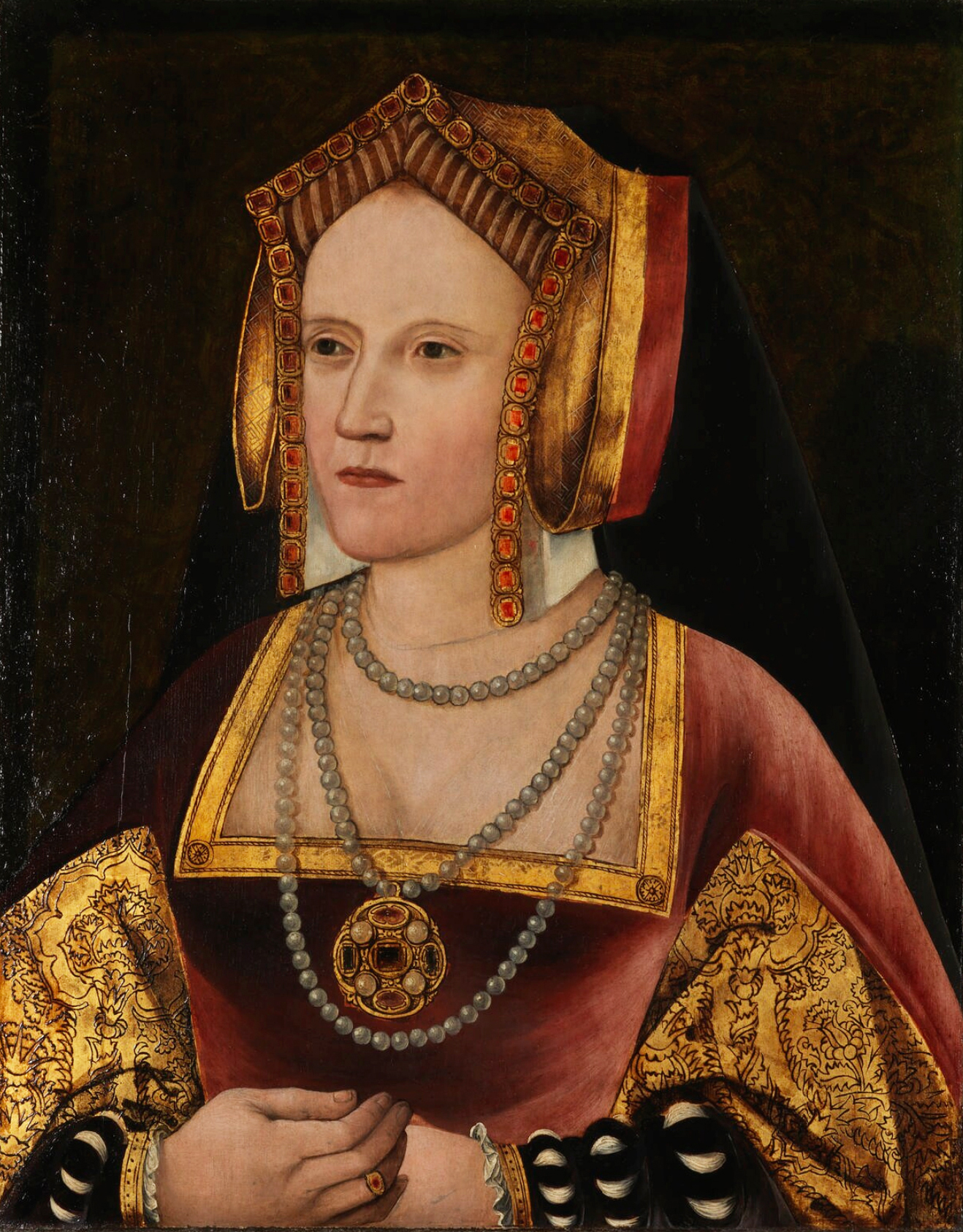
Mary I Of England
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, and as "Bloody Mary" by her Protestant opponents, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain from January 1556 until her death in 1558. She is best known for her vigorous attempt to reverse the English Reformation, which had begun during the reign of her father, Henry VIII. Her attempt to restore to the Church the property confiscated in the previous two reigns was largely thwarted by Parliament, but during her five-year reign, Mary had over 280 religious dissenters burned at the stake in the Marian persecutions. Mary was the only child of Henry VIII by his first wife, Catherine of Aragon, to survive to adulthood. Her younger half-brother, Edward VI, succeeded their father in 1547 at the age of nine. When Edward became terminally ill in 1553, he attempted to remove Mary from the line of succession because he supposed, correctly, that she would reverse the Protestant ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (French Flanders and French Hainaut) and Pas-de-Calais ( Artois). Also within this area were semi-independent fiefdoms, mainly ecclesiastical ones, such as Liège, Cambrai and Stavelot-Malmedy. The Seventeen Provinces arose from the Burgundian Netherlands, a number of fiefs held by the House of Valois-Burgundy and inherited by the Habsburg dynasty in 1482, and held by Habsburg Spain from 1556. Starting in 1512, the Provinces formed the major part of the Burgundian Circle. In 1581, the Seven United Provinces seceded to form the Dutch Republic. Composition After the Habsburg emperor Charles V had re-acquired the Duchy of Guelders from Duke William of Jülich-Cleves-Berg by the 1543 Treaty of Venlo, the Seventeen Provinces comprise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward VI Of England
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and King of Ireland, Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. Edward was the son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour and the first English monarch to be raised as a Protestant. During his reign, the realm was governed by a regent, regency council because he never reached maturity. The council was first led by his uncle Edward Seymour, 1st Duke of Somerset (1547–1549), and then by John Dudley, 1st Earl of Warwick (1550–1553), who from 1551 was Duke of Northumberland. Edward's reign was marked by economic problems and social unrest that in 1549 erupted into riot and rebellion. An expensive war with Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, at first successful, ended with military withdrawal from Scotland and Boulogne-sur-Mer in exchange for peace. The transformation of the Church of England into a recognisably Protestant body also occurred under Edward, who took ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Record Office
The Public Record Office (abbreviated as PRO, pronounced as three letters and referred to as ''the'' PRO), Chancery Lane in the City of London, was the guardian of the national archives of the United Kingdom from 1838 until 2003, when it was merged with the Historical Manuscripts Commission to form The National Archives, based in Kew. It was under the control of the Master of the Rolls, a senior judge. The Public Record Office still exists as a legal entity, as the enabling legislation has not been modified. History 19th century The Public Record Office was established in 1838, to reform the keeping of government and court records which were being held, sometimes in poor conditions, in a variety of places. Some of these were court or departmental archives (established for several centuries) which were well-run and had good or adequate catalogues; others were little more than store-rooms. Many of the professional staff of these individual archives simply continued their ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exchequer
In the civil service of the United Kingdom, His Majesty’s Exchequer, or just the Exchequer, is the accounting process of central government and the government's '' current account'' (i.e., money held from taxation and other government revenues) in the Consolidated Fund. It can be found used in various financial documents including the latest departmental and agency annual accounts. It was the name of a British government department responsible for the collection and the management of taxes and revenues; of making payments on behalf of the sovereign and auditing official accounts. It also developed a judicial role along with its accountancy responsibilities and tried legal cases relating to revenue. Similar offices were later created in Normandy around 1180, in Scotland around 1200 and in Ireland in 1210. Etymology The Exchequer was named after a table used to perform calculations for taxes and goods in the medieval period. According to the '' Dialogus de Scaccario' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michaelmas
Michaelmas ( ; also known as the Feast of Saints Michael, Gabriel, and Raphael, the Feast of the Archangels, or the Feast of Saint Michael and All Angels) is a Christian festival observed in some Western liturgical calendars on 29 September, and on 8 November in the Eastern tradition. Michaelmas has been one of the four quarter days of the English and Irish financial, judicial, and academic year. In Christian angelology, the Archangel Michael is the greatest of all the angels; he is particularly honored for defeating Lucifer in the war in heaven. History In the fifth century, a basilica near Rome was dedicated in honour of Saint Michael the Archangel on 30 September, beginning with celebrations on the eve of that day. 29 September is now kept in honour of Saint Michael and all Angels throughout some western churches. The name Michaelmas comes from a shortening of "Michael's Mass", in the same style as Christmas (Christ's Mass) and Candlemas (Candle Mass, the Mass where t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Augmentations
Thomas Cromwell established the Court of Augmentations, also called Augmentation Court or simply The Augmentation in 1536, during the reign of King Henry VIII of England. It operated alongside three lesser courts (those of General Surveyors (1540-1547), First Fruits and Tenths (1540-1554), and Wards and Liveries (1540-1660)) following the dissolution of the monasteries (1536 onwards). The Court's primary function was to gain better control over the land and finances formerly held by the Roman Catholic Church in the Kingdom of England. The Court of Augmentations was incorporated into the Exchequer in 1554 as the Augmentation Office. History and structure The Court of Augmentations was one of a number of financial courts established during Henry's reign. It was founded in 1536 to administer monastic properties and revenues confiscated by the crown at the dissolution of the monasteries. The court had its own chancellor, treasurer, lawyers, receivers and auditors. In 1547, the Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letters Patent
Letters patent ( la, litterae patentes) ( always in the plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, president or other head of state, generally granting an office, right, monopoly, title or status to a person or corporation. Letters patent can be used for the creation of corporations or government offices, or for granting city status or a coat of arms. Letters patent are issued for the appointment of representatives of the Crown, such as governors and governors-general of Commonwealth realms, as well as appointing a Royal Commission. In the United Kingdom, they are also issued for the creation of peers of the realm. A particular form of letters patent has evolved into the modern intellectual property patent (referred to as a utility patent or design patent in United States patent law) granting exclusive rights in an invention or design. In this case it is essential that the written grant should be in the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beatification
Beatification (from Latin ''beatus'', "blessed" and ''facere'', "to make”) is a recognition accorded by the Catholic Church of a deceased person's entrance into Heaven and capacity to intercede on behalf of individuals who pray in their name. ''Beati'' is the plural form, referring to those who have undergone the process of beatification; they possess the title of "Blessed" (abbreviation "Bl.") before their names and are often referred to in English as "a Blessed" or, plurally, "Blesseds". History Local bishops had the power of beatifying until 1634, when Pope Urban VIII, in the apostolic constitution ''Cœlestis Jerusalem'' of 6 July, reserved the power of beatifying to the Holy See. Since the reforms of 1983, as a rule, one miracle must be confirmed to have taken place through the intercession of the person to be beatified. Miracles are almost always unexplainable medical healings, and are scientifically investigated by commissions comprising physicians and theologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


