|
Reginald Walter Ralph Barnes
Major-General Sir Reginald Walter Ralph Barnes (13 April 1871 – 19 December 1946) was a cavalry officer in the British Army. He served in several regiments, and commanded a battalion of the Imperial Yeomanry, the 10th (Prince of Wales's Own) Royal Hussars, the 111th Brigade, and three divisions. During his career he served in the Cuban War of Independence, the Second Boer War and the First World War. Becoming a Companion of the Distinguished Service Order, and a Knight Commander of The Most Honourable Order of the Bath. He was also awarded a French Croix de Guerre. History Early life Reginald Walter Ralph Barnes was born 13 April 1871, at Stoke Canon Exeter, the son of Prenbendary R H Barnes. He was educated at Westminster School, before in December 1888, becoming a second-lieutenant in the 4th Battalion, King's Shropshire Light Infantry, at the time part of the militia. He was promoted to lieutenant in September 1889. Then in December 1890 he transferred to the regular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoke Canon
Stoke Canon is a small village and civil parish near the confluence of the rivers Exe and Culm on the main A396 between Exeter and Tiverton in the English county of Devon, and the district of East Devon. At the 2001 census it had a population of 660. The population was unchanged in 2011 but the village forms the major part of the Exe Valley electoral ward. The population of this ward was 2,041 at the 2011 Census. There is a pub, The Stoke Canon Inn, and a post office and general stores in the centre of the village. The church The Church (St. Mary Magdalene) was wholly rebuilt in 1836, except for the west tower, at the cost of £1000. The interior is neatly fitted up, and the tower has a clock and four bells. It contains a remarkable font of Norman date, made from a single block of lava, and a number of 17th-century floor slabs to local families. It was here in 1666, at this 14th-century church, that George Boone III, grandfather of the famous American pioneer Daniel Boone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South African Republic and the Orange Free State) over the Empire's influence in Southern Africa from 1899 to 1902. Following the discovery of gold deposits in the Boer republics, there was a large influx of "foreigners", mostly British from the Cape Colony. They were not permitted to have a vote, and were regarded as "unwelcome visitors", invaders, and they protested to the British authorities in the Cape. Negotiations failed and, in the opening stages of the war, the Boers launched successful attacks against British outposts before being pushed back by imperial reinforcements. Though the British swiftly occupied the Boer republics, numerous Boers refused to accept defeat and engaged in guerrilla warfare. Eventually, British scorched eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Richebourg L'Avoue
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Loos
The Battle of Loos took place from 1915 in France on the Western Front, during the First World War. It was the biggest British attack of 1915, the first time that the British used poison gas and the first mass engagement of New Army units. The French and British tried to break through the German defences in Artois and Champagne and restore a war of movement. Despite improved methods, more ammunition and better equipment, the Franco-British attacks were largely contained by the Germans, except for local losses of ground. The British gas attack failed to neutralize the defenders and the artillery bombardment was too short to destroy the barbed wire or machine gun nests. German tactical defensive proficiency was still dramatically superior to the British offensive planning and doctrine, resulting in a British defeat. Background Strategic developments The battle was the British part of the Third Battle of Artois, an Anglo-French offensive (known to the Germans as the (Autumn Batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Frezenberg Ridge
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Ypres
During the First World War, the Second Battle of Ypres was fought from for control of the tactically important high ground to the east and south of the Flemish town of Ypres in western Belgium. The First Battle of Ypres had been fought the previous autumn. The Second Battle of Ypres was the first mass use by Germany of poison gas on the Western Front. Background The eminent German chemist Walther Nernst, who was in the army in 1914 as a volunteer driver, saw how trenches produced deadlock. He proposed to Colonel Max Bauer, the German general staff officer responsible for liaison with scientists, that they could empty the opposing trenches by a surprise attack with tear gas. Observing a field test of this idea, the chemist Fritz Haber instead proposed using heavier-than-air chlorine gas The German commander Erich von Falkenhayn agreed to try the new weapon, but intended to use it in a diversionary attack by his 4th Army. Falkenhayn wanted to use the gas to cover the withdra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Nonne Bosschen
The First Battle of Ypres (french: Première Bataille des Flandres; german: Erste Flandernschlacht – was a battle of the First World War, fought on the Western Front around Ypres, in West Flanders, Belgium. The battle was part of the First Battle of Flanders, in which German, French, Belgian armies and the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) fought from Arras in France to Nieuwpoort (Nieuport) on the Belgian coast, from 10 October to mid-November. The battles at Ypres began at the end of the Race to the Sea, reciprocal attempts by the German and Franco-British armies to advance past the northern flank of their opponents. North of Ypres, the fighting continued in the Battle of the Yser between the German 4th Army, the Belgian army and French marines. The fighting has been divided into five stages, an encounter battle from 19 to 21 October, the Battle of Langemarck from 21 to 24 October, the battles at La Bassée and Armentières to 2 November, coincident with more Allie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
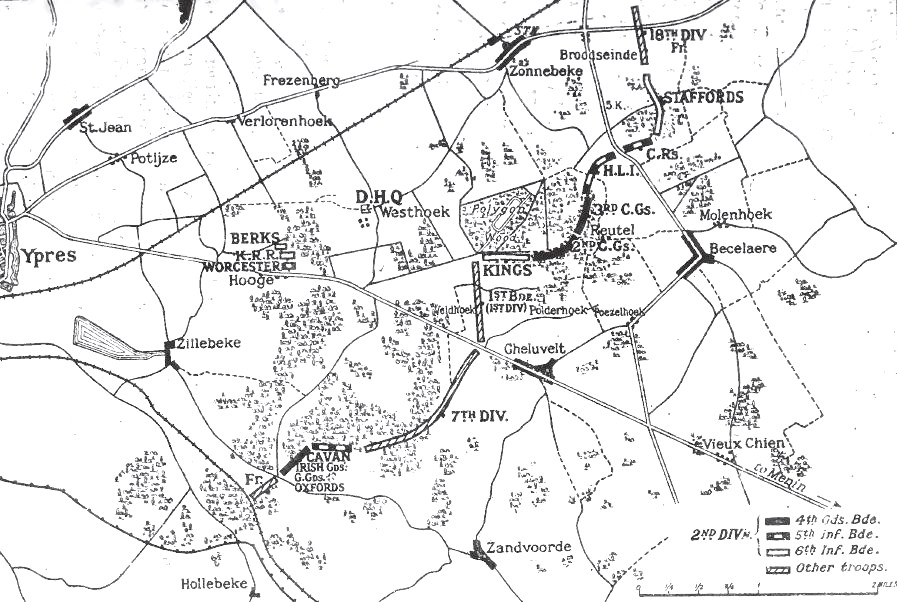
Battle Of Gheluvelt
The First Battle of Ypres (french: Première Bataille des Flandres; german: Erste Flandernschlacht – was a battle of the First World War, fought on the Western Front around Ypres, in West Flanders, Belgium. The battle was part of the First Battle of Flanders, in which German, French, Belgian armies and the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) fought from Arras in France to Nieuwpoort (Nieuport) on the Belgian coast, from 10 October to mid-November. The battles at Ypres began at the end of the Race to the Sea, reciprocal attempts by the German and Franco-British armies to advance past the northern flank of their opponents. North of Ypres, the fighting continued in the Battle of the Yser between the German 4th Army, the Belgian army and French marines. The fighting has been divided into five stages, an encounter battle from 19 to 21 October, the Battle of Langemarck from 21 to 24 October, the battles at La Bassée and Armentières to 2 November, coincident with more Allie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of Ypres
The First Battle of Ypres (french: Première Bataille des Flandres; german: Erste Flandernschlacht – was a battle of the First World War, fought on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front around Ypres, in West Flanders, Belgium. The battle was part of the First Battle of Flanders, in which German Army (German Empire), German, French Army in World War I, French, Belgian Land Component, Belgian armies and the British Expeditionary Force (World War I), British Expeditionary Force (BEF) fought from Arras in France to Nieuwpoort, Belgium, Nieuwpoort (Nieuport) on the Belgian coast, from 10 October to mid-November. The battles at Ypres began at the end of the Race to the Sea, reciprocal attempts by the German and Franco-British armies to advance past the northern flank of their opponents. North of Ypres, the fighting continued in the Battle of the Yser between the German 4th Army (German Empire), 4th Army, the Belgian army and French marines. The fighting has been divide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bergendal
The Battle of Berg-en-dal (also known as the Battle of Belfast or Battle of Dalmanutha) took place in South Africa during the Second Anglo-Boer War. The battle was the last set-piece battle of the war, although the war was still to last another two years. It was also the last time that the Boers' four 155 mm Creusot Long Tom guns were used in the same battle. Before Hostilities commenced in October 1899. On the Cape front the British forces broke through in February 1900 and the next month they were in Bloemfontein, the capital of the Orange Free State. Pretoria, the capital of the Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek (ZAR) was captured in June 1900. The government of the ZAR and a few Boer commandos fled eastwards along the railway line to Lourenço Marques (now Maputo). They were pursued by General Pole-Carew and his 11th Infantry Division (7,500 officers and men) and a cavalry division commanded by Lieutenant-General French. Prior to the Battle of Diamond Hill on 11 June 1900, Gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Mafeking
The siege of Mafeking was a 217-day siege battle for the town of Mafeking (now called Mafikeng) in South Africa during the Second Boer War from October 1899 to May 1900. The siege received considerable attention as Lord Edward Cecil, the son of the British prime minister, was in the besieged town, as also was Lady Sarah Wilson (war correspondent), Sarah Wilson, a daughter of the John Spencer-Churchill, 7th Duke of Marlborough, Duke of Marlborough and aunt of Winston Churchill. The siege turned the British commander, Colonel Robert Baden-Powell, into a national hero. The Relief of Mafeking (the lifting of the siege), while of little military significance, was a morale boost for the struggling British. Prelude Shortly before the outbreak of the Second Boer War in 1899, Garnet Wolseley, 1st Viscount Wolseley, Lord Wolseley, Commander-in-Chief of the British Army, who had failed to persuade the British government to send troops to the region, instead sent Colonel Robert Baden-Powel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)