|
Reference Point Indentation
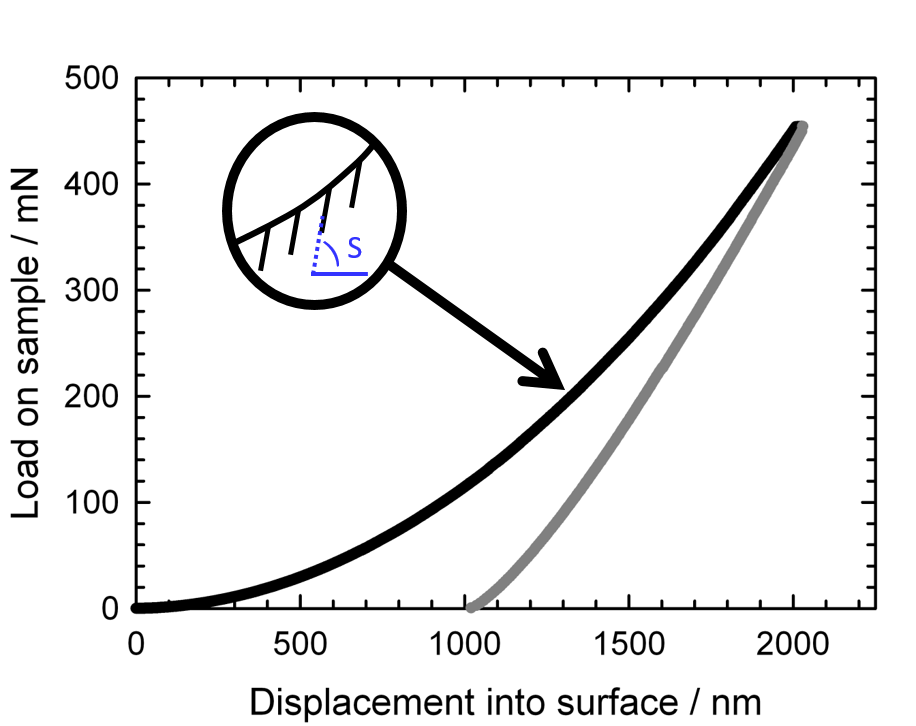
Nanoindentation, also called instrumented indentation testing, is a variety of indentation hardness tests applied to small volumes. Indentation is perhaps the most commonly applied means of testing the mechanical properties of materials. The nanoindentation technique was developed in the mid-1970s to measure the hardness of small volumes of material. Background In a traditional indentation test (macro or micro indentation), a hard tip whose mechanical properties are known (frequently made of a very hard material like diamond) is pressed into a sample whose properties are unknown. The load placed on the indenter tip is increased as the tip penetrates further into the specimen and soon reaches a user-defined value. At this point, the load may be held constant for a period or removed. The area of the residual indentation in the sample is measured and the hardness, H, is defined as the maximum load, P_, divided by the residual indentation area, A_r: :H=\frac . For most techniques, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indentation Hardness
Indentation hardness tests are used in mechanical engineering to determine the hardness of a material to deformation. Several such tests exist, wherein the examined material is indented until an impression is formed; these tests can be performed on a macroscopic or microscopic scale. When testing metals, indentation hardness correlates roughly linearly with tensile strength, but it is an imperfect correlation often limited to small ranges of strength and hardness for each indentation geometry. This relation permits economically important nondestructive testing of bulk metal deliveries with lightweight, even portable equipment, such as hand-held Rockwell hardness testers. Material hardness Different techniques are used to quantify material characteristics at smaller scales. Measuring mechanical properties for materials, for instance, of thin films, cannot be done using conventional uniaxial tensile testing. As a result, techniques testing material "hardness" by indenting a materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poisson's Ratio
In materials science and solid mechanics, Poisson's ratio \nu ( nu) is a measure of the Poisson effect, the deformation (expansion or contraction) of a material in directions perpendicular to the specific direction of loading. The value of Poisson's ratio is the negative of the ratio of transverse strain to axial strain. For small values of these changes, \nu is the amount of transversal elongation divided by the amount of axial compression. Most materials have Poisson's ratio values ranging between 0.0 and 0.5. For soft materials, such as rubber, where the bulk modulus is much higher than the shear modulus, Poisson's ratio is near 0.5. For open-cell polymer foams, Poisson's ratio is near zero, since the cells tend to collapse in compression. Many typical solids have Poisson's ratios in the range of 0.2–0.3. The ratio is named after the French mathematician and physicist Siméon Poisson. Origin Poisson's ratio is a measure of the Poisson effect, the phenomenon in which a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale. The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, American spelling) is a units of measurement, unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one billionth (short scale) of a metre () and to 1000 picometres. One nanometre can be expressed in scientific notation as , and as metres. History The nanometre was formerly known as the millimicrometre – or, more commonly, the millimicron for short – since it is of a micron (micrometre), and was often denoted by the symbol mμ or (more rarely and confusingly, since it logically should refer to a ''millionth'' of a micron) as μμ. Etymology The name combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' (from the Ancient Greek , ', "dwarf") with the parent unit name ''metre'' (from Greek , ', "unit of measurement"). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton (unit)
The newton (symbol: N) is the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI). It is defined as 1 kg⋅m/s, the force which gives a mass of 1 kilogram an acceleration of 1 metre per second per second. It is named after Isaac Newton in recognition of his work on classical mechanics, specifically Newton's second law of motion. Definition A newton is defined as 1 kg⋅m/s (it is a derived unit which is defined in terms of the SI base units). One newton is therefore the force needed to accelerate one kilogram of mass at the rate of one metre per second squared in the direction of the applied force. The units "metre per second squared" can be understood as measuring a rate of change in velocity per unit of time, i.e. an increase in velocity by 1 metre per second every second. In 1946, Conférence Générale des Poids et Mesures (CGPM) Resolution 2 standardized the unit of force in the MKS system of units to be the amount needed to accelerate 1 kilogram of mass at the rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltzmann's Constant
The Boltzmann constant ( or ) is the proportionality factor that relates the average relative kinetic energy of particles in a gas with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin and the gas constant, and in Planck's law of black-body radiation and Boltzmann's entropy formula, and is used in calculating thermal noise in resistors. The Boltzmann constant has dimensions of energy divided by temperature, the same as entropy. It is named after the Austrian scientist Ludwig Boltzmann. As part of the 2019 redefinition of SI base units, the Boltzmann constant is one of the seven " defining constants" that have been given exact definitions. They are used in various combinations to define the seven SI base units. The Boltzmann constant is defined to be exactly . Roles of the Boltzmann constant Macroscopically, the ideal gas law states that, for an ideal gas, the product of pressure and volume is proportional to the product of amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation Volume
Activation, in chemistry and biology, is the process whereby something is prepared or excited for a subsequent reaction. Chemistry In chemistry, "activation" refers to the reversible transition of a molecule into a nearly identical chemical or physical state, with the defining characteristic being that this resultant state exhibits an increased propensity to undergo a specified chemical reaction. Thus, activation is conceptually the opposite of protection, in which the resulting state exhibits a ''decreased'' propensity to undergo a certain reaction. The energy of activation specifies the amount of free energy the reactants must possess (in addition to their rest energy) in order to initiate their conversion into corresponding products—that is, in order to reach the transition state for the reaction. The energy needed for activation can be quite small, and often it is provided by the natural random thermal fluctuations of the molecules themselves (i.e. without any external ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dislocations
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to slide over each other at low stress levels and is known as ''glide'' or slip. The crystalline order is restored on either side of a ''glide dislocation'' but the atoms on one side have moved by one position. The crystalline order is not fully restored with a ''partial dislocation''. A dislocation defines the boundary between ''slipped'' and ''unslipped'' regions of material and as a result, must either form a complete loop, intersect other dislocations or defects, or extend to the edges of the crystal. A dislocation can be characterised by the distance and direction of movement it causes to atoms which is defined by the Burgers vector. Plastic deformation of a material occurs by the creation and movement of many dislocations. The number and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strain (materials Science)
In physics, deformation is the continuum mechanics transformation of a body from a ''reference'' configuration to a ''current'' configuration. A configuration is a set containing the positions of all particles of the body. A deformation can occur because of external loads, intrinsic activity (e.g. muscle contraction), body forces (such as gravity or electromagnetic forces), or changes in temperature, moisture content, or chemical reactions, etc. Strain is related to deformation in terms of ''relative'' displacement of particles in the body that excludes rigid-body motions. Different equivalent choices may be made for the expression of a strain field depending on whether it is defined with respect to the initial or the final configuration of the body and on whether the metric tensor or its dual is considered. In a continuous body, a deformation field results from a stress field due to applied forces or because of some changes in the temperature field of the body. The relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow Stress
In materials science the flow stress, typically denoted as Yf (or \sigma_\text), is defined as the instantaneous value of stress required to continue plastically deforming a material - to keep it flowing. It is most commonly, though not exclusively, used in reference to metals. On a stress-strain curve, the flow stress can be found anywhere within the plastic regime; more explicitly, a flow stress can be found for any value of strain between and including yield point (\sigma_\text) and excluding fracture (\sigma_\text): \sigma_\text \leq Y_\text < \sigma_\text. The flow stress changes as deformation proceeds and usually increases as strain accumulates due to , although the flow stress could decrease due to any recovery process. In continuum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
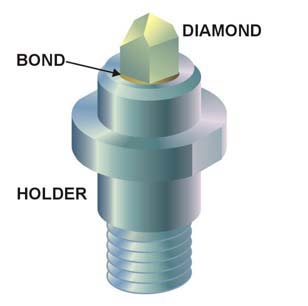
Nanoindenter
A nanoindenter is the main component for indentation hardness tests used in nanoindentation. Since the mid-1970s nanoindentation has become the primary method for measuring and testing very small volumes of mechanical properties. Nanoindentation, also called ''depth sensing indentation'' or ''instrumented indentation'', gained popularity with the development of machines that could record small load and displacement with high accuracy and precision. The load displacement data can be used to determine modulus of elasticity, hardness, yield strength, fracture toughness, scratch hardness and wear properties. Types There are many types of nanoindenters in current use differing mainly on their tip geometry. Among the numerous available geometries are three and four sided pyramids, wedges, cones, cylinders, filaments, and spheres. Several geometries have become a well established common standard due to their extended use and well known properties; such as Berkovich, cube corner, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Force Microscopy
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the optical diffraction limit. Overview Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the optical diffraction limit. The information is gathered by "feeling" or "touching" the surface with a mechanical probe. Piezoelectric elements that facilitate tiny but accurate and precise movements on (electronic) command enable precise scanning. Despite the name, the Atomic Force Microscope does not use the Nuclear force. Abilities The AFM has three major abilities: force measurement, topographic imaging, and manipulation. In force measurement, AFMs can be used to measure the forces between the probe and the sample as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |