|
Red Scare In Japan
The Red Scare in Japan refers to the promotion of fear of the rise of communism or radical leftism in Japan. Throughout the history of Imperial Japan, the government suppressed socialist and communist movements. In order to combat the Communist International, Japan signed the Anti-Comintern Pact with Germany and Italy in Nov. 6, 1937. Near the end of World War II, Prince Konoe Fumimaro promoted the fear of a communist revolution as a result of Japan's defeat. In response to Cold War tensions in Asia, the CIA funded the Japanese Liberal Democratic Party in an effort to turn Japan into a bulwark against communism during the 1950s and 1960s. See also * Japanese dissidence during the Shōwa period * Political repression in Imperial Japan * Japanese Red Army The was a militant communist organization active from 1971 to 2001. It was designated a terrorist organization by Japan and the United States. The JRA was founded by Fusako Shigenobu and Tsuyoshi Okudaira in Februar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Scare
A Red Scare is the promotion of a widespread fear of a potential rise of communism, anarchism or other leftist ideologies by a society or state. The term is most often used to refer to two periods in the history of the United States which are referred to by this name. The First Red Scare, which occurred immediately after World War I, revolved around a perceived threat from the American labor movement, anarchist revolution, and political radicalism. The Second Red Scare, which occurred immediately after World War II, was preoccupied with the perception that national or foreign communists were infiltrating or subverting American society and the federal government. The name refers to the red flag as a common symbol of communism. First Red Scare (1917–1920) The first Red Scare in the United States accompanied the Russian Revolution of 1917 and subsequent communist revolutions in Europe and beyond. Citizens of the United States in the years of World War I (1914-1918) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Liberal Democratic Party
The , frequently abbreviated to LDP or , is a conservativeThe Liberal Democratic Party is widely described as conservative: * * * * * political party in Japan. The LDP has been in power almost continuously since its foundation in 1955—a period called the 1955 System—except between 1993 and 1994, and again from 2009 to 2012. In the 2012 election, it regained control of the government. After the 2021 and 2022 elections it holds 261 seats in the House of Representatives and 119 seats in the House of Councillors, and in coalition with Komeito since 1999, a governing majority in both houses. The LDP is often described as a big tent conservative party, with several different ideological factions. The party's history and internal composition have been characterized by intense factionalism ever since its emergence in 1955, with its parliamentary members currently split among six factions, each of which vies for influence in the party and the government. The incumbent Prime Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-communism In Japan
Anti-communism is political and ideological opposition to communism. Organized anti-communism developed after the 1917 October Revolution in the Russian Empire, and it reached global dimensions during the Cold War, when the United States and the Soviet Union engaged in an intense rivalry. Anti-communism has been an element of movements which hold many different political positions, including conservatism, fascism, liberalism, nationalism, social democracy, libertarianism, or the anti-Stalinist left. Anti-communism has also been expressed in philosophy, by several religious groups, and in literature. Some well-known proponents of anti-communism are former communists. Anti-communism has also been prominent among movements resisting communist governance. The first organization which was specifically dedicated to opposing communism was the Russian White movement which fought in the Russian Civil War starting in 1918 against the recently established Bolshevik government. The W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Movements In Japan
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. It may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and nonviolent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but also often carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or limitedly, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, including w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Purge
The Red Purge (Japanese: レッドパージ; ''reddo pāji'') was an anticommunist movement in occupied Japan from the late 1940s to the early 1950s.: "From 1947, the Japanese government, supported by MacArthur, unleashed a Red Purge that targeted those Japanese considered to have left-wing views." Carried out by the Japanese government and private corporations with the aid and encouragement of the Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers (SCAP), the Red Purge saw tens of thousands of alleged members, supporters, or sympathizers of left-wing groups, especially those said to be affiliated with the Japanese Communist Party, removed from their jobs in government, the private sector, universities, and schools. The Red Purge emerged from rising Cold War tensions and the Red Scare after World War II, and was a significant element within a broader "Reverse Course" in Occupation policies. The Red Purge reached a peak following the outbreak of the Korean War in 1950, began to ease after Gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Red Army
The was a militant communist organization active from 1971 to 2001. It was designated a terrorist organization by Japan and the United States. The JRA was founded by Fusako Shigenobu and Tsuyoshi Okudaira in February 1971 and was most active in the 1970s and 1980s. After the Lod Airport massacre, it sometimes called itself the Arab-JRA. The group was also known as the Anti-Imperialist International Brigade (AIIB), the Holy War Brigade, and the Anti-War Democratic Front. The JRA's stated goals were to overthrow the Japanese government and the monarchy, as well as to start a world revolution. History Fusako Shigenobu had been a leading member in the in Japan, whose roots lay in the militant New Left Communist League. Advocating revolution through terrorism, they set up their own group, declaring war on the state in September 1969. The police quickly arrested many of them, including founder and intellectual leader Takaya Shiomi, who was in jail by 1970. The Red Army Faction lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Repression In Imperial Japan
Political repression in Imperial Japan lasted from the Meiji period to the fall of the Empire of Japan after the end of World War II. Throughout this period, dissidence was curtailed by laws, and police, and dissidents became political prisoners. Several laws were passed to curtail dissidence in Imperial Japan, including the Public Peace Police Law in 1900, and the Peace Preservation Law in 1925. The earliest secret police in Imperial Japan was the Danjodai, established in May 1869. The ''Tokubetsu Kōtō Keisatsu'' (''Tokko'') was established in 1911 following the Great Treason Incident of 1910. See also * Political prisoners in Imperial Japan * Japanese dissidence during the Shōwa period * Censorship in the Empire of Japan * Tenkō is a Japanese term referring to the coerced ideological conversions of Japanese socialists and communists who, between 1925 and 1945, were induced to renounce leftist ideologies and enthusiastically embrace the Emperor-centric, capitalist, and impe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Dissidence During The Shōwa Period
Political dissidence in the Empire of Japan covers individual Japanese dissidents against the policies of the Empire of Japan. Dissidence in the Meiji and Taishō eras High Treason Incident Shūsui Kōtoku, a Japanese anarchist, was critical of imperialism. He would write ''Imperialism: The Specter of the Twentieth Century'' in 1901. In 1911, twelve people, including Kōtoku, were executed for their involvement in the High Treason Incident, a failed plot to assassinate Emperor Meiji. Also executed for involvement with the plot was Kanno Suga, an anarcho-feminist and former common-law wife of Kōtoku. Fumiko Kaneko and Park Yeol Fumiko Kaneko was a Japanese anarchist who lived in Japanese occupied Korea. She, along with a Korean anarchist, Park Yeol, were accused of attempting to procure bombs from a Korean independence group in Shanghai. Both of them were charged with plotting to assassinate members of the Japanese imperial family. The Commoners' Newspaper The (Commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they each supported major regional conflicts known as proxy wars. The conflict was based around the ideological and geopolitical struggle for global influence by these two superpowers, following their temporary alliance and victory against Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan in 1945. Aside from the nuclear arsenal development and conventional military deployment, the struggle for dominance was expressed via indirect means such as psychological warfare, propaganda campaigns, espionage, far-reaching embargoes, rivalry at sports events, and technological competitions such as the Space Race. The Western Bloc was led by the United States as well as a number of other First W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. It encompassed the Japanese archipelago and several colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories. Under the slogans of and following the Boshin War and restoration of power to the Emperor from the Shogun, Japan underwent a period of industrialization and militarization, the Meiji Restoration, which is often regarded as the fastest modernisation of any country to date. All of these aspects contributed to Japan's emergence as a great power and the establishment of a colonial empire following the First Sino-Japanese War, the Boxer Rebellion, the Russo-Japanese War, and World War I. Economic and political turmoil in the 1920s, including the Great Depression, led to the rise of militarism, nationalism and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
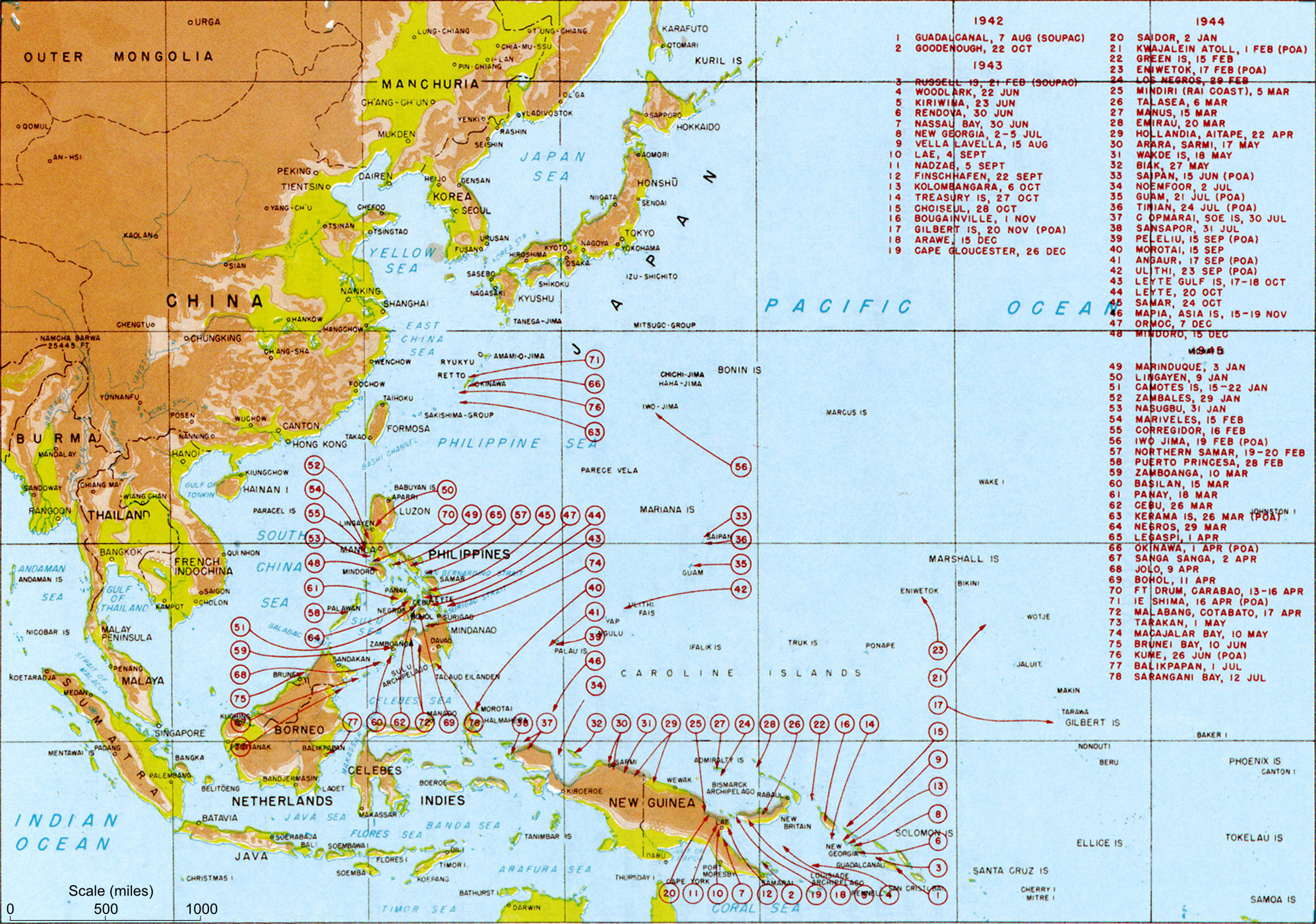
Surrender Of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) had become incapable of conducting major operations and an Allied invasion of Japan was imminent. Together with the United Kingdom and China, the United States called for the unconditional surrender of the Japanese armed forces in the Potsdam Declaration on 26 July 1945—the alternative being "prompt and utter destruction". While publicly stating their intent to fight on to the bitter end, Japan's leaders (the Supreme Council for the Direction of the War, also known as the "Big Six") were privately making entreaties to the publicly neutral Soviet Union to mediate peace on terms more favorable to the Japanese. While maintaining a sufficient level of diplomatic engagement with the Japanese to give them the impression they might be wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konoe Fumimaro
Prince was a Japanese politician and prime minister. During his tenure, he presided over the Japanese invasion of China in 1937 and the breakdown in relations with the United States, which ultimately culminated in Japan's entry into World War II. He also played a central role in transforming his country into a totalitarian state by passing the National Mobilization Law and founding the Imperial Rule Assistance Association. Despite Konoe's attempts to resolve tensions with the United States, the rigid timetable imposed on negotiations by the military and his own government's inflexibility regarding a diplomatic resolution set Japan on the path to war. Upon failing to reach a peace agreement, Konoe resigned as Prime Minister on 18 October 1941, prior to the outbreak of hostilities. However, he remained a close advisor to the Emperor until the end of World War II. Following the end of the war, he committed suicide on 16 December 1945. Early life Fumimaro Konoe was born in To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(cropped).jpg)



.png)