|
Red Book Of The Peoples Of The Russian Empire
''The Red Book of the Peoples of the Russian Empire'' is a book about the small nations of the Russian Empire, the Soviet Union, and Russia and some other post-Soviet states of today. It was published in Estonian in 1991 and in English in 2001. The foreword of the book explains the book's approach by saying, "the authors of the present book, who come from a country (Estonia) which has shared the fate of nations in the Russian and Soviet empires, endeavour to publicize the plight of the small nations whose very existence is threatened as a result of recent history." Described peoples The authors' intention for the book was to include the peoples according to the following criteria: * are not yet extinct, * whose main area of settlement is on ex-Soviet territory, * whose numbers are below 30,000, * of whom less than 70% speak their native language, * who form a minority on their ancient territory, * whose settlement is scattered rather than compact, * who have no vernacular school, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book
A book is a medium for recording information in the form of writing or images, typically composed of many pages (made of papyrus, parchment, vellum, or paper) bound together and protected by a cover. The technical term for this physical arrangement is '' codex'' (plural, ''codices''). In the history of hand-held physical supports for extended written compositions or records, the codex replaces its predecessor, the scroll. A single sheet in a codex is a leaf and each side of a leaf is a page. As an intellectual object, a book is prototypically a composition of such great length that it takes a considerable investment of time to compose and still considered as an investment of time to read. In a restricted sense, a book is a self-sufficient section or part of a longer composition, a usage reflecting that, in antiquity, long works had to be written on several scrolls and each scroll had to be identified by the book it contained. Each part of Aristotle's ''Physics'' is called a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baraba Tatars
The Baraba (Siberian Tatar: параба, бараба, барама, бараба татарлар) are a sub-group of Siberian Tatars and the indigenous people of the Ob-Irtysh interfluve. After a strenuous resistance to Russian conquest and much suffering at a later period from Kyrgyz and Kalmyk raids, they now live by agriculture — either in separate villages or along with Russians. Some of them still speak Baraba dialect of Siberian Tatar language. They traditionally live on the Baraba steppe. Population They were first mentioned as a separate ethnic group in the Russian Empire Census in 1897 and First All-Union Census of the Soviet Union in 1926. According to 1897 Census their population was 4,433. In 1926 there were 7,528 Baraba Tatars. Ethnographers estimated that their population reached 8,380 in 1971. According to the data of the Institute of Philology of the Siberian Branch of the RAS, there were 8,000 Baraba Tatars in Novosibirsk Oblast in 2012. History Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolgans
Dolgans (; Dolgan: , , (Sakha); Yakut: ) are an ethnic group who mostly inhabit Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. They are descended from several groups, particularly Evenks, one of the indigenous peoples of the Russian North. They adopted a Turkic language sometime after the 18th century. The 2010 Census counted 7,885 Dolgans. This number includes 5,517 in former Taymyr Autonomous Okrug. Dolgans speak the Dolgan language, which is closely related to the Yakut language. History In the 17th century, the Dolgans lived in the basins of the Olenyok River and Lena River. They moved to their current location, Taymyr, in the 18th century. The Dolgan identity began to emerge during the 19th and early 20th centuries, under the influence of three groups who migrated to the Krasnoyarsk area from the Lena River and Olenyok River region: Evenks, Yakuts, Enets, and so-called tundra peasants (). Culture and livelihood Originally, the Dolgans were nomadic hunters and reindeer herders. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsez People
The Tsez (also known as the Dido or the Didoi) are a North Caucasian ethnic group. Their unwritten language, also called Tsez or Dido, belongs to the Northeast Caucasian group with some 15,354 speakers.Olson, James Stuart; Pappas, Lee Brigance & Pappas, Nicholas Charles (1994), ''An Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires'', p. 199. Greenwood Publishing Group, . For demographic purposes, today they are classified with the Avars with whom the Tsez share a religion, Sunni Islam, and some cultural traits. They are centered at the Tsunta district of the Republic of Dagestan, Russia. The term “Dido” is sometimes used in a broader sense to refer to the Tsez as well as the Bezhtas, Hinukhs The Hinukh ( Hinukh: гьинухъес ''hinuqes'', av, гьинухъесел , translit=hinuqesel) are a people of Dagestan living in 2 villages: Genukh, Tsuntinsky District - their 'parent village' and Novomonastyrskoe, Kizlyarsky District ..., Khwarshis and Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
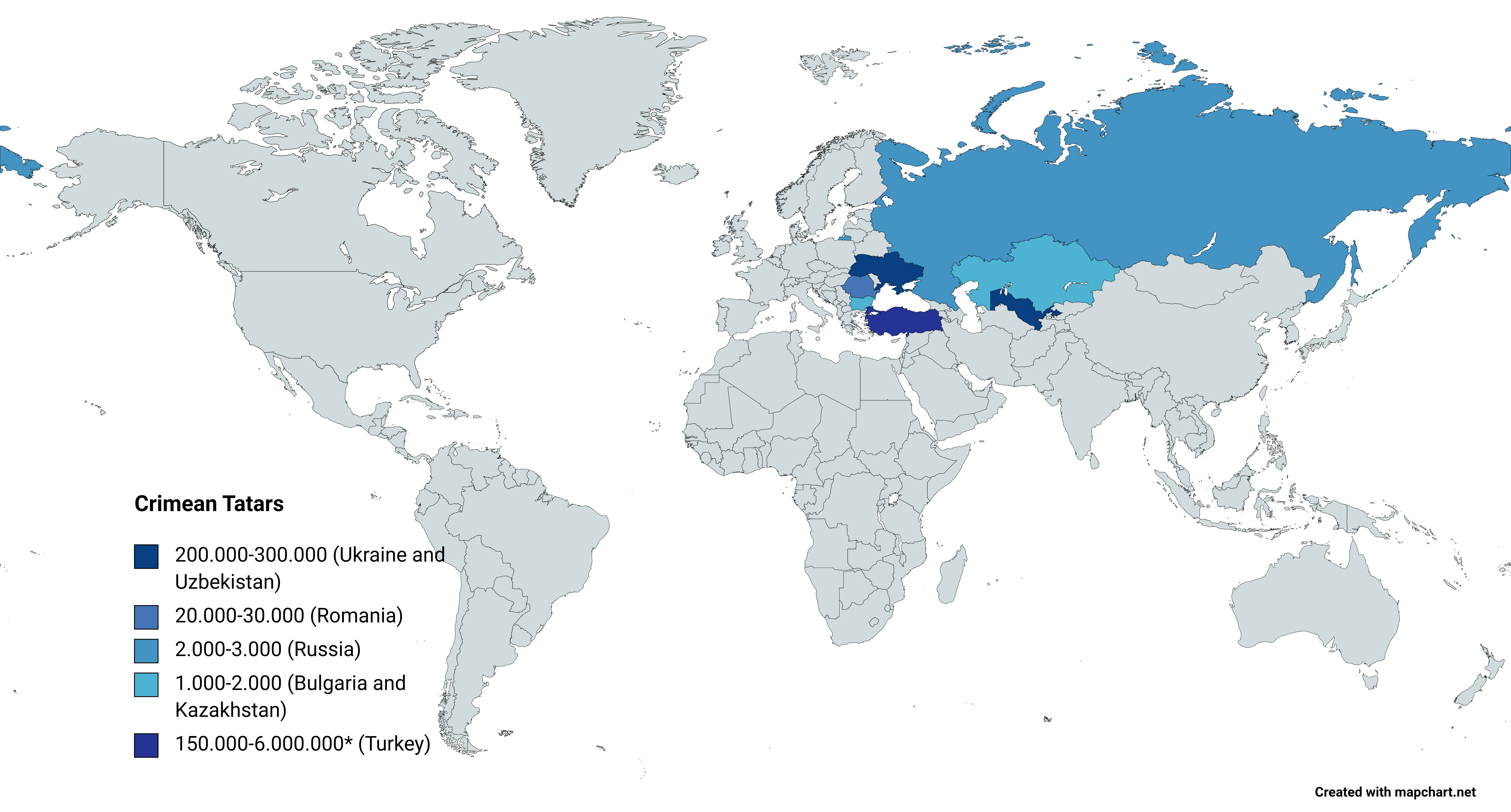
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg , flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars , image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg , caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace , poptime = , popplace = , region1 = , pop1 = 3,500,000 6,000,000 , ref1 = , region2 = * , pop2 = 248,193 , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 239,000 , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 24,137 , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 2,449 , ref5 = , region7 = , pop7 = 1,803 , ref7 = , region8 = , pop8 = 1,532 , ref8 = , region9 = *() , pop9 = 7,000(500–1,000) , ref9 = , region10 = Total , pop10 = 4.024.114 (or 6.524.11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean Jews
The history of the Jews in Ukraine dates back over a thousand years; Jewish communities have existed in the territory of Ukraine from the time of the Kievan Rus' (late 9th to mid-13th century). Some of the most important Jewish religious and cultural movements, from Hasidism to Zionism, rose either fully or to an extensive degree in the territory of modern Ukraine. According to the World Jewish Congress, the Jewish community in Ukraine constitutes the third-largest in Europe and the fifth-largest in the world. The actions of the Soviet government by 1927 led to a growing antisemitism in the area.Сергійчук, В. Український Крим К. 2001, p.156 Total civilian losses during World War II and the Reichskommissariat Ukraine, German occupation of Ukraine are estimated at seven million. More than one million Soviet Jews, of them around 225,000 in Belarus, were shot and killed by the Einsatzgruppen and by their many local Ukrainian supporters. Most of them wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chulym Tatars
The Chulyms, also Chulym Tatars (self-designation: Татарлар, ''Tatarlar''), are a Turkic people in the Tomsk Oblast and Krasnoyarsk Krai in Russia. According to the 2002 census, there were 656 Chulyms in Russia. History The Chulym Tatars first came to the Chulym River when they were driven from their homes in the Sibir Khanate by the forces of Ermak Timofeevich. They used to live along the middle and lower reaches of the Chulym River (tributary of the Ob River). The Russians used to call them the Chulymian Tatars. The Chulyms appeared in the 16th century as a result of mixing of some of the Turkic groups, who had migrated to the East after the fall of the Khanate of Sibir, partially Teleuts, Yenisei Kyrgyz and groups of Tobolsk Tatars. During the 16th century, the Russian conquered the Chulyms and their newly settled land. In 1720, the Chulyms were forcefully converted to Christianity. In the early 19th century, the Chulyms were mandated by an edict from the Russian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chukchi People
The Chukchi, or Chukchee ( ckt, Ԓыгъоравэтԓьэт, О'равэтԓьэт, ''Ḷygʺoravètḷʹèt, O'ravètḷʹèt''), are a Siberian indigenous people native to the Chukchi Peninsula, the shores of the Chukchi Sea and the Bering Sea region of the Arctic Ocean all within modern Russia. They speak the Chukchi language. The Chukchi originated from the people living around the Okhotsk Sea. According to several studies on genomic research conduct from 2014 to 2018, the Chukchi are one of the Indigenous peoples of Siberia, they are also the closest Asiatic relatives of the indigenous peoples of the Americas as well as of the Ainu people and other East Asian people, being the descendants of settlers who did not cross the Bering Strait or settled the Japanese archipelago. Cultural history The majority of Chukchi reside within Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, but some also reside in the neighboring Sakha Republic to the west, Magadan Oblast to the southwest, and Kamchatka K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamalal People
The Chamalals are an indigenous people of Dagestan, North Caucasia living in a few villages in the Tsumadinsky District on the left bank of the Andi-Koisu river. They have their own language, Chamalal, and primarily follow Sunni Islam Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ..., which reached the Chamalal people around the 8th or 9th century. There are about 5,000 ethnic Chamalals (1999, Kubrik). They are culturally similar to the Avars. Neighboring peoples are the Godoberi, Avars, Bagvalals, and Tindis. References The peoples of the Red Book: Chamalals Ethnic groups in Dagestan Muslim communities of Russia Peoples of the Caucasus {{caucasus-ethno-group-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asian Jews
The history of the Jews in Central Asia dates back centuries, where Jews have lived in countries which include Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, Uzbekistan and Tajikistan. Kazakhstan Joseph Stalin forcibly relocated thousands of Jews from other parts of the Soviet Union to the Kazakh SSR. During the Holocaust 8,000 Jews fled to Kazakhstan. Kazakhstan's Jewish population rapidly increased between 1926 and 1959, being almost eight times larger in 1959 than in 1926. Kazakhstan's Jewish population slowly declined between 1959 and 1989, followed by a much larger decline after the fall of Communism between 1989 and 2002 due to massive Jewish emigration, mostly to Israel. Kyrgyzstan Until the 20th century, most Jews living in the Kyrgyz areas were of the Bukharan Jewish community. However, during the 20th century, large numbers of European Jews began to emigrate to Kyrgyzstan which was then part of the Soviet Union, and a small number still lives in that country. According to a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budukh People
The Budukhs ( Budukh: Будад, ''Budad'') are an ethnic group primarily from the mountainous village of Buduq in northeastern Azerbaijan, one of the Shahdagh peoples. They speak the Budukh language, which is a Northeast Caucasian language of the Lezgic branch. The Azerbaijani language is widely spoken. History The area where the Budukh inhabit was part of the Shirvanshah. The Budukh served in the military for the Shah but were given tax and tribute exemptions. In the early 18th century, the Budukh participated in a Sunni-Shia conflict taking place in Shirvan. However, the conflict soon transformed into a revolt against the Shah which also gained the attention of the Ottomans and Safavids. During the late 18th century, the Budukhs were part of the Khuba Khanate but then became incorporated into the Russian Empire in 1806. The Budukhs participated in the Murid War during the mid-19th century. In the Soviet era, the Budukh were faced with collectivization Collect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botlikh People
The Botlikh people (also known as Bótligh, Botlig, Botlog or Buikhatli) are an Andi–Dido people of Dagestan. Until the 1930s they were considered a distinct people. Since that time they have been classified as Caucasian Avars and have faced a campaign to have them assimilate into that population. The Botlikh are primarily Sunni Muslims. They numbered 3,354 people in 1926. They speak the Botlikh language, which belongs to the Northeast Caucasian language family. According to the Russian Census (2002) only 16 people in Russia declared themselves as Botlikhs (none of them in Dagestan), and 90 people declared speaking the Botlikh language. The number of speakers is higher, about 5,500, according to a survey by Koryakov in 2006. The village of Botlikh is just north of the Andi Koysu River. During the Murid War Russian forces gathered here for their final push against Shamil. During the Dagestan Uprising (1920) The Dagestan uprising of 1920-1921 was an event during the Russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |