|
Recovery Testing
In software testing, recovery testing is the activity of testing how well an application is able to recover from crashes, hardware failures and other similar problems. Recovery testing is the forced failure of the software in a variety of ways to verify that recovery is properly performed. Recovery testing should not be confused with reliability testing, which tries to discover the specific point at which failure occurs. Recovery testing is basically done in order to check how fast and better the application can recover against any type of crash or hardware failure etc. Recovery testing is simulating failure modes or actually causing failures in a controlled environment. Following a failure, the failover mechanism is tested to ensure that data is not lost or corrupted and that any agreed service levels are maintained (e.g., function availability or response times). Type or extent of recovery is specified in the requirement specifications. It is basically testing how well a system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Testing
Software testing is the act of examining the artifacts and the behavior of the software under test by validation and verification. Software testing can also provide an objective, independent view of the software to allow the business to appreciate and understand the risks of software implementation. Test techniques include, but not necessarily limited to: * analyzing the product requirements for completeness and correctness in various contexts like industry perspective, business perspective, feasibility and viability of implementation, usability, performance, security, infrastructure considerations, etc. * reviewing the product architecture and the overall design of the product * working with product developers on improvement in coding techniques, design patterns, tests that can be written as part of code based on various techniques like boundary conditions, etc. * executing a program or application with the intent of examining behavior * reviewing the deployment infrastructure a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Software
Application may refer to: Mathematics and computing * Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks ** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a communications network * Function application, in mathematics and computer science Processes and documents * Application for employment, a form or forms that an individual seeking employment must fill out * College application, the process by which prospective students apply for entry into a college or university * Patent application, a document filed at a patent office to support the grant of a patent Other uses * Application (virtue), a characteristic encapsulated in diligence * Topical application, the spreading or putting of medication to body surfaces See also * * Apply {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
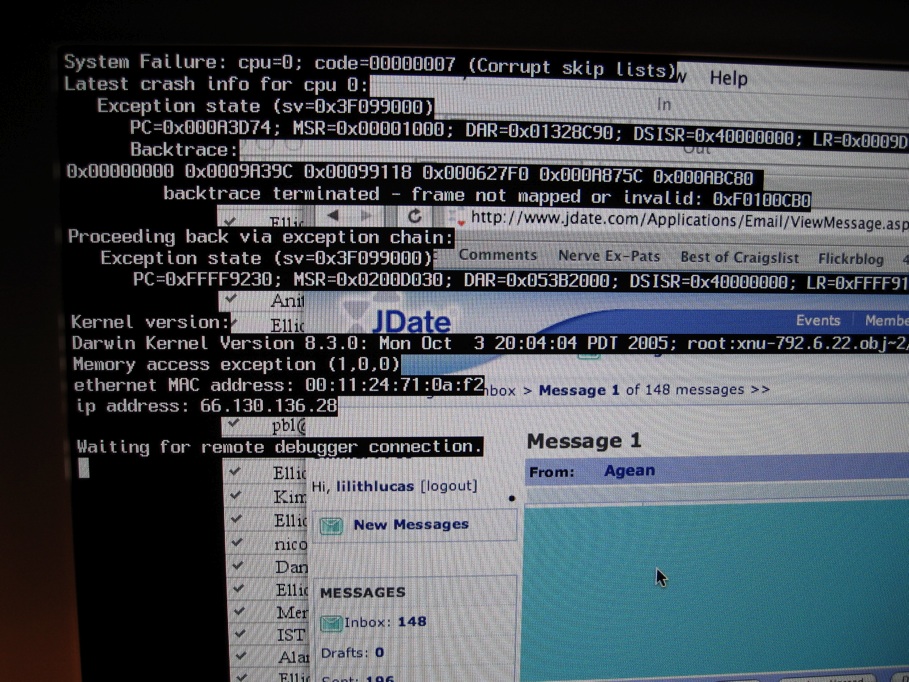
Crash (computing)
In computing, a crash, or system crash, occurs when a computer program such as a software application or an operating system stops functioning properly and exits. On some operating systems or individual applications, a crash reporting service will report the crash and any details relating to it (or give the user the option to do so), usually to the developer(s) of the application. If the program is a critical part of the operating system, the entire system may crash or hang, often resulting in a kernel panic or fatal system error. Most crashes are the result of a software bug. Typical causes include accessing invalid memory addresses, incorrect address values in the program counter, buffer overflow, overwriting a portion of the affected program code due to an earlier bug, executing invalid machine instructions (an illegal opcode), or triggering an unhandled exception. The original software bug that started this chain of events is typically considered to be the cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability Testing
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability describes the ability of a system or component to function under stated conditions for a specified period of time. Reliability is closely related to availability, which is typically described as the ability of a component or system to function at a specified moment or interval of time. The reliability function is theoretically defined as the probability of success at time t, which is denoted R(t). This probability is estimated from detailed (physics of failure) analysis, previous data sets or through reliability testing and reliability modelling. Availability, testability, maintainability and maintenance are often defined as a part of "reliability engineering" in reliability programs. Reliability often plays the key role in the cost-effectiveness of systems. Reliability engineering deals with the prediction, prevention and mana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failover
Failover is switching to a redundant or standby computer server, system, hardware component or network upon the failure or abnormal termination of the previously active application, server, system, hardware component, or network in a computer network. Failover and switchover are essentially the same operation, except that failover is automatic and usually operates without warning, while switchover requires human intervention. Systems designers usually provide failover capability in servers, systems or networks requiring near-continuous availability and a high degree of reliability. At the server level, failover automation usually uses a "heartbeat" system that connects two servers, either through using a separate cable (for example, RS-232 serial ports/cable) or a network connection. As long as a regular "pulse" or "heartbeat" continues between the main server and the second server, the second server will not bring its systems online. There may also be a third "spare parts" s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Network
A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies, based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies. The nodes of a computer network can include personal computers, servers, networking hardware, or other specialised or general-purpose hosts. They are identified by network addresses, and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes, rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the transmission medium used to carry signals, bandwidth, communications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault Injection
In computer science, fault injection is a testing technique for understanding how computing systems behave when stressed in unusual ways. This can be achieved using physical- or software-based means, or using a hybrid approach. Widely studied physical fault injections include the application of high voltages, extreme temperatures and electromagnetic pulses on electronic components, such as computer memory and central processing units. By exposing components to conditions beyond their intended operating limits, computing systems can be coerced into mis-executing instructions and corrupting critical data. In software testing, fault injection is a technique for improving the coverage of a test by introducing faults to test code paths; in particular error handling code paths, that might otherwise rarely be followed. It is often used with stress testing and is widely considered to be an important part of developing robust software. Robustness testing (also known as syntax testing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failsafe
In engineering, a fail-safe is a design feature or practice that in the event of a specific type of failure, inherently responds in a way that will cause minimal or no harm to other equipment, to the environment or to people. Unlike inherent safety to a particular hazard, a system being "fail-safe" does not mean that failure is impossible or improbable, but rather that the system's design prevents or mitigates unsafe consequences of the system's failure. That is, if and when a "fail-safe" system fails, it remains at least as safe as it was before the failure. Since many types of failure are possible, failure mode and effects analysis is used to examine failure situations and recommend safety design and procedures. Some systems can never be made fail-safe, as continuous availability is needed. Redundancy, fault tolerance, or contingency plans are used for these situations (e.g. multiple independently controlled and fuel-fed engines). Examples Mechanical or physical Examples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |