|
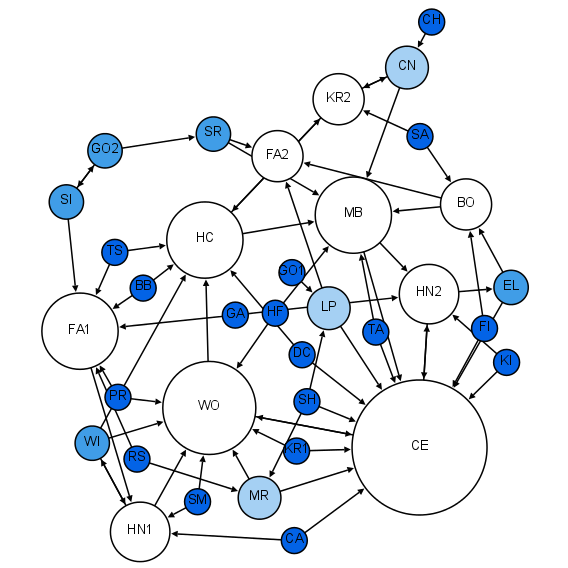
Reciprocity (network Science)
In network science, reciprocity is a measure of the likelihood of vertices in a directed network to be mutually linked. Like the clustering coefficient, scale-free degree distribution, or community structure, reciprocity is a quantitative measure used to study complex networks. Motivation In real network problems, people are interested in determining the likelihood of occurring double links (with opposite directions) between vertex pairs. This problem is fundamental for several reasons. First, in the networks that transport information or material (such as email networks, World Wide Web (WWW), World Trade Web, or Wikipedia ), mutual links facilitate the transportation process. Second, when analyzing directed networks, people often treat them as undirected ones for simplicity; therefore, the information obtained from reciprocity studies helps to estimate the error introduced when a directed network is treated as undirected (for example, when measuring the clustering coeffici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Science
Network science is an academic field which studies complex networks such as telecommunication networks, computer networks, biological networks, cognitive and semantic networks, and social networks, considering distinct elements or actors represented by ''nodes'' (or ''vertices'') and the connections between the elements or actors as ''links'' (or ''edges''). The field draws on theories and methods including graph theory from mathematics, statistical mechanics from physics, data mining and information visualization from computer science, inferential modeling from statistics, and social structure from sociology. The United States National Research Council defines network science as "the study of network representations of physical, biological, and social phenomena leading to predictive models of these phenomena." Background and history The study of networks has emerged in diverse disciplines as a means of analyzing complex relational data. The earliest known paper in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex (graph Theory)
In discrete mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a vertex (plural vertices) or node is the fundamental unit of which graphs are formed: an undirected graph consists of a set of vertices and a set of edges (unordered pairs of vertices), while a directed graph consists of a set of vertices and a set of arcs (ordered pairs of vertices). In a diagram of a graph, a vertex is usually represented by a circle with a label, and an edge is represented by a line or arrow extending from one vertex to another. From the point of view of graph theory, vertices are treated as featureless and indivisible objects, although they may have additional structure depending on the application from which the graph arises; for instance, a semantic network is a graph in which the vertices represent concepts or classes of objects. The two vertices forming an edge are said to be the endpoints of this edge, and the edge is said to be incident to the vertices. A vertex ''w'' is said to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directed Graph
In mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a directed graph (or digraph) is a graph that is made up of a set of vertices connected by directed edges, often called arcs. Definition In formal terms, a directed graph is an ordered pair where * ''V'' is a set whose elements are called '' vertices'', ''nodes'', or ''points''; * ''A'' is a set of ordered pairs of vertices, called ''arcs'', ''directed edges'' (sometimes simply ''edges'' with the corresponding set named ''E'' instead of ''A''), ''arrows'', or ''directed lines''. It differs from an ordinary or undirected graph, in that the latter is defined in terms of unordered pairs of vertices, which are usually called ''edges'', ''links'' or ''lines''. The aforementioned definition does not allow a directed graph to have multiple arrows with the same source and target nodes, but some authors consider a broader definition that allows directed graphs to have such multiple arcs (namely, they allow the arc set to be a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diego Garlaschelli
Diego is a Spanish masculine given name. The Portuguese equivalent is Diogo. The name also has several patronymic derivations, listed below. The etymology of Diego is disputed, with two major origin hypotheses: ''Tiago'' and ''Didacus''. Etymology ''Tiago'' hypothesis Diego has long been interpreted as variant of ''Tiago'' (Brazilian Portuguese: '' Thiago''), an abbreviation of ''Santiago'', from the older ''Sant Yago'' "Saint Jacob", in English known as Saint James or as ''San-Tiago''. This has been the standard interpretation of the name since at least the 19th century, as it was reported by Robert Southey in 1808 and by Apolinar Rato y Hevia (1891). The suggestion that this identification may be a folk etymology, i.e. that ''Diego'' (and ''Didacus''; see below) may be of another origin and only later identified with ''Jacobo'', is made by Buchholtz (1894), though this possibility is judged as improbable by the author himself. ''Didacus'' hypothesis In the later 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Physical Society
The American Physical Society (APS) is a not-for-profit membership organization of professionals in physics and related disciplines, comprising nearly fifty divisions, sections, and other units. Its mission is the advancement and diffusion of knowledge of physics. The society publishes more than a dozen scientific journals, including the prestigious ''Physical Review'' and '' Physical Review Letters'', and organizes more than twenty science meetings each year. APS is a member society of the American Institute of Physics. Since January 2021 the organization has been led by chief executive officer Jonathan Bagger. History The American Physical Society was founded on May 20, 1899, when thirty-six physicists gathered at Columbia University for that purpose. They proclaimed the mission of the new Society to be "to advance and diffuse the knowledge of physics", and in one way or another the APS has been at that task ever since. In the early years, virtually the sole activity of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clustering Coefficient
In graph theory, a clustering coefficient is a measure of the degree to which nodes in a graph tend to cluster together. Evidence suggests that in most real-world networks, and in particular social networks, nodes tend to create tightly knit groups characterised by a relatively high density of ties; this likelihood tends to be greater than the average probability of a tie randomly established between two nodes (Holland and Leinhardt, 1971; Watts and Strogatz, 1998). Two versions of this measure exist: the global and the local. The global version was designed to give an overall indication of the clustering in the network, whereas the local gives an indication of the embeddedness of single nodes. Local clustering coefficient The local clustering coefficient of a vertex (node) in a graph quantifies how close its neighbours are to being a clique (complete graph). Duncan J. Watts and Steven Strogatz introduced the measure in 1998 to determine whether a graph is a small-world ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scale-free Network
A scale-free network is a network whose degree distribution follows a power law, at least asymptotically. That is, the fraction ''P''(''k'') of nodes in the network having ''k'' connections to other nodes goes for large values of ''k'' as : P(k) \ \sim \ k^\boldsymbol where \gamma is a parameter whose value is typically in the range 2<\gamma<3 (wherein the second moment () of is infinite but the first moment is finite), although occasionally it may lie outside these bounds. Many networks have been reported to be scale-free, although statistical analysis has refuted many of these claims and seriously questioned others. Additionally, some have argued that simply knowing that a degree-distribution is [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degree Distribution
In the study of graphs and networks, the degree of a node in a network is the number of connections it has to other nodes and the degree distribution is the probability distribution of these degrees over the whole network. Definition The degree of a node in a network (sometimes referred to incorrectly as the connectivity) is the number of connections or edges the node has to other nodes. If a network is directed, meaning that edges point in one direction from one node to another node, then nodes have two different degrees, the in-degree, which is the number of incoming edges, and the out-degree, which is the number of outgoing edges. The degree distribution ''P''(''k'') of a network is then defined to be the fraction of nodes in the network with degree ''k''. Thus if there are ''n'' nodes in total in a network and ''n''''k'' of them have degree ''k'', we have P(k) = \frac. The same information is also sometimes presented in the form of a ''cumulative degree distribution'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Community Structure
In the study of complex networks, a network is said to have community structure if the nodes of the network can be easily grouped into (potentially overlapping) sets of nodes such that each set of nodes is densely connected internally. In the particular case of ''non-overlapping'' community finding, this implies that the network divides naturally into groups of nodes with dense connections internally and sparser connections between groups. But ''overlapping'' communities are also allowed. The more general definition is based on the principle that pairs of nodes are more likely to be connected if they are both members of the same community(ies), and less likely to be connected if they do not share communities. A related but different problem is community search, where the goal is to find a community that a certain vertex belongs to. Properties In the study of networks, such as computer and information networks, social networks and biological networks, a number of different chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Network
In the context of network theory, a complex network is a graph (network) with non-trivial topological features—features that do not occur in simple networks such as lattices or random graphs but often occur in networks representing real systems. The study of complex networks is a young and active area of scientific research (since 2000) inspired largely by empirical findings of real-world networks such as computer networks, biological networks, technological networks, brain networks, climate networks and social networks. Definition Most social, biological, and technological networks display substantial non-trivial topological features, with patterns of connection between their elements that are neither purely regular nor purely random. Such features include a heavy tail in the degree distribution, a high clustering coefficient, assortativity or disassortativity among vertices, community structure, and hierarchical structure. In the case of directed networks these fea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Likelihood
The likelihood function (often simply called the likelihood) represents the probability of random variable realizations conditional on particular values of the statistical parameters. Thus, when evaluated on a given sample, the likelihood function indicates which parameter values are more ''likely'' than others, in the sense that they would have made the observed data more probable. Consequently, the likelihood is often written as \mathcal(\theta\mid X) instead of P(X \mid \theta), to emphasize that it is to be understood as a function of the parameters \theta instead of the random variable X. In maximum likelihood estimation, the arg max of the likelihood function serves as a point estimate for \theta, while local curvature (approximated by the likelihood's Hessian matrix) indicates the estimate's precision. Meanwhile in Bayesian statistics, parameter estimates are derived from the converse of the likelihood, the so-called posterior probability, which is calculated via Bay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |