|
Recency Bias
Recency bias is a cognitive bias that favors recent events over historic ones; a memory bias. Recency bias gives "greater importance to the most recent event", such as the final lawyer's closing argument a jury hears before being dismissed to deliberate. Recency bias should not be confused with anchoring or confirmation bias. Recency bias is related to the serial-position effect known as the recency effect. It is not to be confused with recency illusion, the belief or impression that a word or language usage is of recent origin when in reality it is long-established. Occurrences It commonly appears in employee evaluations, as a distortion in favor of recently completed activities or recollections, and can be reinforced or offset by the Halo effect. In psychology, primacy bias (excessive focus on earliest events or facts) and recency bias (excessive focus on the most recent events or facts) are often considered together as primacy and recency bias. Recency bias can skew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recentism
Chronocentrism is the assumption that certain time periods (typically the present) are better, more important, or a more significant frame of reference than other time periods, either past or future. The perception of more positive attributes such as morality, technology, and sophistication to one's own time could lead an individual as a member of a collectivity to impose their forms of time on others and impede the efforts towards more homogeneous temporal commons. History Chronocentrism (from the Greek '' chrono-'' meaning "time") was coined by sociologist Jib Fowles in an article in the journal ''Futures'' in February, 1974. Fowles described chronocentrism as "the belief that one's own times are paramount, that other periods pale in comparison". A critical view described it as the belief that only the present counts and that the past is irrelevant except to serve as a reference to a few basic assumptions about what went before. More recently, it has been defined as "the egotis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rookie Of The Year (award)
Rookie of the Year may refer to: * Rookie of the Year (award), a sports award for the most outstanding rookie in a given season * ''Rookie of the Year'' (film), a 1993 film starring Thomas Ian Nicholas * ''Rookie of the Year'' (TV drama), a 1955 short film by John Ford, starring John Wayne * ''Rookie of the Year'' (album) by rapper Ya Boy * Rookie of the Year (band), an indie rock band from Fayetteville, North Carolina * "Rookie of the Year", a song from Funeral for a Friend's album '' Casually Dressed & Deep in Conversation'' * "Rookie of the Year", a song by Moneybagg Yo {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomson/Wadsworth
Cengage Group is an American educational content, technology, and services company for the higher education, K-12, professional, and library markets. It operates in more than 20 countries around the world.(Jun 27, 2014Global Publishing Leaders 2014: Cengage publishersweekly.comCompany Info - Wall Street JournalCengage LearningCompany Overview of Cengage Learning, Inc. BloombergBusiness Company information The company is headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts, and has approximately 5,000 employees worldwide across nearly 38 countries. It was headquartered at its Stamford, Connecticut, office until April 2014. |
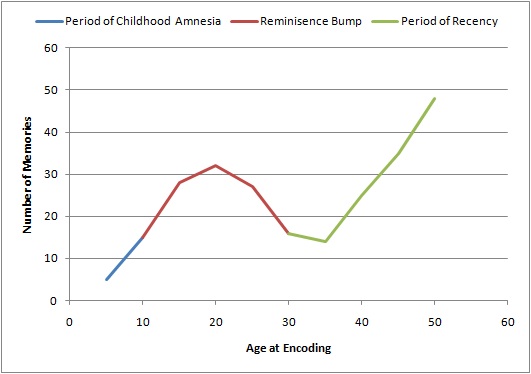
Reminiscence Bump
The reminiscence bump is the tendency for older adults (over forty) to have increased or enhanced recollection for events that occurred during their adolescence and early adulthood. It was identified through the study of autobiographical memory and the subsequent plotting of the age of encoding of memories to form the lifespan retrieval curve. The ''lifespan retrieval curve'' is a graph that represents the number of autobiographical memories encoded at various ages during the life span. The lifespan retrieval curve contains three different parts. From birth to five years old is a period of childhood amnesia, from 16 to 25 years old is the reminiscence bump and last is a period of forgetting from the end of the reminiscence bump to present time. The reminiscence bump has been observed on the lifespan retrieval curve in multiple studies. Theorists have proposed several explanations, ranging from changes in brain biology to the type of events that typically occur during this time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak End Rule
Peak or The Peak may refer to: Basic meanings Geology * Mountain peak ** Pyramidal peak, a mountaintop that has been sculpted by erosion to form a point Mathematics * Peak hour or rush hour, in traffic congestion * Peak (geometry), an (''n''-3)-dimensional element of a polytope * Peak electricity demand or peak usage * Peak-to-peak, the highest (or sometimes the highest and lowest) points on a varying waveform * Peak (pharmacology), the time at which a drug reaches its maximum plasma concentration * Peak experience, psychological term for a euphoric mental state Resource production In terms of resource production, the peak is the moment when the production of a resource reaches a maximum level, after which it declines; in particular see: * Peak oil * Peak car * Peak coal * Peak copper * Peak farmland * Peak gas * Peak gold * Peak minerals * Peak phosphorus * Peak uranium * Peak water * Peak wheat * Peak wood Other basic meanings * Visor, a part of a hat, known as a "peak" in Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principles Of Learning
Educational psychology & Educational psychologists have identified several principles of learning, also referred to as ''laws of learning'' which seem generally applicable to the learning process. These principles have been discovered, tested, and used in practical situations. They provide additional insight into what makes people learn most effectively. Edward Thorndike developed the first three "Laws of learning:" readiness, exercise and effect. Readiness Since learning is an active process, students must have adequate rest, health, and physical ability. Basic needs of students must be satisfied before they are ready or capable of learning. Students who are exhausted or in ill health cannot learn much. If they are distracted by outside responsibilities, interests, or worries, have overcrowded schedules, or other unresolved issues, students may have little interest in learning. For example, we may identify the situation of an academic examination of a school, in which the cause o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nostalgia
Nostalgia is a sentimentality for the past, typically for a period or place with happy personal associations. The word ''nostalgia'' is a learned formation of a Greek compound, consisting of (''nóstos''), meaning "homecoming", a Homeric word, and (''álgos''), meaning "sorrow" or "despair", and was coined by a 17th-century medical student to describe the anxieties displayed by Swiss mercenaries fighting away from home. Described as a medical condition—a form of melancholy—in the Early Modern period, it became an important trope in Romanticism. Nostalgia is associated with a longing for the past, its personalities, possibilities, and events, especially the " good ol' days" or a "warm childhood". There is a predisposition, caused by cognitive biases such as rosy retrospection, for people to view the past more favourably and future more negatively. When applied to one's beliefs about a society or institution, this is called declinism, which has been described as "a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cognitive Biases
Cognitive biases are systematic patterns of deviation from norm and/or rationality in judgment. They are often studied in psychology, sociology and behavioral economics. Although the reality of most of these biases is confirmed by reproducible research, there are often controversies about how to classify these biases or how to explain them. Several theoretical causes are known for some cognitive biases, which provides a classification of biases by their common generative mechanism (such as noisy information-processingMartin Hilbert (2012) "Toward a synthesis of cognitive biases: How noisy information processing can bias human decision making"'. Psychological Bulletin, 138(2), 211–237; free access to the study here: https://www.martinhilbert.net/toward-a-synthesis-of-cognitive-biases/). Gerd Gigerenzer has criticized the framing of cognitive biases as errors in judgment, and favors interpreting them as arising from rational deviations from logical thought. Explanations inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Memory Biases
Cognitive biases are systematic patterns of deviation from norm and/or rationality in judgment. They are often studied in psychology, sociology and behavioral economics. Although the reality of most of these biases is confirmed by reproducible research, there are often controversies about how to classify these biases or how to explain them. Several theoretical causes are known for some cognitive biases, which provides a classification of biases by their common generative mechanism (such as noisy information-processingMartin Hilbert (2012) "Toward a synthesis of cognitive biases: How noisy information processing can bias human decision making"'. Psychological Bulletin, 138(2), 211–237; free access to the study here: https://www.martinhilbert.net/toward-a-synthesis-of-cognitive-biases/). Gerd Gigerenzer has criticized the framing of cognitive biases as errors in judgment, and favors interpreting them as arising from rational deviations from logical thought. Explanations include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Learning Curve
A learning curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between how proficient people are at a task and the amount of experience they have. Proficiency (measured on the vertical axis) usually increases with increased experience (the horizontal axis), that is to say, the more someone, groups, companies or industries perform a task, the better their performance at the task.Compare: The common expression "a steep learning curve" is a misnomer suggesting that an activity is difficult to learn and that expending much effort does not increase proficiency by much, although a learning curve with a steep start actually represents rapid progress., see the "Discussions" section, Dr. Smith's remark about the usage of the term "steep learning curve": "First, semantics. A steep learning curve is one where you gain proficiency over a short number of trials. That means the curve is steep. I think semantically we are really talking about a prolonged or long learning curve. I know it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Primacy In Persuasion
In persuasive communication, the order of the information's presentation influences opinion formation. The law of primacy in persuasion, otherwise known as a primacy effect, as postulated by Frederick Hansen Lund in 1925 holds that the side of an issue presented first will have greater effectiveness in persuasion than the side presented subsequently. Lund presented college students with a document in support of one side of a controversial issue and then presented a second document which supported the opposite position. He found the document read first had greater influence, regardless of which position it expressed. This empirical evidence was generally accepted until 1950, when Cromwell published findings of the opposite: a recency effect in which arguments presented later had greater effectiveness in persuasion than arguments presented first. It now appears that both primacy and recency effects occur in persuasion. Theoretical background There are many different theoretical mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |