|
Rec. 2100
ITU-R Recommendation BT.2100, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 2100 or BT.2100, introduced high-dynamic-range television (HDR-TV) by recommending the use of the perceptual quantizer (PQ) or hybrid log–gamma (HLG) transfer functions instead of the traditional "gamma" previously used for SDR-TV. It defines various aspects of HDR-TV such as display resolution (HDTV and UHDTV), frame rate, chroma subsampling, bit depth, color space, color primaries, white point, and transfer function. It was posted on the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) website on July 4, 2016. Rec. 2100 uses a wide color gamut (WCG) which is the same as Rec. 2020's. Technical details Transfer functions Rec. 2100 defines two sets of HDR transfer functions which are perceptual quantization (PQ) and hybrid log-gamma (HLG). HLG is supported in Rec. 2100 with a nominal peak luminance of 1,000 cd/m2 and a system gamma value that can be adjusted depending on background lumina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-dynamic-range Video
High-dynamic-range television (HDR or HDR-TV) is a technology that improves the quality of display signals. It is contrasted with the retroactively-named standard dynamic range (SDR). HDR changes the way the luminance and colors of videos and images are represented in the signal, and allows brighter and more detailed highlight representation, darker and more-detailed shadows, and a wider array of more intense colors. HDR allows compatible displays to receive a higher quality image source. It does not improve a display's intrinsic properties (brightness, contrast, and color capabilities). Not all HDR displays have the same capabilities, and HDR content will look different depending on the display used. HDR-TV was first used in 2014 to enhance videos, and it is now also available for still pictures. HDR-TV is a part of HDR imaging, an end-to-end process of increasing the dynamic range of images and videos from their capture and creation, to their storage, distribution and displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perceptual Quantization
The perceptual quantizer (PQ), published by SMPTE as SMPTE ST 2084, is a transfer function that allows for HDR display by replacing the gamma curve used in SDR. It is capable of representing luminance level up to 10000 cd/m2 (nits) and down to 0.0001 nits. It has been developed by Dolby and standardized in 2014 by SMPTE and also in 2016 by ITU in Rec. 2100. ITU specifies the use of PQ or HLG as transfer functions for HDR-TV. PQ is the basis of HDR video formats (such as Dolby Vision, HDR10 and HDR10+) and is also used for HDR still picture formats. PQ is not backward compatible with the BT.1886 EOTF (i.e. the gamma curve of SDR), while HLG is compatible. PQ is a non-linear transfer function based on the human visual perception of banding and is able to produce no visible banding in 12 bits. A power function (used as EOTFs in standard dynamic range applications) extended to 10000 cd/m2 would have required 15 bits. Technical details The PQ EOTF (electro-optical transfer f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspect Ratio (image)
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of its width to its height, and is expressed with two numbers separated by a colon, such as ''16:9'', sixteen-to-nine. For the ''x'':''y'' aspect ratio, the image is ''x'' units wide and ''y'' units high. Common aspect ratios are 1.85:1 and 2.39:1 in cinematography, 4:3 and 16:9 in television photography, and 3:2 in still photography. Some common examples The common film aspect ratios used in cinemas are 1.85:1 and 2.39:1.The 2.39:1 ratio is commonly labeled 2.40:1, e.g., in the American Society of Cinematographers' ''American Cinematographer Manual'' (Many widescreen films before the 1970 SMPTE revision used 2.35:1). Two common videographic aspect ratios are 4:3 (1.:1), the universal video format of the 20th century, and 16:9 (1.:1), universal for high-definition television and European digital television. Other cinema and video aspect ratios exist, but are used infrequently. In still camera photography, the most common aspect ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8K Resolution
8K resolution refers to an image or display resolution with a width of approximately 8,000 pixels. 8K UHD () is the highest resolution defined in the Rec. 2020 (UHDTV) standard. 8K display resolution is the successor to 4K resolution. TV manufacturers pushed to make 4K a new standard by 2017. At CES 2019, the first 8K TVs were unveiled. The feasibility of a fast transition to this new standard is questionable in view of the absence of broadcasting resources. It is predicted (2018 forecast by Strategy Analytics) that 8K-ready devices will still only account for 3% of UHD TVs by 2023 with global sales of 11 million units a year. However, TV manufacturers remain optimistic as the 4K market grew much faster than expected, with actual sales exceeding projections nearly six-fold in 2016. In 2013, a transmission network's capability to carry HDTV resolution was limited by internet speeds and relied on satellite broadcast to transmit the high data rates. The demand is expected to dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4K Resolution
4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 38402160 (4K Ultra-high-definition television, UHD) is the dominant 4K standard, whereas the digital cinema, movie projection industry uses 40962160 (Digital Cinema Initiatives, DCI 4K). The 4K television market share increased as prices fell dramatically during 2014 and 2015. 4K standards and terminology The term "4K" is generic and refers to any resolution with a horizontal pixel count of approximately 4,000. Several different 4K resolutions have been standardized by various organizations. The terms "4K" and "Ultra HD" are used more widely in marketing than "2160p". While typically referring to motion pictures, some digital camera vendors have used the term "4K photo" for still photographs, making it appear like an especially high resolution even though 3840×2160 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
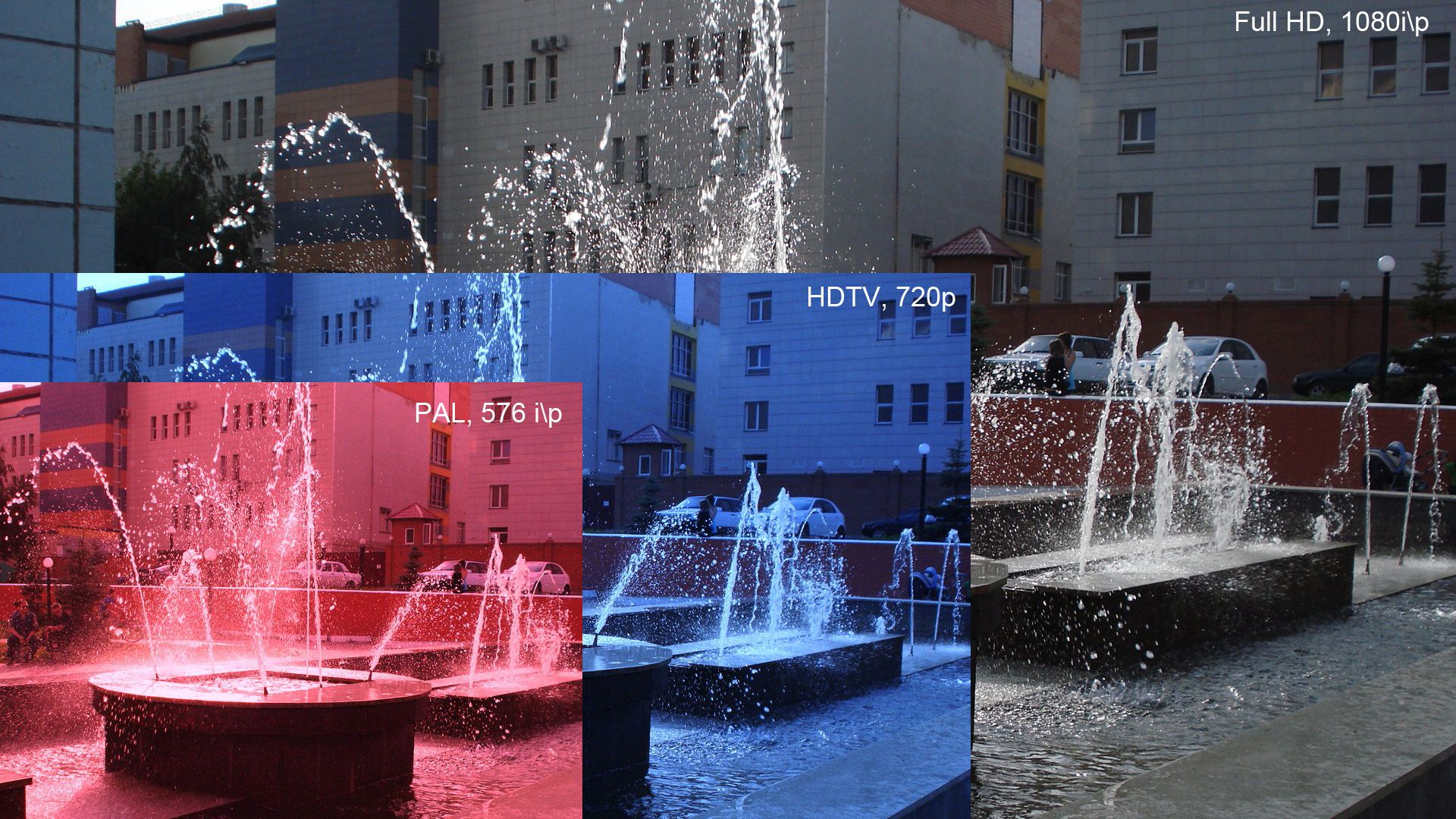
1080p
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movies, consumer-grade televisions and projector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Point
A white point (often referred to as reference white or target white in technical documents) is a set of tristimulus values or chromaticity coordinates that serve to define the color "white" in image capture, encoding, or reproduction. Depending on the application, different definitions of white are needed to give acceptable results. For example, photographs taken indoors may be lit by incandescent lights, which are relatively orange compared to daylight. Defining "white" as daylight will give unacceptable results when attempting to color-correct a photograph taken with incandescent lighting. Illuminants An illuminant is characterized by its relative spectral power distribution (SPD). The white point of an illuminant is the chromaticity of a white object under the illuminant, and can be specified by chromaticity coordinates, such as the ''x'', ''y'' coordinates on the CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram (hence the use of the relative SPD and not the absolute SPD, because the white po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital representation. A color space may be arbitrary, i.e. with physically realized colors assigned to a set of physical color swatches with corresponding assigned color names (including discrete numbers infor examplethe Pantone collection), or structured with mathematical rigor (as with the NCS System, Adobe RGB and sRGB). A "color space" is a useful conceptual tool for understanding the color capabilities of a particular device or digital file. When trying to reproduce color on another device, color spaces can show whether shadow/highlight detail and color saturation can be retained, and by how much either will be compromised. A "color model" is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers (e.g. tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wide Color Gamut
In color reproduction, including computer graphics and photography, the gamut, or color gamut , is a certain ''complete subset'' of colors. The most common usage refers to the subset of colors which can be accurately represented in a given circumstance, such as within a given color space or by a certain output device. Another sense, less frequently used but still correct, refers to the complete set of colors found within an image at a given time. In this context, digitizing a photograph, converting a digitized image to a different color space, or outputting it to a given medium using a certain output device generally alters its gamut, in the sense that some of the colors in the original are lost in the process. Introduction The term ''gamut'' was adopted from the field of music, where in middle age Latin "gamut" meant the entire range of musical notes of which musical melodies are composed; Shakespeare's use of the term in ''The Taming of the Shrew'' is sometimes attributed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
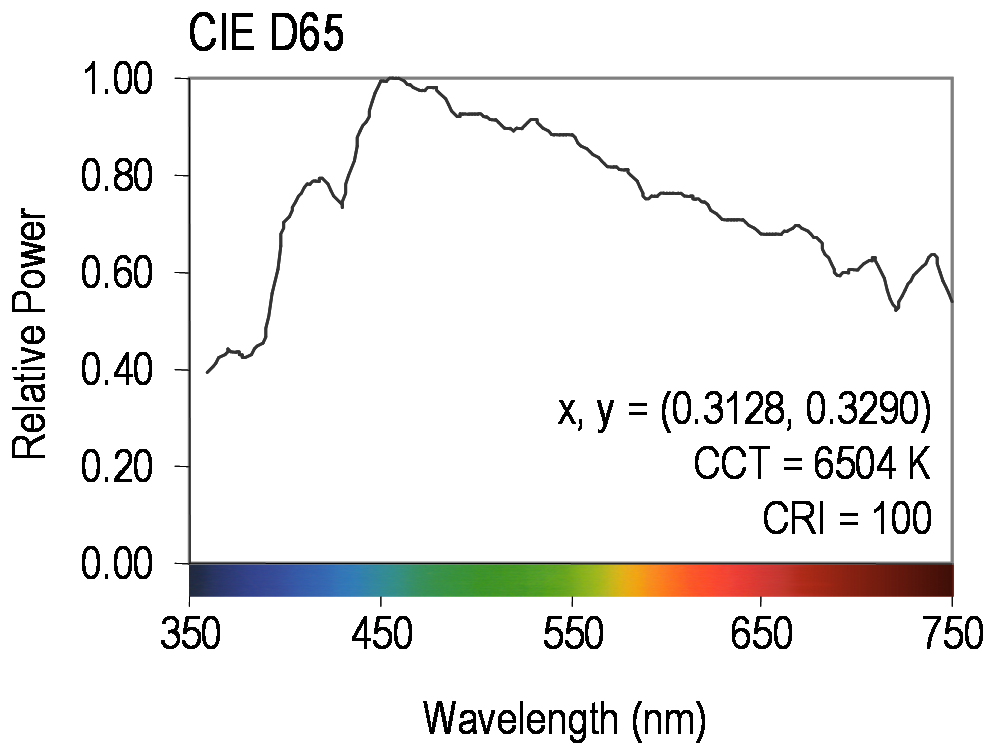
Illuminant D65
CIE standard illuminant D65 (sometimes written D65) is a commonly used standard illuminant defined by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE). It is part of the D series of illuminants that try to portray standard illumination conditions at open-air in different parts of the world. D65 corresponds roughly to the average midday light in Western Europe / Northern Europe (comprising both direct sunlight and the light diffused by a clear sky), hence it is also called a daylight illuminant. As any standard illuminant is represented as a table of averaged spectrophotometric data, any light source which statistically has the same relative spectral power distribution (SPD) can be considered a D65 light source. There are no actual D65 light sources, only simulators. The quality of a simulator can be assessed with the CIE metamerism index. The CIE positions D65 as the standard daylight illuminant: History The CIE introduced three standard illuminants in 1931: * A: Inca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Illuminant
A standard illuminant is a theoretical source of visible light with a spectral power distribution that is published. Standard illuminants provide a basis for comparing images or colors recorded under different lighting. CIE illuminants The International Commission on Illumination (usually abbreviated CIE for its French name) is the body responsible for publishing all of the well-known standard illuminants. Each of these is known by a letter or by a letter-number combination. Illuminants A, B, and C were introduced in 1931, with the intention of respectively representing average incandescent light, direct sunlight, and average daylight. Illuminants D represent variations of daylight, illuminant E is the equal-energy illuminant, while illuminants F represent fluorescent lamps of various composition. There are instructions on how to experimentally produce light sources ("standard sources") corresponding to the older illuminants. For the relatively newer ones (such as series D), exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |