|
Rebecca Langlands
Rebecca Langlands is Professor of Classics at the University of Exeter. She is known in particular for her work on the history of sexuality and ethics in the Roman world. Career Langlands studied at the University of Cambridge and wrote her PhD dissertation on Valerius Maximus at Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge funded by the British Academy and examined by Susanna Morton Braund. Langlands moved to the University of Exeter in 1998 to teach in the Department of Classics. She was awarded a grant from the Arts and Humanities Research Council for the project ''Pudicitia: Sexual Ethics in Ancient Rome'' in February–June 2003 under its Research Leave scheme. Langlands was a visiting faculty member (2014/15) at UCLA Department of Classics. She was promoted to a full Professorship at Exeter in 2017 and delivered her Inaugural Lecture, entitled 'Stories that Slice, Scald and Bounce: Why Roman Exempla Matter' on 21 January 2019. Langlands works on morality in the Roman world, st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Cambridge
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts. Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge. , established = , other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Scholars of the University of Cambridge , type = Public research university , endowment = £7.121 billion (including colleges) , budget = £2.308 billion (excluding colleges) , chancellor = The Lord Sainsbury of Turville , vice_chancellor = Anthony Freeling , students = 24,450 (2020) , undergrad = 12,850 (2020) , postgrad = 11,600 (2020) , city = Cambridge , country = England , campus_type = , sporting_affiliations = The Sporting Blue , colours = Cambridge Blue , website = , logo = University of Cambridge log ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classics
Classics or classical studies is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, classics traditionally refers to the study of Classical Greek and Roman literature and their related original languages, Ancient Greek and Latin. Classics also includes Greco-Roman philosophy, history, archaeology, anthropology, art, mythology and society as secondary subjects. In Western civilization, the study of the Greek and Roman classics was traditionally considered to be the foundation of the humanities, and has, therefore, traditionally been the cornerstone of a typical elite European education. Etymology The word ''classics'' is derived from the Latin adjective '' classicus'', meaning "belonging to the highest class of citizens." The word was originally used to describe the members of the Patricians, the highest class in ancient Rome. By the 2nd century AD the word was used in literary criticism to describe writers of the highest quality. For example, Aulus Gellius, in his ''Att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Exeter
, mottoeng = "We Follow the Light" , established = 1838 - St Luke's College1855 - Exeter School of Art1863 - Exeter School of Science 1955 - University of Exeter (received royal charter) , type = Public , endowment = £49.5 million , budget = £503.1 million , chancellor = Sir Michael Barber , vice_chancellor = Lisa Roberts , head_label = Visitor , head = Charles III '' ex officio'' , city = Exeter, Devon Penryn, Cornwall , country = England , coor = , administrative_staff = 2,647 , faculty = 3,145 (2020) , students = 23,613 (2018/19) , undergrad = 18,932 (2018/19) , postgrad = 4,681 (2018/19) , colours = Green and white , doctoral = , campus = Streatham – Penryn – St Luke's – , affiliations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valerius Maximus
Valerius Maximus () was a 1st-century Latin writer and author of a collection of historical anecdotes: '' Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX'' ("Nine books of memorable deeds and sayings", also known as ''De factis dictisque memorabilibus'' or ''Facta et dicta memorabilia''). He worked during the reign of Tiberius (14 AD to 37 AD). During the Middle Ages, Valerius Maximus was one of the most copied Latin prose authors, second only to Priscian. More than 600 medieval manuscripts of his books have survived as a result.Briscoe, ''Valerius Maximus'', p. 15. Biography Nothing is known of his life except that his family was poor and undistinguished, and that he owed everything to Sextus Pompeius (consul AD 14), proconsul of Asia, whom he accompanied to the East in 27. Pompeius was the center of a literary circle to which Ovid belonged; he was also an intimate friend of the most literary prince of the imperial family, Germanicus. Although he shared the same name as a prestigious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
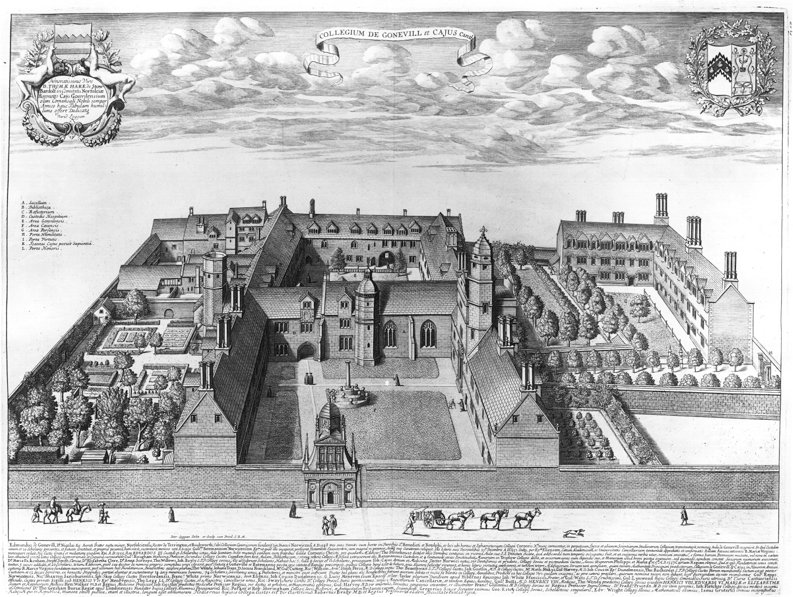
Gonville And Caius College, Cambridge
Gonville and Caius College, often referred to simply as Caius ( ), is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1348, it is the fourth-oldest of the University of Cambridge's 31 colleges and one of the wealthiest. The college has been attended by many students who have gone on to significant accomplishment, including fifteen Nobel Prize winners, the second-highest of any Oxbridge college after Trinity College, Cambridge. The college has long historical associations with the teaching of medicine, especially due to its prominent alumni in the medical profession. It also has globally-recognized and prestigious academic programmes in law, economics, English literature, and history. Famous Gonville and Caius alumni include physicians John Caius (who gave the college the caduceus in its insignia) and William Harvey. Other alumni in the sciences include Francis Crick (joint discoverer of the structure of DNA with James Watson), Jame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Academy
The British Academy is the United Kingdom's national academy for the humanities and the social sciences. It was established in 1902 and received its royal charter in the same year. It is now a fellowship of more than 1,000 leading scholars spanning all disciplines across the humanities and social sciences and a funding body for research projects across the United Kingdom. The academy is a self-governing and independent registered charity, based at 10–11 Carlton House Terrace in London. The British Academy is funded with an annual grant from the Department for Business, Innovation and Skills (BIS). In 2014–15, the British Academy's total income was £33,100,000, including £27,000,000 from BIS. £32,900,000 was distributed during the year in research grants, awards and charitable activities. Purposes The academy states that it has five fundamental purposes: * To speak up for the humanities and the social sciences * To invest in the very best researchers and research * To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arts And Humanities Research Council
The Arts and Humanities Research Council (AHRC), formerly Arts and Humanities Research Board (AHRB), is a British research council, established in 1998, supporting research and postgraduate study in the arts and humanities. History The Arts and Humanities Research Board (AHRB) was founded in 1998 and became a Research Council in April 2005. Description The AHRC is a non-departmental public body that provides approximately £102 million from the UK government to support research and postgraduate study in the arts and humanities, from languages and law, archaeology and English literature to design and creative and performing arts. In any one year, the AHRC makes approximately 700 research awards and around 1,350 postgraduate awards. Postgraduate funding is organised through Doctoral Training Partnerships in 10 consortia that bring together a total of 72 higher education institutions throughout the UK. Awards are made after a rigorous peer review process, to ensure that only ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant university and the founding campus of the University of California system. Its fourteen colleges and schools offer over 350 degree programs and enroll some 31,800 undergraduate and 13,200 graduate students. Berkeley ranks among the world's top universities. A founding member of the Association of American Universities, Berkeley hosts many leading research institutes dedicated to science, engineering, and mathematics. The university founded and maintains close relationships with three national laboratories at Berkeley, Livermore and Los Alamos, and has played a prominent role in many scientific advances, from the Manhattan Project and the discovery of 16 chemical elements to breakthroughs in computer science and genomics. Berkeley i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Classical Scholars
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Brito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women Classical Scholars
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female humans regardless of age. Typically, women inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and are capable of pregnancy and giving birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, SRY-gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. A fully developed woman generally has a wider pelvis, broader hips, and larger breasts than an adult man. Women have significantly less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less muscular than men. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alumni Of The University Of Cambridge
Alumni (singular: alumnus (masculine) or alumna (feminine)) are former students of a school, college, or university who have either attended or graduated in some fashion from the institution. The feminine plural alumnae is sometimes used for groups of women. The word is Latin and means "one who is being (or has been) nourished". The term is not synonymous with "graduate"; one can be an alumnus without graduating ( Burt Reynolds, alumnus but not graduate of Florida State, is an example). The term is sometimes used to refer to a former employee or member of an organization, contributor, or inmate. Etymology The Latin noun ''alumnus'' means "foster son" or "pupil". It is derived from PIE ''*h₂el-'' (grow, nourish), and it is a variant of the Latin verb ''alere'' "to nourish".Merriam-Webster: alumnus .. Separate, but from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
