|
Reading–Basingstoke Line
The Reading–Basingstoke line is a railway link between the South West Main Line and the Great Western Main Line, constructed by the Great Western Railway between 1846 and 1848. The line is served by GWR local services between and , stopping at the intermediate stations of , and Bramley. The line is also an important through route for longer distance passenger and freight services: CrossCountry services from Bournemouth and Southampton to Birmingham and the North of England and freight trains between the Port of Southampton and the Midlands use the line. South Western Railway weekend workings also operate between Reading and Salisbury. The northern part of the line, including Reading West station, is shared with the Reading–Taunton line, which branches off to the west at Southcote Junction in the Reading suburbs. To the north of Reading West, the line joins the Great Western Main Line with curves facing both east and west. The main line here comprises two pairs of tracks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Western Railway (train Operating Company)
Great Western Railway (GWR) is a British train operating company owned by FirstGroup that operates the Greater Western passenger railway franchise. It manages 197 stations and its trains call at over 270. GWR operates long-distance inter-city services along the Great Western Main Line to and from the West of England and South Wales, inter-city services from London to the West Country via the Reading–Taunton line, and the ''Night Riviera'' sleeper service between London and Penzance. It also provides commuter and outer-suburban services from its London terminus at Paddington to West London, the Thames Valley region including parts of Berkshire, parts of Buckinghamshire and Oxfordshire; and regional services throughout the West of England and South Wales to the South coast of England. Great Western Railway also provides and maintains the Electrostar Class 387 fleet for Heathrow Express. The company began operating in February 1996 as Great Western Trains, as part of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the West Midlands metropolitan county, and approximately 4.3 million in the wider metropolitan area. It is the largest UK metropolitan area outside of London. Birmingham is known as the second city of the United Kingdom. Located in the West Midlands region of England, approximately from London, Birmingham is considered to be the social, cultural, financial and commercial centre of the Midlands. Distinctively, Birmingham only has small rivers flowing through it, mainly the River Tame and its tributaries River Rea and River Cole – one of the closest main rivers is the Severn, approximately west of the city centre. Historically a market town in Warwickshire in the medieval period, Birmingham grew during the 18th century during the Midla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Gauge
In railway engineering, "gauge" is the transverse distance between the inner surfaces of the heads of two rails, which for the vast majority of railway lines is the number of rails in place. However, it is sometimes necessary for track to carry railway vehicles with wheels matched to two different gauges. Such track is described as dual gauge – achieved either by addition of a third rail, if it will fit, or by two additional rails. Dual-gauge tracks are more expensive to configure with signals and sidings, and to maintain, than two separate single-gauge tracks. It is therefore usual to build dual-gauge or other multi-gauge tracks only when necessitated by lack of space or when tracks of two different gauges meet in marshalling yards or passenger stations. Dual-gauge tracks are by far the most common configuration, but triple-gauge tracks have been built in some situations. Background The rail gauge is the most fundamental specification of a railway. Rail tracks and whee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad Gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways. Broad gauge of , commonly known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union (CIS states, Baltic states, Georgia and Ukraine), Mongolia and Finland. Broad gauge of , commonly known as Irish Gauge, is the dominant track gauge in Ireland, and the Australian states of Victoria and Adelaide. Broad gauge of , commonly known as Iberian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in Spain and Portugal. Broad gauge of , commonly known as Indian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Argentina, Chile, and on BART (Bay Area Rapid Transit) in the San Francisco Bay Area. This is the widest gauge in common use anywhere in the world. It is possible for trains on both Iberian gauge and Indian gauge to travel on each other's tracks with no modifications in the vast majority of cases. History In Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one of the greatest figures of the Industrial Revolution, hochanged the face of the English landscape with his groundbreaking designs and ingenious constructions." Brunel built dockyards, the Great Western Railway (GWR), a series of steamships including the first propeller-driven transatlantic steamship, and numerous important bridges and tunnels. His designs revolutionised public transport and modern engineering. Though Brunel's projects were not always successful, they often contained innovative solutions to long-standing engineering problems. During his career, Brunel achieved many engineering firsts, including assisting in the building of the first tunnel under a navigable river (the River Thames) and the development of the , the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exeter and Plymouth, and to Padstow, Ilfracombe and Bude. It developed a network of routes in Hampshire, Surrey and Berkshire, including Portsmouth and Reading. The LSWR became famous for its express passenger trains to Bournemouth and Weymouth, and to Devon and Cornwall. Nearer London it developed a dense suburban network and was pioneering in the introduction of a widespread suburban electrified passenger network. It was the prime mover of the development of Southampton Docks, which became an important ocean terminal as well as a harbour for cross channel services and for Isle of Wight ferries. Although the LSWR's area of influence was not the home of large-scale heavy industry, the transport goods and mineral traffic was a major activity, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Didcot Parkway Railway Station
Didcot Parkway is a railway station serving the town of Didcot in Oxfordshire, England. The station was opened as Didcot on 12 June 1844 and renamed Didcot Parkway on 29 July 1985 by British Rail to reflect its role as a park and ride railhead. It is down the line from and is situated between to the east and to the west. The station is served by local services operated by Great Western Railway from to Didcot and , and by main line services from Paddington to the south-west of England and south Wales. Just to the north of the station is the Didcot Railway Centre, which is accessed through the station. The centre is a comprehensive exhibition of original Great Western Railway rolling stock, with demonstration running tracks and including a reconstructed station named Didcot Halt. History The railway has run through Didcot since 1 June 1840, when the Great Western Railway extended its main line from Reading to . During this period a stagecoach transported passengers to Oxfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newbury Railway Station
Newbury railway station is located in the centre of the town of Newbury, in the English county of Berkshire. The station is from the zero point at . It is served by stopping services between and Newbury and , and by faster services between and and other parts of Devon and Cornwall. All train services at the station are operated by the Great Western Railway. The station was once a junction with the now-defunct north–south Didcot, Newbury and Southampton Railway. It was also the junction for the also defunct Lambourn Valley Railway. History Line opening Newbury station was opened on 21 December 1847 as part of the Berks and Hants Railway from Reading to Hungerford. Newbury was an important junction on the Didcot, Newbury and Southampton Railway (DN&SR), the first section of which opened between Didcot and Newbury in 1881. The route to Winchester was then opened in 1885 but it was not until 1891 that a route to Southampton was completed. However, the route did not include t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Level Crossing
A level crossing is an intersection where a railway line crosses a road, Trail, path, or (in rare situations) airport runway, at the same level, as opposed to the railway line crossing over or under using an Overpass#Railway, overpass or tunnel. The term also applies when a light rail line with separate Right-of-way (railroad), right-of-way or reserved track crosses a road in the same fashion. Other names include railway level crossing, railway crossing (chiefly international), grade crossing or railroad crossing (chiefly American), road through railroad, criss-cross, train crossing, and RXR (abbreviated). There are more than 100,000 level crossings in Europe and more than 200,000 in North America. History The history of level crossings depends on the location, but often early level crossings had a Flagman (rail), flagman in a nearby booth who would, on the approach of a train, wave a red flag or lantern to stop all traffic and clear the tracks. Gated crossings bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Track
A double-track railway usually involves running one track in each direction, compared to a single-track railway where trains in both directions share the same track. Overview In the earliest days of railways in the United Kingdom, most lines were built as double-track because of the difficulty of co-ordinating operations before the invention of the telegraph. The lines also tended to be busy enough to be beyond the capacity of a single track. In the early days the Board of Trade did not consider any single-track railway line to be complete. In the earliest days of railways in the United States most lines were built as single-track for reasons of cost, and very inefficient timetable working systems were used to prevent head-on collisions on single lines. This improved with the development of the telegraph and the train order system. Operation Handedness In any given country, rail traffic generally runs to one side of a double-track line, not always the same side a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southcote Junction
Reading West railway station serves West Reading, Berkshire, about west from the town's main retail and commercial areas. The station is served by local services operated by Great Western Railway. It is down the line the zero point at . History The line through Reading West station opened on 21 December 1847, as part of the Great Western Railway backed Berks and Hants Railway's route from to . On 1 November 1848, Berks and Hants Railway's second route to opened. The two lines merged at Southcote Junction, just south of the eventual station site, running together through that site to Reading station. Reading West station itself did not open until 1 July 1906, by which time the Berks and Hants Railway had been subsumed into the Great Western Railway. The station was originally intended to serve trains between the north of England and the south coast which could thus avoid a reversal at Reading. In 2021, work began on a new station building on Oxford Road, as well as a new en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
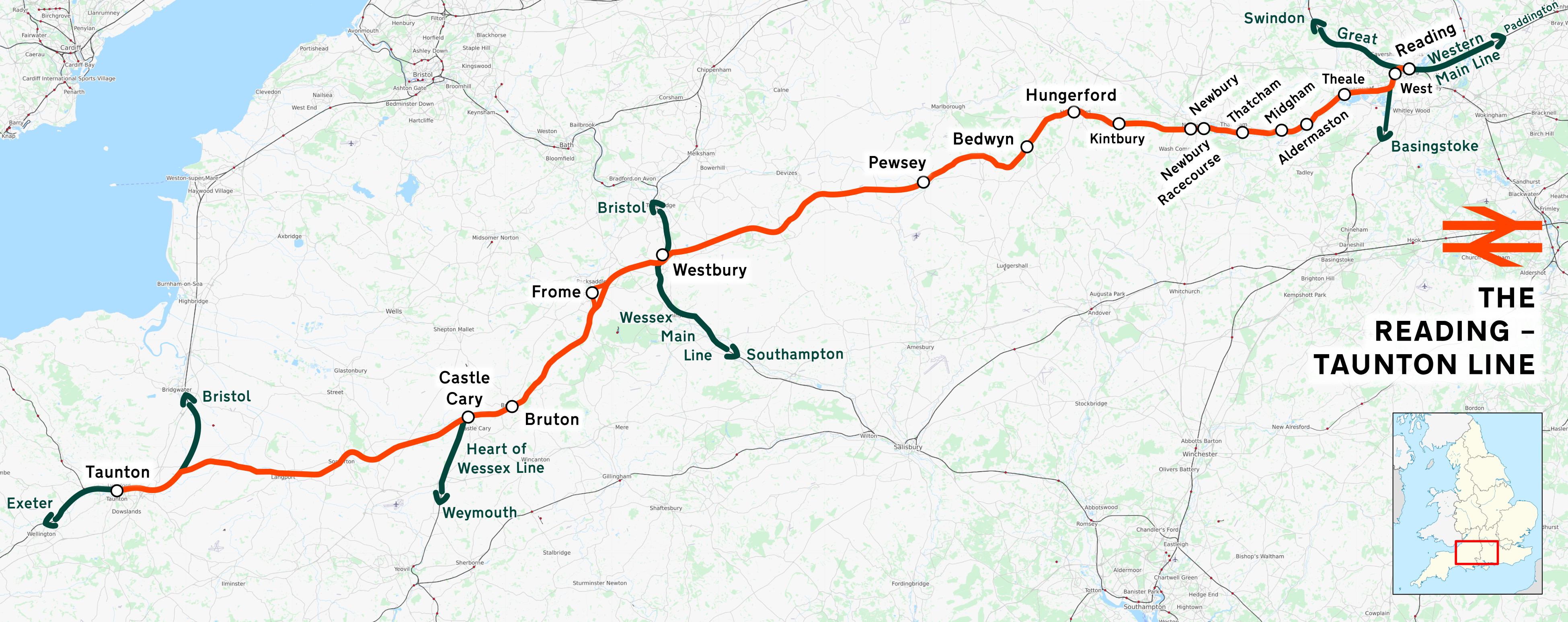
Reading–Taunton Line
The Reading–Taunton line is a major branch of the Great Western Main Line from which it diverges at Reading railway station. It runs to Cogload Junction (east of Taunton) where it joins the Bristol to Exeter line, Bristol to Exeter and Penzance line. Since 1906 it has served as the principal route from Paddington railway station, London Paddington to Devon and Cornwall, having been built by the Great Western Railway (GWR) joining up several earlier railway lines. These included the Berks and Hants Railway from Reading to and part of the Wilts, Somerset and Weymouth Railway from to . The section from Reading to Westbury is sometimes called the Berks and Hants Line. History The Great Western Railway first ran trains from London to Plymouth in 1848. These trains ran via Bristol Temple Meads railway station, Bristol. The London and South Western Railway completed the rival West of England line in 1860, which provided a more direct route from London to Exeter. The GWR's longer r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_track%2C_South_Australian_Railways.jpg)