|
Reactive Oxygen Species Production In Marine Microalgae
All living cells produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) as a byproduct of metabolism. ROS are reduced oxygen intermediates that include the superoxide radical (O2−) and the hydroxyl radical (OH•), as well as the non-radical species hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). These ROS are important in the normal functioning of cells, playing a role in signal transduction and the expression of transcription factors. However, when present in excess, ROS can cause damage to proteins, lipids and DNA by reacting with these biomolecules to modify or destroy their intended function. As an example, the occurrence of ROS have been linked to the aging process in humans, as well as several other diseases including Alzheimer's, rheumatoid arthritis, Parkinson's, and some cancers. Their potential for damage also makes reactive oxygen species useful in direct protection from invading pathogens, as a defense response to physical injury, and as a mechanism for stopping the spread of bacteria and viruses by ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Oxygen Species
In chemistry, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (). Examples of ROS include peroxides, superoxide, hydroxyl radical, singlet oxygen, and alpha-oxygen. The reduction of molecular oxygen () produces superoxide (), which is the precursor to most other reactive oxygen species: :O2 + e^- -> \ ^\bullet O2- Dismutation of superoxide produces hydrogen peroxide (): :2 H+ + \ ^\bullet O2^- + \ ^\bullet O2^- -> H2O2 + O2 Hydrogen peroxide in turn may be partially reduced, thus forming hydroxide ions and hydroxyl radicals (), or fully reduced to water: :H2O2 + e^- -> HO^- + \ ^\bullet OH :2 H+ + 2 e- + H2O2 -> 2 H2O In a biological context, ROS are byproducts of the normal metabolism of oxygen. ROS have roles in cell signaling and homeostasis. ROS are intrinsic to cellular functioning, and are present at low and stationary levels in normal cells. In plants, ROS are involved in metabolic processes related to photoprotection and toleran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name ''photosynthesis'', from the Greek ''phōs'' (), "light", and ''synthesis'' (), "putting together". Most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies most of the energy necessary for life on Earth. Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centers that contain green chlorophyll (and other colored) pigments/chromoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
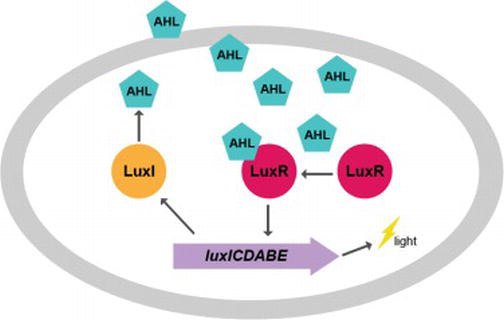
Vibrio Fischeri
''Aliivibrio fischeri'' (also called ''Vibrio fischeri'') is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium found globally in marine environments. This species has bioluminescent properties, and is found predominantly in symbiosis with various marine animals, such as the Hawaiian bobtail squid. It is heterotrophic, oxidase-positive, and motile by means of a single polar flagella. Free-living ''A. fischeri'' cells survive on decaying organic matter. The bacterium is a key research organism for examination of microbial bioluminescence, quorum sensing, and bacterial-animal symbiosis. It is named after Bernhard Fischer, a German microbiologist. Ribosomal RNA comparison led to the reclassification of this species from genus ''Vibrio'' to the newly created ''Aliivibrio'' in 2007. However, the name change is not generally accepted by most researchers, who still publish ''Vibrio fischeri'' (see Google Scholar for 2018-2019). Genome The genome for ''A. fischeri'' was completely sequenced in 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrio Alginolyticus
''Vibrio alginolyticus'' is a Gram-negative marine bacterium. It is medically important since it causes otitis and wound infection. It is also present in the bodies of animals such as pufferfish, where it is responsible for the production of the potent neurotoxin, tetrodotoxin. ''Vibrio alginolyticus'' are commonly found in aquatic environments. Some strains of ''V. alginolyticus'' are highly salt tolerant and commonly found in marine environment. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and identified many strains of ''Vibrio alginolyticus'' from nine marine sponges of the Saint Martin's Island Area of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos .... ''V. alginolyticus'' was first identified as a pathogen of humans in 1973.Longo, Dan, et al. Harriso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chattonella Marina
''Chattonella'' is a genus of marine raphidophytes associated with red tides. A technique using monoclonal antibodies can be used to identify the genus, while the RAPD reaction can be used to distinguish between different species within the genus. It includes the species ''Chattonella antiqua'', a bloom forming alga responsible for large scale fish deaths due to the synthesis of toxic compounds related to brevetoxin Brevetoxin (PbTx), or brevetoxins, are a suite of cyclic polyether compounds produced naturally by a species of dinoflagellate known as '' Karenia brevis''. Brevetoxins are neurotoxins that bind to voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve cells, le .... References Heterokont genera Ochrophyta {{Heterokont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chattonella Antiqua
''Chattonella'' is a genus of marine raphidophytes associated with red tides. A technique using monoclonal antibodies can be used to identify the genus, while the RAPD reaction can be used to distinguish between different species within the genus. It includes the species ''Chattonella antiqua'', a bloom forming alga responsible for large scale fish deaths due to the synthesis of toxic compounds related to brevetoxin Brevetoxin (PbTx), or brevetoxins, are a suite of cyclic polyether compounds produced naturally by a species of dinoflagellate known as '' Karenia brevis''. Brevetoxins are neurotoxins that bind to voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve cells, le .... References Heterokont genera Ochrophyta {{Heterokont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterosigma Akashiwo
''Heterosigma akashiwo'' is a species of microscopic algae of the class Raphidophyceae. It is a swimming marine alga that episodically forms toxic surface aggregations known as harmful algal bloom. The species name ''akashiwo'' is from the Japanese for "red tide". Synonyms include ''Olisthodiscus luteus'' (Hulburt 1965), and ''Entomosigma akashiwo'' (Hada 1967). ''H. akashiwo'' and ''H. inlandica'' have been recognized as two species of ''Heterosigma''. However, Hara and Chihara (1987) described both specimens as one species, validly describing them as ''H. akashiwo''. Description ''H. akashiwo'' cells are relatively small, ranging in size from 18 to 34 μm in diameter. They appear golden brown, and appear in clusters. Morphology is highly variable, but does not appear to vary significantly between locations. One culture may contain flat or round individual cells. Molecular techniques for identification (including quantitative PCR) are preferred over traditional mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haber–Weiss Reaction
The Haber–Weiss reaction generates •OH (hydroxyl radicals) from H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) and superoxide (•O2−) catalyzed by iron ions. It was first proposed by Fritz Haber and his student Joseph Joshua Weiss in 1932. This reaction has long been studied and revived in different contexts, including organic chemistry, free radicals, radiochemistry, and water radiolysis. In the 1970, with the emerging interest for the effect of free radicals onto the ageing mechanisms of living cells due to oxygen (O2), it was proposed that the Haber–Weiss reaction was a source of radicals responsible for cellular oxidative stress. However, this hypothesis was later disproved by several research works. The oxidative stress toxicity is not caused by the Haber–Weiss reaction as a whole, but by the Fenton reaction, which is one specific part of it. The reaction is kinetically slow, but is catalyzed by dissolved iron ions. The first step of the catalytic cycle involves the reduction of the fer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superoxide Dismutase
Superoxide dismutase (SOD, ) is an enzyme that alternately catalyzes the dismutation (or partitioning) of the superoxide () radical into ordinary molecular oxygen (O2) and hydrogen peroxide (). Superoxide is produced as a by-product of oxygen metabolism and, if not regulated, causes many types of cell damage. Hydrogen peroxide is also damaging and is degraded by other enzymes such as catalase. Thus, SOD is an important antioxidant defense in nearly all living cells exposed to oxygen. One exception is ''Lactobacillus plantarum'' and related lactobacilli, which use a different mechanism to prevent damage from reactive . Chemical reaction SODs catalyze the disproportionation of superoxide: : 2 HO2 → O2 + H2O2 In this way, is converted into two less damaging species. The pathway by which SOD-catalyzed dismutation of superoxide may be written, for Cu,Zn SOD, with the following reactions: * Cu2+-SOD + → Cu+-SOD + O2 (reduction of copper; oxidation of superoxide) * Cu+-S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superoxide
In chemistry, a superoxide is a compound that contains the superoxide ion, which has the chemical formula . The systematic name of the anion is dioxide(1−). The reactive oxygen ion superoxide is particularly important as the product of the one-electron reduction of dioxygen , which occurs widely in nature. Molecular oxygen (dioxygen) is a diradical containing two unpaired electrons, and superoxide results from the addition of an electron which fills one of the two degenerate molecular orbitals, leaving a charged ionic species with a single unpaired electron and a net negative charge of −1. Both dioxygen and the superoxide anion are free radicals that exhibit paramagnetism. Superoxide was historically also known as "hyperoxide". Salts Superoxide forms salts with alkali metals and alkaline earth metals. The salts caesium superoxide (), rubidium superoxide (), potassium superoxide (), and sodium superoxide () are prepared by the reaction of with the respective alkali me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disproportionation
In chemistry, disproportionation, sometimes called dismutation, is a redox reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation states. More generally, the term can be applied to any desymmetrizing reaction of the following type, regardless of whether it is a redox or some other type of process: :2A -> A' + A'' Examples *Mercury(I) chloride disproportionates upon UV-irradiation: :Hg2Cl2 → Hg + HgCl2 *Phosphorous acid disproportionates upon heating to give phosphoric acid and phosphine: :4 → 3 H3PO4 + PH3 *Desymmetrizing reactions are sometimes referred to as disproportionation, as illustrated by the thermal degradation of bicarbonate: :2 → + H2CO3 :The oxidation numbers remain constant in this acid-base reaction. This process is also called autoionization. *Another variant on disproportionation is radical disproportionation, in which two radicals form an alkene and an alkane. : Reverse r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |