|
Ray–Dutt Twist
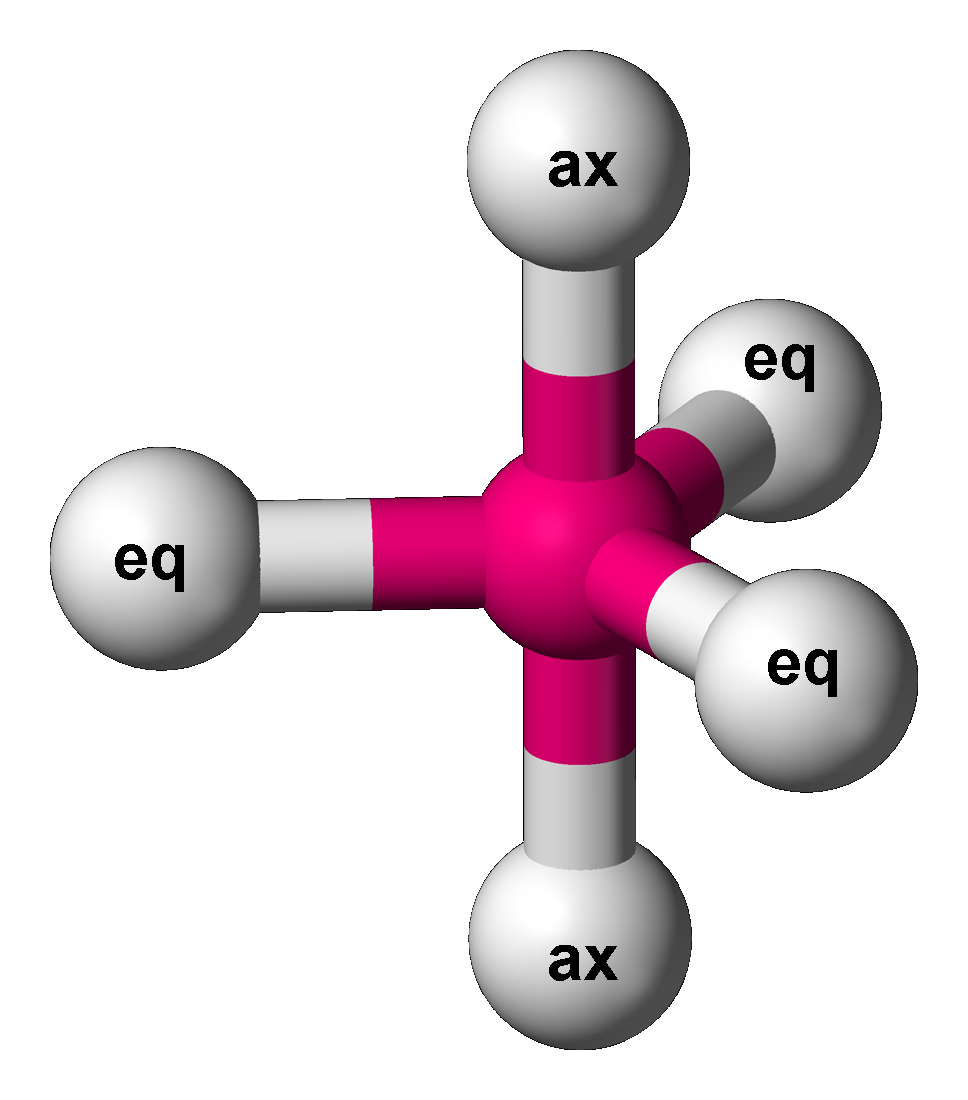
The Ray–Dutt twist is a mechanism proposed for the racemization of octahedral complexes containing three bidentate chelate rings. Such complexes typically adopt an octahedral molecular geometry in their ground states, in which case they possess helical chirality. The pathway entails formation of an intermediate of C2v point group symmetry. An alternative pathway that also does not break any metal-ligand bonds is called the Bailar twist. Both of these mechanism product complexes wherein the ligating atoms (X in the scheme) are arranged in an approximate trigonal prism. This pathway is called the Ray–Dutt twist in honor of Priyadaranjan Ray (not Prafulla Chandra Ray) and N. K. Dutt, inorganic chemists at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science abbr. ''IACS'' who proposed this process. See also * Pseudorotation * Bailar twist * Bartell mechanism * Berry mechanism The Berry mechanism, or Berry pseudorotation mechanism, is a type of vibration causing mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racemization
In chemistry, racemization is a conversion, by heat or by chemical reaction, of an optically active compound into a racemic (optically inactive) form. This creates a 1:1 molar ratio of enantiomers and is referred too as a racemic mixture (i.e. contain equal amount of (+) and (−) forms). Plus and minus forms are called Dextrorotation and levorotation. The D and L enantiomers are present in equal quantities, the resulting sample is described as a racemic mixture or a racemate. Racemization can proceed through a number of different mechanisms, and it has particular significance in pharmacology as different enantiomers may have different pharmaceutical effects. Stereochemistry Chiral molecules have two forms (at each point of asymmetry), which differ in their optical characteristics: The ''levorotatory form'' (the ''(−)-form'') will rotate counter-clockwise on the plane of polarization of a beam of light, whereas the ''dextrorotatory'' form (the ''(+)-form'') will rotate clock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Association For The Cultivation Of Science
Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS) is a public, deemed, research university for higher education and research in basic sciences under the Department of Science & Technology, Government of India, situated at the heart of the Cultural capital of India. Established in 1876 by Mahendralal Sarkar, a private medical practitioner, it focuses on fundamental research in basic sciences. It is Asia's oldest research institute Located at Jadavpur, South Kolkata near Jadavpur University, Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute and Indian Institute of Chemical Biology. It is spread over a limited area of 9.5 acres and currently in the process of building a super-advanced SMART campus at Baruipur. The association is engaged in research in various fields of physics, chemistry, biological sciences, mathematical and computational sciences, materials sciences and various interdisciplinary areas. Indian Journal of Physics (IJP) ''Indian Journal of Physics'' w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional space, three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom. Molecular geometry influences several properties of a substance including its Reactivity (chemistry), reactivity, Chemical polarity, polarity, Phase (matter), phase of matter, color, magnetism and biological activity. The angles between bonds that an atom forms depend only weakly on the rest of molecule, i.e. they can be understood as approximately local and hence Transferability (chemistry), transferable properties. Determination The molecular geometry can be determined by various spectroscopy, spectroscopic methods and diffraction methods. Infrared spectroscopy, IR, Rotational spectroscopy, microwave and Raman spectroscopy can give information about the molecule geometry from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluxional Molecule
In chemistry and molecular physics, fluxional (or non-rigid) molecules are molecules that undergo dynamics such that some or all of their atoms interchange between symmetry-equivalent positions. Because virtually all molecules are fluxional in some respects, e.g. bond rotations in most organic compounds, the term fluxional depends on the context and the method used to assess the dynamics. Often, a molecule is considered fluxional if its spectroscopic signature exhibits line-broadening (beyond that dictated by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle) due to chemical exchange. In some cases, where the rates are slow, fluxionality is not detected spectroscopically, but by isotopic labeling and other methods. Spectroscopic studies Many organometallic compounds exhibit fluxionality. Fluxionality is however pervasive. NMR spectroscopy Temperature dependent changes in the NMR spectra result from dynamics associated with the fluxional molecules when those dynamics proceed at rates compara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berry Mechanism
The Berry mechanism, or Berry pseudorotation mechanism, is a type of vibration causing molecules of certain geometries to isomerize by exchanging the two axial ligands (see Figure at right) for two of the equatorial ones. It is the most widely accepted mechanism for pseudorotation and most commonly occurs in trigonal bipyramidal molecules such as PF5, though it can also occur in molecules with a square pyramidal geometry. The Berry mechanism is named after R. Stephen Berry Richard Stephen Berry (April 9, 1931 – July 26, 2020) was an American professor of physical chemistry. He was the James Franck Distinguished Service Professor Emeritus at The University of Chicago. He was also Special Advisor for National Sec ..., who first described this mechanism in 1960.RS Berry, 1960, "Correlation of rates of intramolecular tunneling processes, with application to some Group V compounds," ''J. Chem. Phys.'' 32:933-938, DOI 10.1063/1.1730820; seo accessed 28 May 2014M Cass, KK Hii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartell Mechanism
The Bartell mechanism is a pseudorotational mechanism similar to the Berry mechanism. It occurs only in molecules with a pentagonal bipyramidal molecular geometry, such as IF7. This mechanism was first predicted by H. B. Bartell. The mechanism exchanges the axial atoms with one pair of the equatorial atoms with an energy requirement of about 2.7 kcal/mol. Similarly to the Berry mechanism in square planar molecules, the symmetry of the intermediary phase of the vibrational mode is "chimeric"LS Bartell, MJ Rothman & A Gavezzotti, 1982, , ''J. Chem. Phys.'' 76:4136-4413.M Cass, KK Hii & HS Rzepa, 2005, "Mechanisms that interchange axial and equatorial atoms in fluxional processes: Illustration of the Berry pseudorotation, the turnstile and the lever mechanisms via animation of transition state normal vibrational modes", ''J. Chem. Educ.'' (online), 2005; se, accessed 28 May 2014 of other mechanisms; it displays characteristics of the Berry mechanism, a "lever" mechanism seen in pseudo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudorotation
In chemistry, a pseudorotation is a set of intramolecular movements of attached groups (i.e., ligands) on a highly symmetric molecule, leading to a molecule indistinguishable from the initial one. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry ( IUPAC) defines a pseudorotation as a " ereoisomerization resulting in a structure that ''appears'' to have been produced by rotation of the entire initial molecule", the result of which is a "product" that is "superposable on the initial one, unless different positions are distinguished by substitution, including isotopic substitution." Well-known examples are the intramolecular isomerization of trigonal bipyramidal compounds by the Berry pseudorotation mechanism, and the out-of-plane motions of carbon atoms exhibited by cyclopentane, leading to the interconversions it experiences between its many possible conformers (envelope, twist). Note, no angular momentum is generated by this motion. In these and related examples, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Chemistry
Inorganic chemistry deals with synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, as there is much overlap in the subdiscipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry, including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medications, fuels, and agriculture. Key concepts Many inorganic compounds are ionic compounds, consisting of cations and anions joined by ionic bonding. Examples of salts (which are ionic compounds) are magnesium chloride MgCl2, which consists of magnesium cations Mg2+ and chloride anions Cl−; or sodium oxide Na2O, which consists of sodium cations Na+ and oxide anions O2−. In any salt, the proportions of the ions are such that the electric charges cancel out, so that the bulk compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedral Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry, also called square bipyramidal, describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron. The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix ''octa''. The octahedron is one of the Platonic solids, although octahedral molecules typically have an atom in their centre and no bonds between the ligand atoms. A perfect octahedron belongs to the point group Oh. Examples of octahedral compounds are sulfur hexafluoride SF6 and molybdenum hexacarbonyl Mo(CO)6. The term "octahedral" is used somewhat loosely by chemists, focusing on the geometry of the bonds to the central atom and not considering differences among the ligands themselves. For example, , which is not octahedral in the mathematical sense due to the orientation of the bonds, is referred to as octahedral. The concept of octahedral coordination geometry was developed by Alfred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prafulla Chandra Ray
Sir Prafulla Chandra Ray, CIE, FNI, FRASB, FIAS, FCS (also spelled Prafulla Chandra Rây and Prafulla Chandra Roy; bn, প্রফুল্ল চন্দ্র রায় ''Praphulla Chandra Rāy''; 2 August 1861 – 16 June 1944) was an eminent Indian chemist, educationist, historian, industrialist and philanthropist. He established the first modern Indian research school in chemistry (post classical age) and is regarded as the father of chemical science in India. The Royal Society of Chemistry honoured his life and work with the first ever Chemical Landmark Plaque outside Europe. He was the founder of Bengal Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals, India's first pharmaceutical company. He is the author of '' A History of Hindu Chemistry from the Earliest Times to the Middle of the Sixteenth Century'' (1902). Biography Family background Prafulla Chandra Ray was born in the village of Raruli-Katipara, then in Jessore District (subsequently in Khulna District), in the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priyadaranjan Ray
Priyadaranjan Ray FNA, FIAS (16 January 1888 – 11 December 1982) was an Indian inorganic chemist and historian of chemistry noted for proposing the Ray-Dutt twist mechanism. Life and career Ray was born in Chittagong District, Bengal Presidency (now in Bangladesh) to a ''zamindari'' family originally from Hooghly district (now in West Bengal), which had first migrated to the princely state of Tripura in the late 17th century, and had subsequently entered the service of the Nawabs of Bengal. The family were granted the estate of Noapara in the early 18th century by Nawab Murshid Quli Khan, the first Nawab of Bengal. After matriculating with distinction from the Chittagong Collegiate School in 1904, Ray secured a scholarship to Chittagong Government College and in 1906 joined Presidency College Calcutta as an undergraduate. He secured an honours degree in chemistry and physics in 1908, and then studied under Prafulla Chandra Ray for his master's degree, which he secured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)