|
Raytheon 704
The Raytheon 704 is a 16-bit minicomputer introduced by Raytheon in 1970. The basic machine contained 4 Word (computer architecture), kwords (8 kB) of memory and a simple arithmetic logic unit (ALU) running at 1 MHz. It was normally operated with a Teletype Model 33 acting as a computer terminal. It sold for "less than $10,000" (). A key feature of the design was the ability to expand the central processing unit (CPU) using plug-in cards. Options included a hardware multiply/divide unit, an 8-level vectored interrupt controller, a DMA controller, among others. Memory could also be added using the same cards, allowing up to 32 kW in total. Memory was based on an 18-bit word, not 16-bit, with the extra bits for use with an optional parity check card. Another unique feature was that general input/output expansion was external, using a Daisy chain (electrical engineering), daisy chained cable system known as DIO. This allowed devices like lab equipment and low-spee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Datamation
''Datamation'' is a computer magazine that was published in print form in the United States between 1957 and 1998,Venerable IS Journal Shuts Down Sharon Machlis // ComputerWorld, page 15, 19 January 1998 and has since continued publication on the web. ''Datamation'' was previously owned by and acquired by TechnologyAdvice in 2020. Datamation is published as an online magazine at Datamation.com. History and profile When ''Datamation'' was first launched in 1957, it was not clear there would be a significant market for a computer magazine given how few |
Play-by-mail Game
A play-by-mail game (also known as a PBM game, PBEM game, or a turn-based game) is a game played through postal mail, email or other digital media. Correspondence chess and Go were among the first PBM games. ''Diplomacy'' has been played by mail since 1963, introducing a multi-player aspect to PBM games. Flying Buffalo Inc. pioneered the first commercially available PBM game in 1970. A small number of PBM companies followed in the 1970s, with an explosion of hundreds of startup PBM companies in the 1980s at the peak of PBM gaming popularity, many of them small hobby companies—more than 90 percent of which eventually folded. A number of independent PBM magazines also started in the 1980s, including '' The Nuts & Bolts of PBM'', '' Gaming Universal'', ''Paper Mayhem'' and '' Flagship''. These magazines eventually went out of print, replaced in the 21st century by the online PBM journal '' Suspense and Decision''. Play-by-mail games—becoming known as "turn-based games" in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expansion Card
In computing, an expansion card (also called an expansion board, adapter card, peripheral card or accessory card) is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot (also referred to as a bus slot) on a computer's motherboard (see also backplane) to add functionality to a computer system. Sometimes the design of the computer's case and motherboard involves placing most (or all) of these slots onto a separate, removable card. Typically such cards are referred to as a riser card in part because they project upward from the board and allow expansion cards to be placed above and parallel to the motherboard. Expansion cards allow the capabilities and interfaces of a computer system to be extended or supplemented in a way appropriate to the tasks it will perform. For example, a high-speed multi-channel data acquisition system would be of no use in a personal computer used for bookkeeping, but might be a key part of a system used for ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Termination
In electronics, electrical termination is the practice of ending a transmission line with a device that matches the characteristic impedance of the line. Termination prevents signals from reflecting off the end of the transmission line. Reflections at the ends of unterminated transmission lines cause distortion which can produce ambiguous digital signal levels and mis-operation of digital systems. Reflections in analog signal systems cause such effects as video ghosting, or power loss in radio transmitter transmission lines. Transmission lines Signal termination often requires the installation of a terminator at the beginning and end of a wire or cable to prevent an RF signal from being reflected back from each end, causing interference, or power loss. The terminator is usually placed at the end of a transmission line or daisy chain bus (such as in SCSI), and is designed to match the AC impedance of the cable and hence minimize signal reflections, and power losses. Less com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Memory
Computer data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers. The central processing unit (CPU) of a computer is what manipulates data by performing computations. In practice, almost all computers use a storage hierarchy, which puts fast but expensive and small storage options close to the CPU and slower but less expensive and larger options further away. Generally, the fast volatile technologies (which lose data when off power) are referred to as "memory", while slower persistent technologies are referred to as "storage". Even the first computer designs, Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine and Percy Ludgate's Analytical Machine, clearly distinguished between processing and memory (Babbage stored numbers as rotations of gears, while Ludgate stored numbers as displacements of rods in shuttles). This distinction was extended in the Von Neumann arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two's Complement
Two's complement is a mathematical operation to reversibly convert a positive binary number into a negative binary number with equivalent (but negative) value, using the binary digit with the greatest place value (the leftmost bit in big- endian numbers, rightmost bit in little-endian numbers) to indicate whether the binary number is positive or negative (the sign). It is used in computer science as the most common method of representing signed (positive, negative, and zero) integers on computers, and more generally, fixed point binary values. When the most significant bit is a one, the number is signed as negative. . Two's complement is executed by 1) inverting (i.e. flipping) all bits, then 2) adding a place value of 1 to the inverted number. For example, say the number −6 is of interest. +6 in binary is 0110 (the leftmost most significant bit is needed for the sign; positive 6 is not 110 because it would be interpreted as -2). Step one is to flip all bits, yielding 1001. St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASCII
ASCII ( ), abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because of technical limitations of computer systems at the time it was invented, ASCII has just 128 code points, of which only 95 are , which severely limited its scope. All modern computer systems instead use Unicode, which has millions of code points, but the first 128 of these are the same as the ASCII set. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) prefers the name US-ASCII for this character encoding. ASCII is one of the List of IEEE milestones, IEEE milestones. Overview ASCII was developed from telegraph code. Its first commercial use was as a seven-bit teleprinter code promoted by Bell data services. Work on the ASCII standard began in May 1961, with the first meeting of the American Standards Association's (ASA) (now the American Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rack Mount
A 19-inch rack is a standardized frame or enclosure for mounting multiple electronic equipment modules. Each module has a front panel that is wide. The 19 inch dimension includes the edges or "ears" that protrude from each side of the equipment, allowing the module to be fastened to the rack frame with screws or bolts. Common uses include computer servers, telecommunications equipment and networking hardware, audiovisual production gear, and scientific equipment. Overview and history Equipment designed to be placed in a rack is typically described as rack-mount, rack-mount instrument, a rack-mounted system, a rack-mount chassis, subrack, rack cabinet, rack-mountable, or occasionally simply shelf. The height of the electronic modules is also standardized as multiples of or one rack unit or U (less commonly RU). The industry-standard rack cabinet is 42U tall; however, 45U racks are also common. The term ''relay rack'' appeared first in the world of telephony. By 1911, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raytheon 704 Rechner (16758021979)
Raytheon Technologies Corporation is an American multinational aerospace and defense conglomerate headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. It is one of the largest aerospace and defense manufacturers in the world by revenue and market capitalization. In addition, it is one of the largest providers of intelligence services. Raytheon Technologies manufactures aircraft engines, avionics, aerostructures, cybersecurity, guided missiles, air defense systems, satellites, and drones. The company is also a large military contractor, getting a significant portion of its revenue from the U.S. government. The company is the result of the merger of equals between the aerospace subsidiaries of United Technologies Corporation (UTC) and the Raytheon Company, which was completed on April 3, 2020. Before the merger, UTC spun off its non-aerospace subsidiaries Otis Elevator Company and Carrier Corporation. UTC is the nominal survivor of the merger but it changed its name to Raytheon Techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data General Nova
The Data General Nova is a series of 16-bit minicomputers released by the American company Data General. The Nova family was very popular in the 1970s and ultimately sold tens of thousands of units. The first model, known simply as "Nova", was released in 1969. The Nova was packaged into a single 3U rack-mount case and had enough computing power to handle most simple tasks. The Nova became popular in science laboratories around the world. It was followed the next year by the SuperNOVA, which ran roughly four times as fast. Introduced during a period of rapid progress in integrated circuit (or "microchip") design, the line went through several upgrades over the next five years, introducing the 800 and 1200, the Nova 2, Nova 3, and ultimately the Nova 4. A single-chip implementation was also introduced as the microNOVA in 1977, but did not see widespread use as the market moved to new microprocessor designs. Fairchild Semiconductor also introduced a microprocessor version of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HP 2100
The HP 2100 is a series of 16-bit minicomputers that were produced by Hewlett-Packard (HP) from the mid-1960s to early 1990s. Tens of thousands of machines in the series were sold over its twenty-five year lifetime, making HP the fourth largest minicomputer vendor during the 1970s. The design started at Data Systems Inc (DSI), and was originally known as the DSI-1000. HP purchased the company in 1964 and merged it into their Dymec division. The original model, the 2116A built using integrated circuits and magnetic-core memory, was released in 1966. Over the next four years, models A through C were released with different types of memory and expansion, as well as the cost-reduced 2115 and 2114 models. All of these models were replaced by the HP 2100 series in 1971, and then again as the 21MX series in 1974 when the magnetic-core memory was replaced with semiconductor memory. All of these models were also packaged as the HP 2000 series, combining a 2100-series machine with optional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
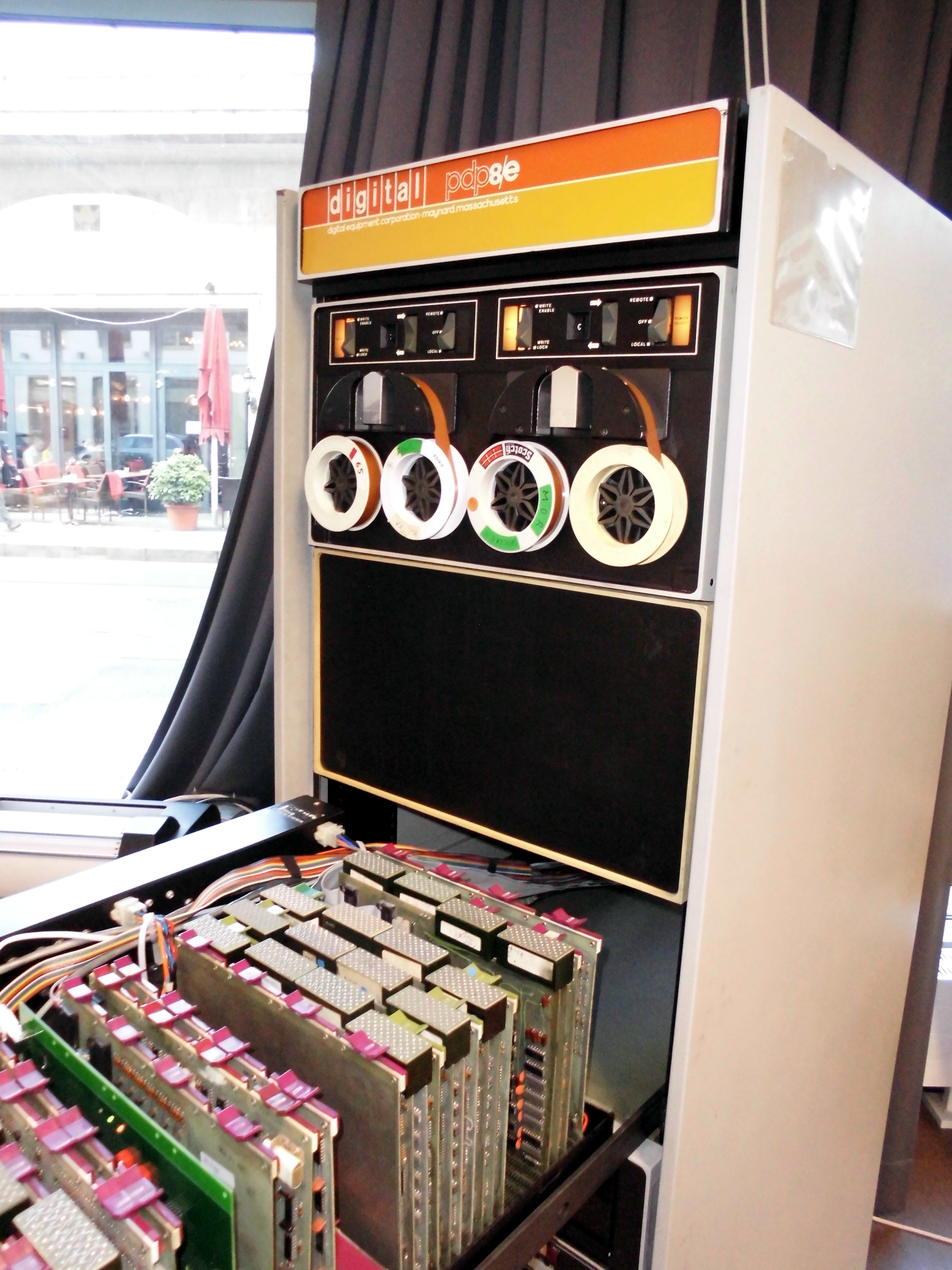
PDP-8
The PDP-8 is a 12-bit computing, 12-bit minicomputer that was produced by Digital Equipment Corporation, Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). It was the first commercially successful minicomputer, with over 50,000 units being sold over the model's lifetime. Its basic design follows the pioneering LINC but has a smaller instruction set, which is an expanded version of the PDP-5 instruction set. Similar machines from DEC are the PDP-12 which is a modernized version of the PDP-8 and LINC concepts, and the PDP-14 industrial controller system. Overview The earliest PDP-8 model, informally known as a "Straight-8", was introduced on 22 March 1965 priced at $18,500 (). It used diode–transistor logic packaged on Flip Chip (trademark), flip chip cards in a machine about the size of a small household refrigerator. It was the first computer to be sold for under $20,000, making it the best-selling computer in history at that time. The Straight-8 was supplanted in 1966 by the PDP-8/S, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.png)


.jpg)


