|
Raymonden
Raymonden is a prehistoric cave near Chancelade in the France, French département Dordogne (département), Dordogne. The cave was inhabited during the Upper Paleolithic and contained, besides many artefacts, a human skeleton. Geography, geology and site description The Raymonden cave occurs about one kilometer north of Chancelade on the left bank of the Beauronne, Dordogne, Beauronne river, a right-hand tributary of the Isle (river), Isle river. Just north of the cave the Beauronne starts to meander forming a first loop which is accompanied on its left side by a steep, rocky ledge. The rocks are composed of flat-lying Angoumian limestones, a local formation of the Turonian. The Angoumian used to be extensively quarried for building stones, and an enclosed resistant layer was mined for mill stones. The entry to the cave is hemmed in between two quarries, not far from the borough of ''les Grèzes''. In front of the cave passes the D 939 from Périgueux to Brantôme, Dordogne, Bran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
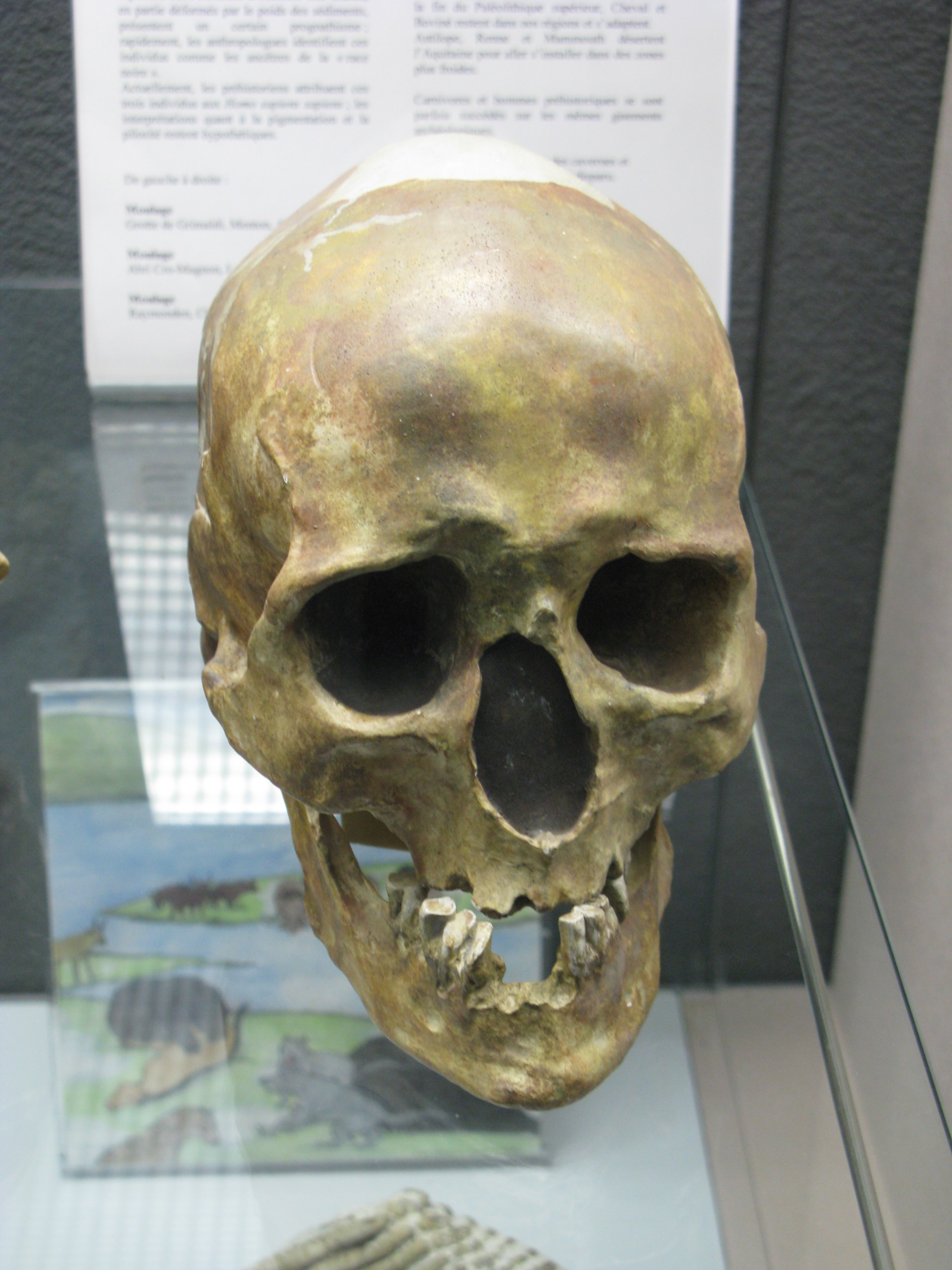
Chancelade Man
Chancelade man (the Chancelade cranium) is an ancient Anatomically modern humans, anatomically modern human fossil of a male found in Chancelade in France in 1888. The skeleton was that of a rather short man, who stood a mere tall. Due to morphological differences with the Cro-Magnon 1 cranium, early interpretations postulated that the individual belonged to a separate lineage, possibly ancestral to Eskimos. G. M. Morant in 1930 recognized the skeleton as within the morphological range of EEMH, Upper Paleolithic European populations, and this interpretation has remained accepted since. Discovery The Chancelade find was discovered in 1888 in the cave of Raymonden Chancelade in the Dordogne. Lying all the way down by the bedrock, below three layers containing Magdalenian tools, the find contained a single skeleton. The skeleton was that of an adult man, estimated to have been between 55 and 65 at death. The man had been intentionally buried and liberally coated with ochre. The sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancelade Grotte Reymonden (1)
Chancelade (; oc, Chancelada) is a commune in the Dordogne department in Nouvelle-Aquitaine in southwestern France. The village is the site of Chancelade Abbey. The so-called " Chancelade man" was found in the nearby Raymonden rock shelter in 1888, the skeleton of an approximately 60-year-old male who was buried there in the Magdalenian, roughly 15,000 years ago. Population See also *Communes of the Dordogne department The following is a list of the 503 communes of the Dordogne department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Dordogne {{Dordogne-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancelade
Chancelade (; oc, Chancelada) is a Communes of France, commune in the Dordogne Departments of France, department in Nouvelle-Aquitaine in southwestern France. The village is the site of Chancelade Abbey. The so-called "Chancelade man" was found in the nearby Raymonden rock shelter in 1888, the skeleton of an approximately 60-year-old male who was buried there in the Magdalenian, roughly 15,000 years ago. Population See also *Communes of the Dordogne department References Communes of Dordogne {{Dordogne-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
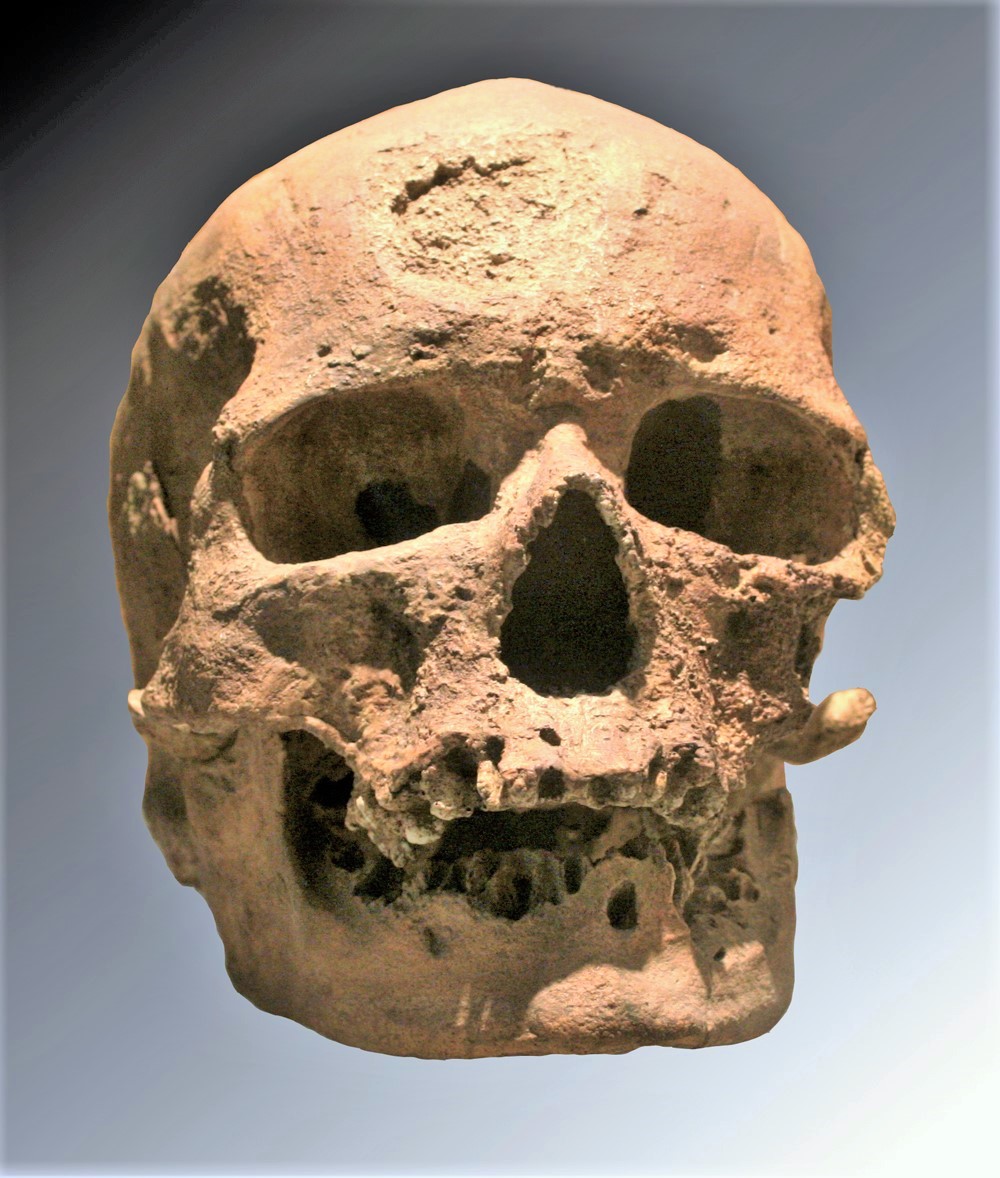
Cro-Magnon 1
Cro-Magnon (, ; french: Abri de Cro-Magnon )French ''abri'' means "rock shelter", ''crô'' means "hole" in Occitan (standard French ''creux''), and ''Magnon'' is the surname of the land owner at the time. is an Aurignacian (Upper Paleolithic) site, located in a rock shelter at Les Eyzies, a hamlet in the commune of Les Eyzies-de-Tayac-Sireuil, Dordogne, southwestern France. Most notably, it is the site of the discovery of anatomically modern human remains, apparently buried at the site, dated to about 28,000 years ago.Cro-Magnon 1: 27,680 ± 270 BP Because of its archeological importance, ''Abri de Cro-Magnon'' was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List as part of the Prehistoric Sites and Decorated Caves of the Vézère Valley site. Human remains In 1868, workmen found animal bones, flint tools, and human skulls in the rock shelter. French geologist Louis Lartet was called for excavations, and found the partial skeletons of four prehistoric adults and one infant, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurignacian
The Aurignacian () is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic associated with European early modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the Levant, where the Emiran period and the Ahmarian period form the first periods of the Upper Paleolithic, corresponding to the first stages of the expansion of ''Homo sapiens'' out of Africa. They then migrated to Europe and created the first European culture of modern humans, the Aurignacian. An Early Aurignacian or Proto-Aurignacian stage is dated between about 43,000 and 37,000 years ago. The Aurignacian proper lasts from about 37,000 to 33,000 years ago. A Late Aurignacian phase transitional with the Gravettian dates to about 33,000 to 26,000 years ago. The type site is the Cave of Aurignac, Haute-Garonne, south-west France. The main preceding period is the Mousterian of the ''Neanderthals''. One of the oldest examples of figurative art, the Venus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinniped
Pinnipeds (pronounced ), commonly known as seals, are a widely distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semiaquatic, mostly marine mammals. They comprise the extant families Odobenidae (whose only living member is the walrus), Otariidae (the eared seals: sea lions and fur seals), and Phocidae (the earless seals, or true seals). There are 34 extant species of pinnipeds, and more than 50 extinct species have been described from fossils. While seals were historically thought to have descended from two ancestral lines, molecular evidence supports them as a monophyletic lineage (descended from one ancestral line). Pinnipeds belong to the order Carnivora; their closest living relatives are musteloids (weasels, raccoons, skunks, and red pandas), having diverged about 50 million years ago. Seals range in size from the and Baikal seal to the and southern elephant seal male, which is also the largest member of the order Carnivora. Several species exh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saiga
The saiga antelope (, ''Saiga tatarica''), or saiga, is a critically endangered antelope which during antiquity inhabited a vast area of the Eurasian steppe spanning the foothills of the Carpathian Mountains in the northwest and Caucasus in the southwest into Mongolia in the northeast and Dzungaria in the southeast. During the Pleistocene, they also occurred in Beringian North America and the British Isles. Today, the dominant subspecies (''S. t. tatarica'') is only found in one region in Russia (in the Republic of Kalmykia and Astrakhan Oblast) and three areas in Kazakhstan (the Ural, Ustiurt, and Betpak-Dala populations). A portion of the Ustiurt population migrates south to Uzbekistan and occasionally Turkmenistan in winter. It is extirpated from China, Ukraine, and southwestern Mongolia. The Mongolian subspecies (''S. t. mongolica'') is found only in western Mongolia. Taxonomy and phylogeny The scientific name ''Capra tatarica'' was coined by Carl Linnaeus in 1766 in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subspecies. A 2022 revision of the genus elevated five of the subspecies to species (see Taxonomy below). They have a circumpolar distribution and are native to the Arctic, sub-Arctic, tundra, boreal forest, and mountainous regions of northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. Reindeer occur in both migratory and sedentary populations, and their herd sizes vary greatly in different regions. The tundra subspecies are adapted for extreme cold, and some are adapted for long-distance migration. Reindeer vary greatly in size and color from the smallest species, the Svalbard reindeer (''R. t. platyrhynchus''), to the largest subspecies, Osborn's caribou (''R. t. osborni''). Although reindeer are quite numerous, some species and subspecies are in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burin (lithic Flake)
Burin from the Upper Paleolithic (Gravettian) (ca. 29,000–22,000 BP) In the field of lithic reduction, a burin (from the French ''burin'', meaning "cold chisel" or modern engraving burin) is a type of handheld lithic flake with a chisel-like edge which prehistoric humans used for engraving or for carving wood or bone. In archaeology, burin use is often associated with "burin spalls", which are a form of debitage created when toolmakers strike a small flake obliquely from the edge of the burin flake in order to form the graving edge. Documented use left, 180px, Carinated "burin"/microblade core with multiple facets Standardized burin usage is typical of the Middle Paleolithic and Upper Palaeolithic cultures in Europe, but archaeologists have also identified them in North American cultural assemblages, and in his book ''Early Man in China'', Jia Lanpo of Beijing University lists dihedral burins and burins for truncation among artifacts uncovered along the banks of the Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scraper (archaeology)
In prehistoric archaeology, scrapers are unifacial tools thought to have been used for hideworking and woodworking. Many lithic analysts maintain that the only true scrapers are defined on the base of use-wear, and usually are those that were worked on the distal ends of blades—i.e., "end scrapers" (french: grattoir, link=no). Other scrapers include the so-called "side scrapers" or racloirs, which are made on the longest side of a flake, and notched scrapers, which have a cleft on either side that may have been used to attach them to something else. Scrapers are typically formed by chipping the end of a flake of stone in order to create one sharp side and to keep the rest of the sides dull to facilitate grasping it. Most scrapers are either circle or blade-like in shape. The working edges of scrapers tend to be convex, and many have trimmed and dulled lateral edges to facilitate hafting. One important variety of scraper is the thumbnail scraper, a scraper shaped much like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blade
A blade is the portion of a tool, weapon, or machine with an edge that is designed to puncture, chop, slice or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they are to be used on. Historically, humans have made blades from flaking stones such as flint or obsidian, and from various metal such as copper, bronze and iron. Modern blades are often made of steel or ceramic. Blades are one of humanity's oldest tools, and continue to be used for combat, food preparation, and other purposes. Blades work by concentrating force on the cutting edge. Certain blades, such as those used on bread knives or saws, are serrated, further concentrating force on the point of each tooth. Uses During food preparation, knives are mainly used for slicing, chopping, and piercing. In combat, a blade may be used to slash or puncture, and may also be thrown or otherwise propelled. The function is to sever a nerve, muscle or tendon fibers, or bloo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knife
A knife ( : knives; from Old Norse 'knife, dirk') is a tool or weapon with a cutting edge or blade, usually attached to a handle or hilt. One of the earliest tools used by humanity, knives appeared at least 2.5 million years ago, as evidenced by the Oldowan tools. Originally made of wood, bone, and stone (such as flint and obsidian), over the centuries, in step with improvements in both metallurgy and manufacturing, knife blades have been made from copper, bronze, iron, steel, ceramic, and titanium. Most modern knives have either fixed or folding blades; blade patterns and styles vary by maker and country of origin. Knives can serve various purposes. Hunters use a hunting knife, soldiers use the combat knife, scouts, campers, and hikers carry a pocket knife; there are kitchen knives for preparing foods (the chef's knife, the paring knife, bread knife, cleaver), table knives (butter knives and steak knives), weapons (daggers or switchblades), knives for throwing or juggling, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)