|
Raychaudhuri Equation
In general relativity, the Raychaudhuri equation, or Landau–Raychaudhuri equation, is a fundamental result describing the motion of nearby bits of matter. The equation is important as a fundamental lemma for the Penrose–Hawking singularity theorems and for the study of exact solutions in general relativity, but has independent interest, since it offers a simple and general validation of our intuitive expectation that gravitation should be a universal attractive force between any two bits of mass–energy in general relativity, as it is in Newton's theory of gravitation. The equation was discovered independently by the Indian physicist Amal Kumar Raychaudhuri and the Soviet physicist Lev Landau. Mathematical statement Given a timelike unit vector field \vec (which can be interpreted as a family or congruence of nonintersecting world lines via the integral curve, not necessarily geodesics), Raychaudhuri's equation in D spacetime dimensions can be written as :\dot = - \frac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity, and as Einstein's theory of gravity, is the differential geometry, geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General theory of relativity, relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time in physics, time, or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the ''curvature of spacetime'' is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever is present, including matter and radiation. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second-order partial differential equations. Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes gravity in classical mechanics, can be seen as a prediction of general relativity for the almost flat spacetime geometry around stationary mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proper Time
In relativity, proper time (from Latin, meaning ''own time'') along a timelike world line is defined as the time as measured by a clock following that line. The proper time interval between two events on a world line is the change in proper time, which is independent of coordinates, and is a Lorentz scalar. The interval is the quantity of interest, since proper time itself is fixed only up to an arbitrary additive constant, namely the setting of the clock at some event along the world line. The proper time interval between two events depends not only on the events, but also the world line connecting them, and hence on the motion of the clock between the events. It is expressed as an integral over the world line (analogous to arc length in Euclidean space). An accelerated clock will measure a smaller elapsed time between two events than that measured by a non-accelerated ( inertial) clock between the same two events. The twin paradox is an example of this effect. By conventio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causal Past
In mathematical physics, the causal structure of a Lorentzian manifold describes the possible causal relationships between points in the manifold. Lorentzian manifolds can be classified according to the types of causal structures they admit (''causality conditions''). Introduction In modern physics (especially general relativity) spacetime is represented by a Lorentzian manifold. The causal relations between points in the manifold are interpreted as describing which events in spacetime can influence which other events. The causal structure of an arbitrary (possibly curved) Lorentzian manifold is made more complicated by the presence of curvature. Discussions of the causal structure for such manifolds must be phrased in terms of smooth curves joining pairs of points. Conditions on the tangent vectors of the curves then define the causal relationships. Tangent vectors If \,(M,g) is a Lorentzian manifold (for metric g on manifold M) then the nonzero tangent vectors at each po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Event Horizon
In astrophysics, an event horizon is a boundary beyond which events cannot affect an outside observer. Wolfgang Rindler coined the term in the 1950s. In 1784, John Michell proposed that gravity can be strong enough in the vicinity of massive compact objects that even light cannot escape. At that time, the Newtonian theory of gravitation and the so-called corpuscular theory of light were dominant. In these theories, if the escape velocity of the gravitational influence of a massive object exceeds the speed of light, then light originating inside or from it can escape temporarily but will return. In 1958, David Finkelstein used general relativity to introduce a stricter definition of a local black hole event horizon as a boundary beyond which events of any kind cannot affect an outside observer, leading to information and firewall paradoxes, encouraging the re-examination of the concept of local event horizons and the notion of black holes. Several theories were subsequently d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Parameter
In geometry, a geodesic () is a curve representing in some sense the locally shortest path ( arc) between two points in a surface, or more generally in a Riemannian manifold. The term also has meaning in any differentiable manifold with a connection. It is a generalization of the notion of a "straight line". The noun ''geodesic'' and the adjective ''geodetic'' come from ''geodesy'', the science of measuring the size and shape of Earth, though many of the underlying principles can be applied to any ellipsoidal geometry. In the original sense, a geodesic was the shortest route between two points on the Earth's surface. For a spherical Earth, it is a segment of a great circle (see also great-circle distance). The term has since been generalized to more abstract mathematical spaces; for example, in graph theory, one might consider a geodesic between two vertices/nodes of a graph. In a Riemannian manifold or submanifold, geodesics are characterised by the property of having vanis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null Energy Condition
In relativistic classical field theories of gravitation, particularly general relativity, an energy condition is a generalization of the statement "the energy density of a region of space cannot be negative" in a relativistically phrased mathematical formulation. There are multiple possible alternative ways to express such a condition such that can be applied to the matter content of the theory. The hope is then that any reasonable matter theory will satisfy this condition or at least will preserve the condition if it is satisfied by the starting conditions. Energy conditions are not physical constraints , but are rather mathematically imposed boundary conditions that attempt to capture a belief that "energy should be positive". Many energy conditions are known to not correspond to physical reality—for example, the observable effects of dark energy are well known to violate the strong energy condition. In general relativity, energy conditions are often used (and required) in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
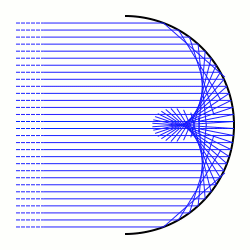
Caustic (mathematics)
In differential geometry, a caustic is the envelope of rays either reflected or refracted by a manifold. It is related to the concept of caustics in geometric optics. The ray's source may be a point (called the radiant) or parallel rays from a point at infinity, in which case a direction vector of the rays must be specified. More generally, especially as applied to symplectic geometry and singularity theory, a caustic is the critical value set of a Lagrangian mapping where is a Lagrangian immersion of a Lagrangian submanifold ''L'' into a symplectic manifold ''M'', and is a Lagrangian fibration of the symplectic manifold ''M''. The caustic is a subset of the Lagrangian fibration's base space ''B''. Explanation Concentration of light, especially sunlight, can burn. The word ''caustic'', in fact, comes from the Greek καυστός, burnt, via the Latin ''causticus'', burning. A common situation where caustics are visible is when light shines on a drinking glass. The g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Conditions
In relativistic classical field theories of gravitation, particularly general relativity, an energy condition is a generalization of the statement "the energy density of a region of space cannot be negative" in a relativistically phrased mathematical formulation. There are multiple possible alternative ways to express such a condition such that can be applied to the matter content of the theory. The hope is then that any reasonable matter theory will satisfy this condition or at least will preserve the condition if it is satisfied by the starting conditions. Energy conditions are not physical constraints , but are rather mathematically imposed boundary conditions that attempt to capture a belief that "energy should be positive". Many energy conditions are known to not correspond to physical reality—for example, the observable effects of dark energy are well known to violate the strong energy condition. In general relativity, energy conditions are often used (and required) in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gödel Metric
The Gödel metric, also known as the Gödel solution or Gödel universe, is an exact solution, found in 1949 by Kurt Gödel, of the Einstein field equations in which the stress–energy tensor contains two terms: the first representing the matter density of a homogeneous distribution of swirling dust particles (see dust solution), and the second associated with a negative cosmological constant (see Lambdavacuum solution). This solution has many unusual properties—in particular, the existence of closed time-like curves that would allow time travel in a universe described by the solution. Its definition is somewhat artificial, since the value of the cosmological constant must be carefully chosen to correspond to the density of the dust grains, but this spacetime is an important pedagogical example. Definition Like any other Lorentzian spacetime, the Gödel solution represents the metric tensor in terms of a local coordinate chart. It may be easiest to understand the Gödel u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometrized Unit System
A geometrized unit system or geometrodynamic unit system is a system of natural units in which the base physical units are chosen so that the speed of light in vacuum, ''c'', and the gravitational constant, ''G'', are set equal to unity. : c = 1 \ : G = 1 \ The geometrized unit system is not a completely defined system. Some systems are geometrized unit systems in the sense that they set these, in addition to other constants, to unity, for example Stoney units and Planck units. This system is useful in physics, especially in the special and general theories of relativity. All physical quantities are identified with geometric quantities such as areas, lengths, dimensionless numbers, path curvatures, or sectional curvatures. Many equations in relativistic physics appear simpler when expressed in geometric units, because all occurrences of ''G'' and of ''c'' drop out. For example, the Schwarzschild radius of a nonrotating uncharged black hole with mass ''m'' becomes . For thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Force
In physics, a body force is a force that acts throughout the volume of a body.Springer site - Book 'Solid mechanics'preview paragraph 'Body forces'./ref> Forces due to gravity, electric fields and magnetic fields are examples of body forces. Body forces contrast with ''contact forces'' or '' surface forces'' which are exerted to the surface of an object. Fictitious forces such as the centrifugal force, Euler force, and the Coriolis effect are other examples of body forces. Definition Qualitative A body force is simply a type of force, and so it has the same dimensions as force, L] sup>−2. However, it is often convenient to talk about a body force in terms of either the force per unit volume or the force per unit mass. If the force per unit volume is of interest, it is referred to as the force density throughout the system. A body force is distinct from a contact force in that the force does not require contact for transmission. Thus, common forces associated with press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrostatic Equilibrium
In fluid mechanics, hydrostatic equilibrium, also called hydrostatic balance and hydrostasy, is the condition of a fluid or plastic solid at rest, which occurs when external forces, such as gravity, are balanced by a pressure-gradient force. In the planetary physics of Earth, the pressure-gradient force prevents gravity from collapsing the atmosphere of Earth into a thin, dense shell, whereas gravity prevents the pressure-gradient force from diffusing the atmosphere into outer space. In general, it is what causes objects in space to be spherical. Hydrostatic equilibrium is the distinguishing criterion between dwarf planets and small solar system bodies, and features in astrophysics and planetary geology. Said qualification of equilibrium indicates that the shape of the object is symmetrically rounded, mostly due to rotation, into an ellipsoid, where any irregular surface features are consequent to a relatively thin solid crust. In addition to the Sun, there are a dozen or s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |