|
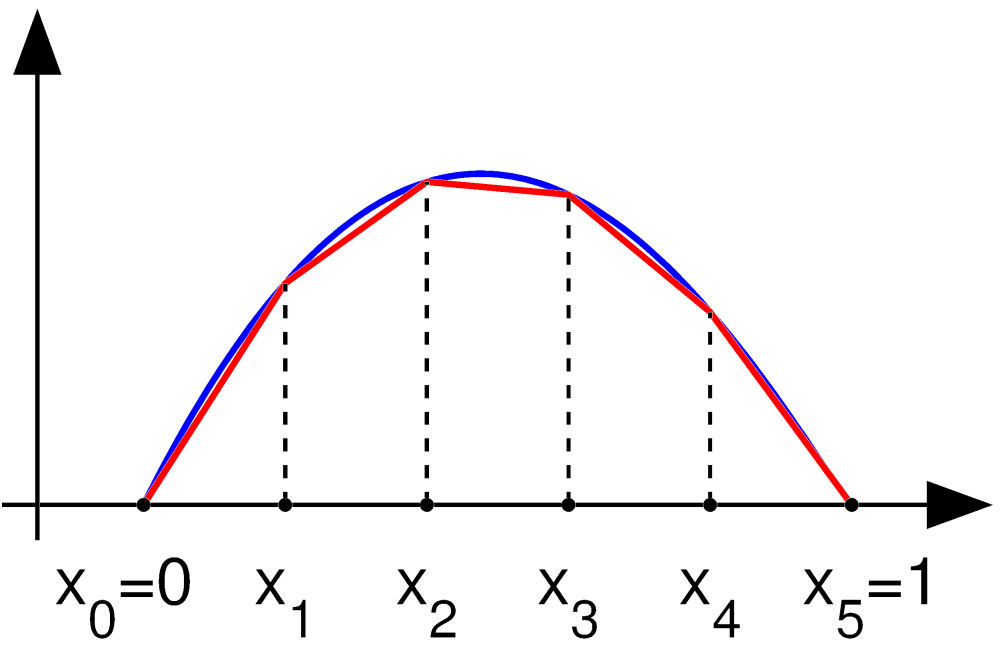
Raviart–Thomas Basis Functions
In applied mathematics, Raviart–Thomas basis functions are vector basis functions used in finite element and boundary element methods. They are regularly used as basis functions when working in electromagnetics. They are sometimes called Rao-Wilton-Glisson basis functions. The space \mathrm_q spanned by the Raviart–Thomas basis functions of order q is the smallest polynomial space such that the divergence In vector calculus, divergence is a vector operator that operates on a vector field, producing a scalar field giving the quantity of the vector field's source at each point. More technically, the divergence represents the volume density of the ... maps \mathrm_q onto \mathrm_q, the space of piecewise polynomials of order q. Order 0 Raviart-Thomas Basis Functions in 2D In two-dimensional space, the lowest order Raviart Thomas space, \mathrm_0, has degrees of freedom on the edges of the elements of the finite element mesh. The nth edge has an associated basis function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Function
A vector-valued function, also referred to as a vector function, is a mathematical function of one or more variables whose range is a set of multidimensional vectors or infinite-dimensional vectors. The input of a vector-valued function could be a scalar or a vector (that is, the dimension of the domain could be 1 or greater than 1); the dimension of the function's domain has no relation to the dimension of its range. Example: Helix A common example of a vector-valued function is one that depends on a single real parameter ''t'', often representing time, producing a vector v(''t'') as the result. In terms of the standard unit vectors i, j, k of Cartesian , these specific types of vector-valued functions are given by expressions such as \mathbf(t) = f(t)\mathbf + g(t)\mathbf + h(t)\mathbf where ''f''(''t''), ''g''(''t'') and ''h''(''t'') are the coordinate functions of the parameter ''t'', and the domain of this vector-valued function is the intersection of the domains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basis Function
In mathematics, a basis function is an element of a particular basis for a function space. Every function in the function space can be represented as a linear combination of basis functions, just as every vector in a vector space can be represented as a linear combination of basis vectors. In numerical analysis and approximation theory, basis functions are also called blending functions, because of their use in interpolation: In this application, a mixture of the basis functions provides an interpolating function (with the "blend" depending on the evaluation of the basis functions at the data points). Examples Monomial basis for ''Cω'' The monomial basis for the vector space of analytic functions is given by \. This basis is used in Taylor series, amongst others. Monomial basis for polynomials The monomial basis also forms a basis for the vector space of polynomials. After all, every polynomial can be written as a_0 + a_1x^1 + a_2x^2 + \cdots + a_n x^n for some n \in \m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Element Method
The finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic potential. The FEM is a general numerical method for solving partial differential equations in two or three space variables (i.e., some boundary value problems). To solve a problem, the FEM subdivides a large system into smaller, simpler parts that are called finite elements. This is achieved by a particular space discretization in the space dimensions, which is implemented by the construction of a mesh of the object: the numerical domain for the solution, which has a finite number of points. The finite element method formulation of a boundary value problem finally results in a system of algebraic equations. The method approximates the unknown function over the domain. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Element Method
The boundary element method (BEM) is a numerical computational method of solving linear partial differential equations which have been formulated as integral equations (i.e. in ''boundary integral'' form), including fluid mechanics, acoustics, electromagnetics (where the technique is known as method of moments or abbreviated as MoM), fracture mechanics, and contact mechanics. Mathematical basis The integral equation may be regarded as an exact solution of the governing partial differential equation. The boundary element method attempts to use the given boundary conditions to fit boundary values into the integral equation, rather than values throughout the space defined by a partial differential equation. Once this is done, in the post-processing stage, the integral equation can then be used again to calculate numerically the solution directly at any desired point in the interior of the solution domain. BEM is applicable to problems for which Green's functions can be calculated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetics
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions of atoms and molecules. Electromagnetism can be thought of as a combination of electricity and magnetism, two distinct but closely intertwined phenomena. In essence, electric forces occur between any two charged particles, causing an attraction between particles with opposite charges and repulsion between particles with the same charge, while magnetism is an interaction that occurs exclusively between ''moving'' charged particles. These two effects combine to create electromagnetic fields in the vicinity of charge particles, which can exert influence on other particles via the Lorentz force. At high energy, the weak force and electromagnetic force are unified as a single electroweak force. The electromagnetic force is responsible for m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Function Space
In mathematics, a function space is a set of functions between two fixed sets. Often, the domain and/or codomain will have additional structure which is inherited by the function space. For example, the set of functions from any set into a vector space has a natural vector space structure given by pointwise addition and scalar multiplication. In other scenarios, the function space might inherit a topological or metric structure, hence the name function ''space''. In linear algebra Let be a vector space over a field and let be any set. The functions → can be given the structure of a vector space over where the operations are defined pointwise, that is, for any , : → , any in , and any in , define \begin (f+g)(x) &= f(x)+g(x) \\ (c\cdot f)(x) &= c\cdot f(x) \end When the domain has additional structure, one might consider instead the subset (or subspace) of all such functions which respect that structure. For example, if is also a vector space over , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divergence
In vector calculus, divergence is a vector operator that operates on a vector field, producing a scalar field giving the quantity of the vector field's source at each point. More technically, the divergence represents the volume density of the outward flux of a vector field from an infinitesimal volume around a given point. As an example, consider air as it is heated or cooled. The velocity of the air at each point defines a vector field. While air is heated in a region, it expands in all directions, and thus the velocity field points outward from that region. The divergence of the velocity field in that region would thus have a positive value. While the air is cooled and thus contracting, the divergence of the velocity has a negative value. Physical interpretation of divergence In physical terms, the divergence of a vector field is the extent to which the vector field flux behaves like a source at a given point. It is a local measure of its "outgoingness" – the extent t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raviart Thomas Labelled
Raviart is a town in central Ivory Coast. It is a sub-prefecture of Didiévi Department in Bélier Region, Lacs District. Raviart was a commune A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or comune or other derivations may also refer to: Administrative-territorial entities * Commune (administrative division), a municipality or township ** Communes of ... until March 2012, when it became one of 1126 communes nationwide that were abolished. ''news.abidjan.net'', 7 March 2012. In 2014, the population of the sub-prefecture of Raviart was 17,113. Village ...
|
Two-dimensional Space
In mathematics, a plane is a Euclidean ( flat), two-dimensional surface that extends indefinitely. A plane is the two-dimensional analogue of a point (zero dimensions), a line (one dimension) and three-dimensional space. Planes can arise as subspaces of some higher-dimensional space, as with one of a room's walls, infinitely extended, or they may enjoy an independent existence in their own right, as in the setting of two-dimensional Euclidean geometry. Sometimes the word ''plane'' is used more generally to describe a two-dimensional surface, for example the hyperbolic plane and elliptic plane. When working exclusively in two-dimensional Euclidean space, the definite article is used, so ''the'' plane refers to the whole space. Many fundamental tasks in mathematics, geometry, trigonometry, graph theory, and graphing are performed in a two-dimensional space, often in the plane. Euclidean geometry Euclid set forth the first great landmark of mathematical thought, an axio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Element Method
The finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic potential. The FEM is a general numerical method for solving partial differential equations in two or three space variables (i.e., some boundary value problems). To solve a problem, the FEM subdivides a large system into smaller, simpler parts that are called finite elements. This is achieved by a particular space discretization in the space dimensions, which is implemented by the construction of a mesh of the object: the numerical domain for the solution, which has a finite number of points. The finite element method formulation of a boundary value problem finally results in a system of algebraic equations. The method approximates the unknown function over the domain. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Differential Equations
{{disambig ...
Numerical may refer to: * Number * Numerical digit * Numerical analysis Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation (as opposed to symbolic manipulations) for the problems of mathematical analysis (as distinguished from discrete mathematics). It is the study of numerical methods th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |