|
Raumschach
Three-dimensional chess (or 3‑D chess) is any chess variant that replaces the two-dimensional board with a three-dimensional array of cells between which the pieces can move. In practical play, this is usually achieved by boards representing different layers being laid out next to each other. Three-dimensional variants have existed since at least the late 19th century, one of the oldest being ''Raumschach'' (), invented in 1907 by Ferdinand Maack and considered the classic 3‑D game. Maack founded a Raumschach club in Hamburg in 1919, which remained active until World War II. Chapter 25 of David Pritchard's ''The Classified Encyclopedia of Chess Variants'' discusses some 50 such variations extending chess to three dimensions as well as a handful of higher-dimensional variants. Chapter 11 covers variants using multiple boards normally set side by side which can also be considered to add an extra dimension to chess. "Three-dimensional chess" is used collo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tri-D Chess
Three-dimensional chess (or 3‑D chess) is any chess variant that replaces the two-dimensional board with a three-dimensional array of cells between which the pieces can move. In practical play, this is usually achieved by boards representing different layers being laid out next to each other. Three-dimensional variants have existed since at least the late 19th century, one of the oldest being ''Raumschach'' (), invented in 1907 by Ferdinand Maack and considered the classic 3‑D game. Maack founded a Raumschach club in Hamburg in 1919, which remained active until World War II. Chapter 25 of David Pritchard's ''The Classified Encyclopedia of Chess Variants'' discusses some 50 such variations extending chess to three dimensions as well as a handful of higher-dimensional variants. Chapter 11 covers variants using multiple boards normally set side by side which can also be considered to add an extra dimension to chess. "Three-dimensional chess" is used collo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Trek Tri-D Chess
Three-dimensional chess (or 3‑D chess) is any chess variant that replaces the two-dimensional board with a three-dimensional array of cells between which the pieces can move. In practical play, this is usually achieved by boards representing different layers being laid out next to each other. Three-dimensional variants have existed since at least the late 19th century, one of the oldest being ''Raumschach'' (), invented in 1907 by Ferdinand Maack and considered the classic 3‑D game. Maack founded a Raumschach club in Hamburg in 1919, which remained active until World War II. Chapter 25 of David Pritchard's ''The Classified Encyclopedia of Chess Variants'' discusses some 50 such variations extending chess to three dimensions as well as a handful of higher-dimensional variants. Chapter 11 covers variants using multiple boards normally set side by side which can also be considered to add an extra dimension to chess. "Three-dimensional chess" is used coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
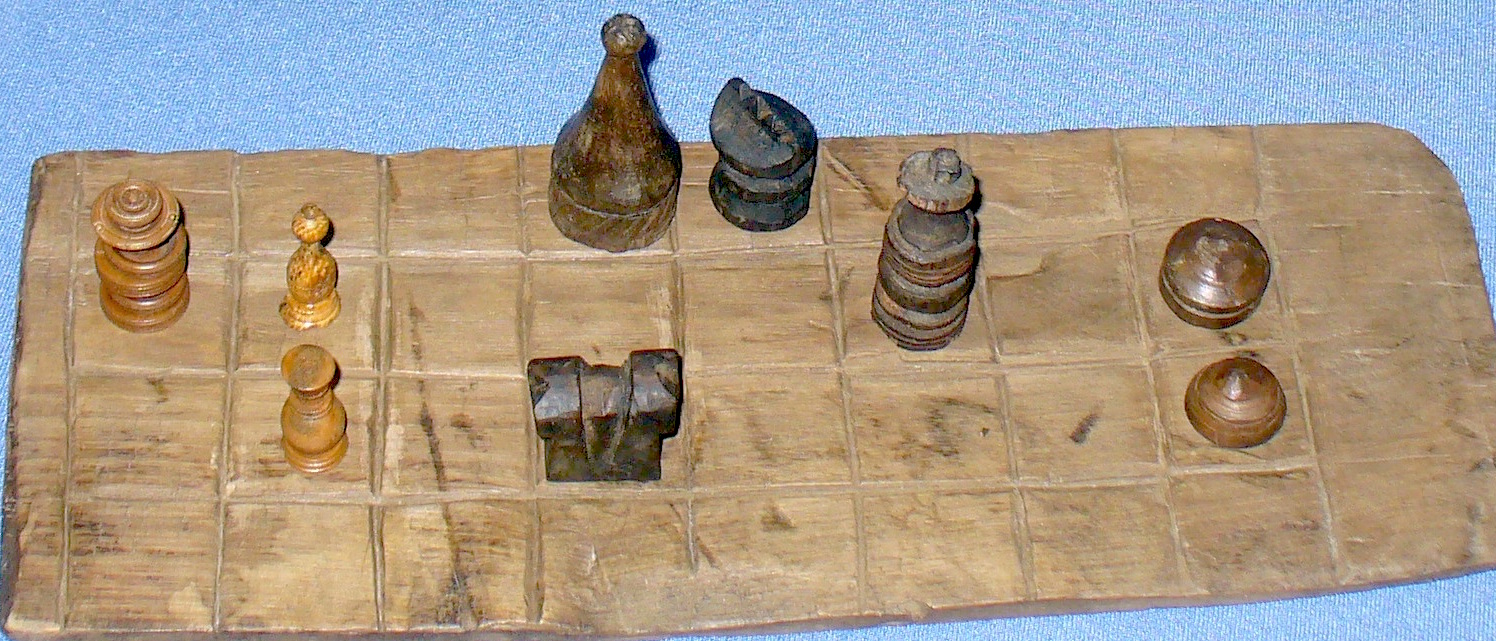
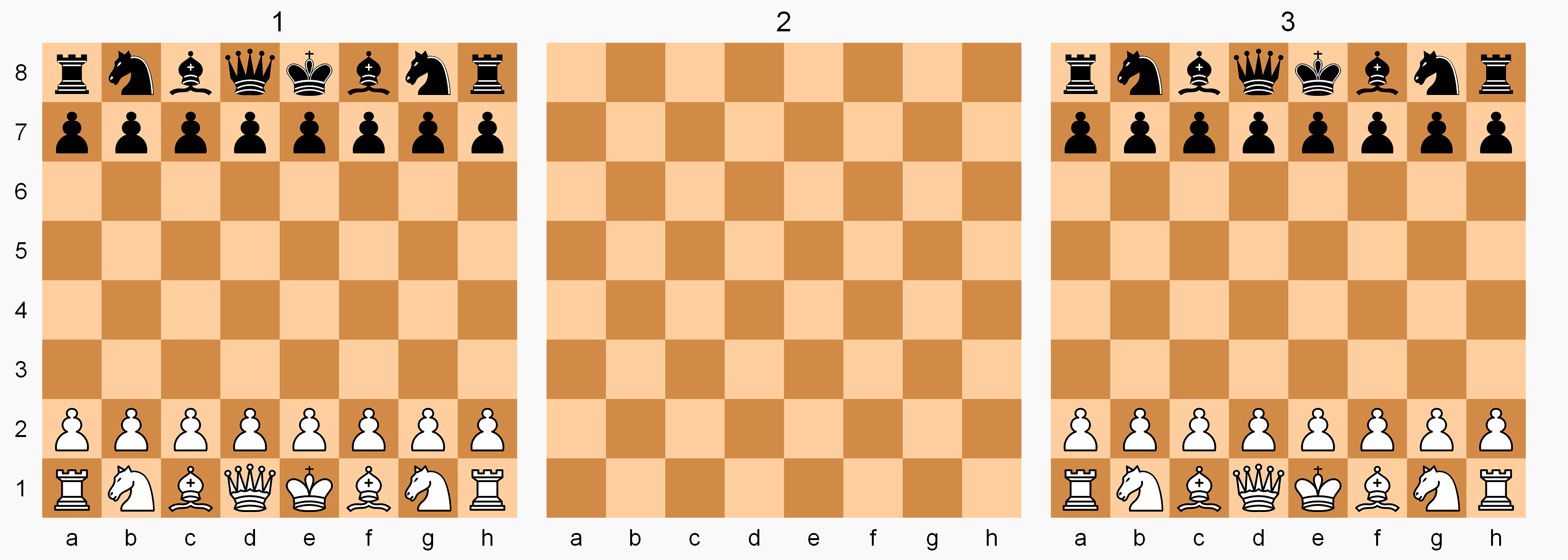
Raumschach Gameboard
Three-dimensional chess (or 3‑D chess) is any chess variant that replaces the two-dimensional chessboard, board with a three-dimensional array of cells between which the pieces can move. In practical play, this is usually achieved by boards representing different layers being laid out next to each other. Three-dimensional variants have existed since at least the late 19th century, one of the oldest being ''Raumschach'' (), invented in 1907 by Ferdinand Maack and considered the classic 3‑D game. Maack founded a Raumschach club in Hamburg in 1919, which remained active until World War II. Chapter 25 of David Pritchard (chess writer), David Pritchard's ''The Classified Encyclopedia of Chess Variants'' discusses some 50 such variations extending chess to three dimensions as well as a handful of higher-dimensional variants. Chapter 11 covers variants using multiple boards normally set side by side which can also be considered to add an extra dimension to chess. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Trek 3D Chess
Three-dimensional chess (or 3‑D chess) is any chess variant that replaces the two-dimensional board with a three-dimensional array of cells between which the pieces can move. In practical play, this is usually achieved by boards representing different layers being laid out next to each other. Three-dimensional variants have existed since at least the late 19th century, one of the oldest being ''Raumschach'' (), invented in 1907 by Ferdinand Maack and considered the classic 3‑D game. Maack founded a Raumschach club in Hamburg in 1919, which remained active until World War II. Chapter 25 of David Pritchard's ''The Classified Encyclopedia of Chess Variants'' discusses some 50 such variations extending chess to three dimensions as well as a handful of higher-dimensional variants. Chapter 11 covers variants using multiple boards normally set side by side which can also be considered to add an extra dimension to chess. "Three-dimensional chess" is used collo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Trek Chess
Three-dimensional chess (or 3‑D chess) is any chess variant that replaces the two-dimensional board with a three-dimensional array of cells between which the pieces can move. In practical play, this is usually achieved by boards representing different layers being laid out next to each other. Three-dimensional variants have existed since at least the late 19th century, one of the oldest being ''Raumschach'' (), invented in 1907 by Ferdinand Maack and considered the classic 3‑D game. Maack founded a Raumschach club in Hamburg in 1919, which remained active until World War II. Chapter 25 of David Pritchard's ''The Classified Encyclopedia of Chess Variants'' discusses some 50 such variations extending chess to three dimensions as well as a handful of higher-dimensional variants. Chapter 11 covers variants using multiple boards normally set side by side which can also be considered to add an extra dimension to chess. "Three-dimensional chess" is used coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairy Chess Piece
A fairy chess piece, variant chess piece, unorthodox chess piece, or heterodox chess piece is a chess piece not used in conventional chess but incorporated into certain chess variants and some chess problems. Compared to conventional pieces, fairy pieces vary mostly in the way they move, but they may also follow special rules for capturing, promotions, etc. Because of the distributed and uncoordinated nature of unorthodox chess development, the same piece can have different names, and different pieces can have the same name in various contexts. Most are symbolised as inverted or rotated icons of the standard pieces in diagrams, and the meanings of these "wildcards" must be defined in each context separately. Pieces invented for use in chess variants rather than problems sometimes instead have special icons designed for them, but with some exceptions (the princess, empress, and occasionally amazon), many of these are not used beyond the individual games for which they were invented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chessboard
A chessboard is a used to play chess. It consists of 64 squares, 8 rows by 8 columns, on which the chess pieces are placed. It is square in shape and uses two colours of squares, one light and one dark, in a chequered pattern. During play, the board is oriented such that each player's near-right corner square is a light square. The columns of a chessboard are known as ', the rows are known as ', and the lines of adjoining same-coloured squares (each running from one edge of the board to an adjacent edge) are known as '. Each square of the board is named using algebraic, descriptive, or numeric chess notation; algebraic notation is the FIDE standard. In algebraic notation, using White's perspective, files are labeled ''a'' through ''h'' from left to right, and ranks are labeled ''1'' through ''8'' from bottom to top; each square is identified by the file and rank which it occupies. The a- through d-files comprise the , while the e- through h-files comprise the . History and evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Maack
Ferdinand Maack (1861–1930) was a German doctor, inventor and occultist. He invented Raumschach Three-dimensional chess (or 3‑D chess) is any chess variant that replaces the two-dimensional board with a three-dimensional array of cells between which the pieces can move. In practical play, this is usually achieved by boards representing d ..., the classic 3D chess game, first described by him in the ''Frankfurter Zeitung'' in 1907. He promoted the game with demonstrations, articles, specialist magazines and several books. He founded the Hamburg Raumschach Club in 1919, which remained active until World War II. Notes References Bibliography * * * * External links * 1861 births 1930 deaths Chess variant inventors 20th-century German inventors 20th-century German physicians {{Germany-chess-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lionel Kieseritzky
Lionel Adalbert Bagration Felix Kieseritzky (russian: Лионель Адальберт Багратион Феликс Кизерицкий; – ) was a Baltic Germans, Baltic German chess master and Chess theoretician, theoretician, famous for his contributions to chess theory, as well for a game he lost against Adolf Anderssen, which because of its brilliance was named "Immortal Game, The Immortal Game". Kieseritzky is the namesake of several openings and opening variations, such as the Kieseritzky Gambit, Two Knights Defense#4.Ng5, Kieseritzky attack, and the Boden–Kieseritzky Gambit. Early life Kieseritzky was born in Tartu, Dorpat (now Tartu), Governorate of Livonia, Livonia, Russian Empire into a Baltic Germans, Baltic German family. From 1825 to 1829 he studied at the University of Tartu, University of Dorpat, and then worked as a mathematics teacher, like Anderssen. From 1838 to 1839, he played a correspondence chess, correspondence match against Carl Jaenisch – unfi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
En Passant
''En passant'' (, "in passing") is a method of capturing in chess that occurs when a pawn captures a horizontally adjacent enemy pawn that has just made an initial two-square advance. The capturing pawn moves to the square that the enemy pawn passed over, as if the enemy pawn had advanced only one square. The rule ensures that a pawn cannot use its two-square move to safely skip past an enemy pawn. Capturing ''en passant'' is permitted only on the turn immediately after the two-square advance; it cannot be done on a later turn. The capturing move is sometimes notated by appending the abbreviation e.p. Rules The conditions for a pawn to capture an enemy pawn ''en passant'' are as follows: * the enemy pawn advanced two squares on the previous move; * the capturing pawn attacks the square that the enemy pawn passed over. If these conditions are met, the capturing pawn can move diagonally forward to the square that the enemy pawn passed, capturing the enemy pawn as if it h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Games In Star Trek
The fictional ''Star Trek'' universe includes a variety of sports, games and other pastimes. Some of these fictional recreational activities are closely associated with one race, although they may have gained adherents from other backgrounds. Others thrive on the interaction of different species. Some of the games below were central to the plot of a single episode. Others were recurring plot elements, spanning multiple television series of the ''Star Trek'' franchise. Holodeck games The holodeck is a facility that simulates reality; it can replicate a wide variety of environments. It is found on starships and starbases in all the series that are set in the 24th century, i.e. '' Star Trek: The Next Generation'', '' Star Trek: Deep Space Nine'' and '' Star Trek: Voyager''. The holodeck is sometimes used for research or training, but is frequently shown in use for various forms of entertainment. Some programs depicted in the various ''Star Trek'' shows include a Klingon calisthenics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |