|
Rational Planning Model
The rational planning model is a model of the planning process involving a number of rational actions or steps. Taylor (1998) outlines five steps, as follows: * Definition of the problems and/or goals; * Identification of alternative plans/policies; * Evaluation of alternative plans/policies; * Implementation of plans/policies; * Monitoring of effects of plans/policies. The rational planning model is used in planning and designing neighborhoods, cities, and regions. It has been central in the development of modern urban planning and transportation planning. The model has many limitations, particularly the lack of guidance on involving stakeholders and the community affected by planning, and other models of planning, such as collaborative planning, are now also widely used. The very similar rational decision-making model, as it is called in organizational behavior, is a process for making logically sound decisions. This multi-step model and aims to be logical and follow the orderly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Planning
Urban planning, also known as town planning, city planning, regional planning, or rural planning, is a technical and political process that is focused on the development and design of land use and the built environment, including air, water, and the infrastructure passing into and out of urban areas, such as transportation, communications, and distribution networks and their accessibility. Traditionally, urban planning followed a top-down approach in master planning the physical layout of human settlements. The primary concern was the public welfare, which included considerations of efficiency, sanitation, protection and use of the environment, as well as effects of the master plans on the social and economic activities. Over time, urban planning has adopted a focus on the social and environmental bottom-lines that focus on planning as a tool to improve the health and well-being of people while maintaining sustainability standards. Sustainable development was added as one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Efficiency
In microeconomics, economic efficiency, depending on the context, is usually one of the following two related concepts: * Allocative or Pareto efficiency: any changes made to assist one person would harm another. * Productive efficiency: no additional output of one good can be obtained without decreasing the output of another good, and production proceeds at the lowest possible average total cost. These definitions are not equivalent: a market or other economic system may be allocatively but not productively efficient, or productively but not allocatively efficient. There are also other definitions and measures. All characterizations of economic efficiency are encompassed by the more general engineering concept that a system is efficient or optimal when it maximizes desired outputs (such as utility) given available inputs. Standards of thought There are two main standards of thought on economic efficiency, which respectively emphasize the distortions created by ''gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Analysis
Decision analysis (DA) is the discipline comprising the philosophy, methodology, and professional practice necessary to address important decisions in a formal manner. Decision analysis includes many procedures, methods, and tools for identifying, clearly representing, and formally assessing important aspects of a decision; for prescribing a recommended course of action by applying the maximum expected-utility axiom to a well-formed representation of the decision; and for translating the formal representation of a decision and its corresponding recommendation into insight for the decision maker, and other corporate and non-corporate stakeholders. History In 1931, mathematical philosopher Frank Ramsey pioneered the idea of subjective probability as a representation of an individual’s beliefs or uncertainties. Then, in the 1940s, mathematician John von Neumann and economist Oskar Morgenstern developed an axiomatic basis for utility theory as a way of expressing an individua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rationality And Power
''Rationality and Power: Democracy in Practice'' is a 1998 book by Bent Flyvbjerg, published by the University of Chicago Press. The book focuses on "the application of critical theory to urban and community development". Flyvbjerg here deploys the methodology for doing social science, which he developed in ''Making Social Science Matter'' (2001). Upon publication, the ''International Journal of Urban and Regional Research'' called ''Rationality and Power'', "a notable addition to the literature," the reviewer adding, "I cannot think of a better account of how power relations are embodied in local governance." Synopsis Flyvbjerg focuses on the study of how power influences rationality and democracy. Theoretically and methodologically, he stands on the shoulders of thinkers like Thucydides, Machiavelli, Nietzsche, and Max Weber. He specifically highlights Machiavelli's power studies in Florence as a source of influence for the choice of in-depth case studies to understand the dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Benveniste
Guy Benveniste (born February 27, 1927 and deceased December 3. 2022) was an organization theorist who has written about the politics of planning and ways of encouraging bureaucracies to be more adaptive to change. Early life Benveniste was born in Paris, France, on February 27, 1927. He left Vichy France in May 1942 to take refuge in Mexico. He attended Harvard University, where he received a BS and MS in engineering in 1948 and 1950. He worked as a construction engineer and an economist for the Mexican Light and Power Company before emigrating to the United States in 1954. He then joined the Stanford Research Institute in Menlo Park, California, where he undertook economic studies including the economics of solar energy and later became involved in economic development in third world countries. In 1961, at the beginning of the Kennedy administration, he was named to a task force on the reorganization of the US AID agency. He joined the Kennedy administration in December 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Situated Action
{{dictionary In artificial intelligence and cognitive science, the term situated refers to an agent which is embedded in an environment. The term ''situated'' is commonly used to refer to robots, but some researchers argue that software agents can also be situated if: * they exist in a dynamic (rapidly changing) environment, which * they can manipulate or change through their actions, and which * they can sense or perceive. Examples might include web-based agents, which can alter data or trigger processes (such as purchases) over the internet, or virtual-reality bots which inhabit and change virtual worlds, such as Second Life. Being situated is generally considered to be part of being embodied, but it is useful to consider each perspective individually. The situated perspective emphasizes that intelligent behaviour derives from the environment and the agent's interaction Interaction is action that occurs between two or more objects, with broad use in philosophy and the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucy Suchman
Lucy Suchman is a Professor of Anthropology of Science and Technology in the Department of Sociology at Lancaster University, in the United Kingdom. Her current research extends her longstanding critical engagement with the field of human-computer interaction to the domain of contemporary war fighting, including problems of ‘situational awareness’ in military training and simulation, and in the design and deployment of automated weapon systems. At the center of this research is the question of whose bodies are incorporated into military systems, how and with what consequences for social justice and the possibility for a less violent world. Suchman is a member of International Committee for Robot Arms Control and the author of the blog dedicated to the problems of ethical robotics and 'technocultures of humanlike machines' Before coming to Lancaster, she worked for 22 years at Xerox's Palo Alto Research Center (PARC) in California, where she held the positions of principal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post–Kyoto Protocol Negotiations On Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Post-Kyoto negotiations refers to high level talks attempting to address global warming by limiting greenhouse gas emissions. Generally part of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), these talks concern the period after the first "commitment period" of the Kyoto Protocol, which expired at the end of 2012. Negotiations have been mandated by the adoption of the Bali Road Map and Decision 1/CP.13 ("The Bali Action Plan"). UNFCCC negotiations are conducted within two subsidiary bodies, the Ad Hoc Working Group on Long-term Cooperative Action under the Convention (AWG-LCA) and the Ad Hoc Working Group on Further Commitments for Annex I Parties under the Kyoto Protocol (AWG-KP) and were expected to culminate in the United Nations Climate Change Conference taking place in December 2009 in Copenhagen (COP-15); negotiations are supported by a number of external processes, including the G8 process, a number of regional meetings and the Major Economies Forum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implementation
Implementation is the realization of an application, or execution of a plan, idea, model, design, specification, standard, algorithm, or policy. Industry-specific definitions Computer science In computer science, an implementation is a realization of a technical specification or algorithm as a program, software component, or other computer system through computer programming and deployment. Many implementations may exist for a given specification or standard. For example, web browsers contain implementations of World Wide Web Consortium-recommended specifications, and software development tools contain implementations of programming languages. A special case occurs in object-oriented programming, when a concrete class implements an interface; in this case the concrete class is an ''implementation'' of the interface and it includes methods which are ''implementations'' of those methods specified by the interface. Information technology In the information technology d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value Theory
In ethics and the social sciences, value theory involves various approaches that examine how, why, and to what degree humans value things and whether the object or subject of valuing is a person, idea, object, or anything else. Within philosophy, it is also known as ethics or axiology. Traditionally, philosophical investigations in value theory have sought to understand the concept of " the good". Today, some work in value theory has trended more towards empirical sciences, recording what people do value and attempting to understand why they value it in the context of psychology, sociology, and economics. In ecological economics, value theory is separated into two types: donor-type value and receiver-type value. Ecological economists tend to believe that 'real wealth' needs an accrual-determined value as a measure of what things were needed to make an item or generate a service ( H. T. Odum, ''Environmental Accounting: Emergy and environmental decision-making'', 1996). In o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norm (social)
Social norms are shared standards of acceptance, acceptable behavior by groups. Social norms can both be informal understandings that govern the behavior of members of a society, as well as be codified into wikt:rule, rules and laws. Social normative influences or social norms, are deemed to be powerful drivers of human behavioural changes and well organized and incorporated by major theories which explain human behaviour. Institutions are composed of multiple norms. Norms are shared social beliefs about behavior; thus, they are distinct from "ideas", "Attitude (psychology), attitudes", and "Value (ethics), values", which can be held privately, and which do not necessarily concern behavior. Norms are contingent on context, social group, and historical circumstances. Scholars distinguish between regulative norms (which constrain behavior), constitutive norms (which shape interests), and prescriptive norms (which prescribe what actors ''ought'' to do). The effects of norms can be det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
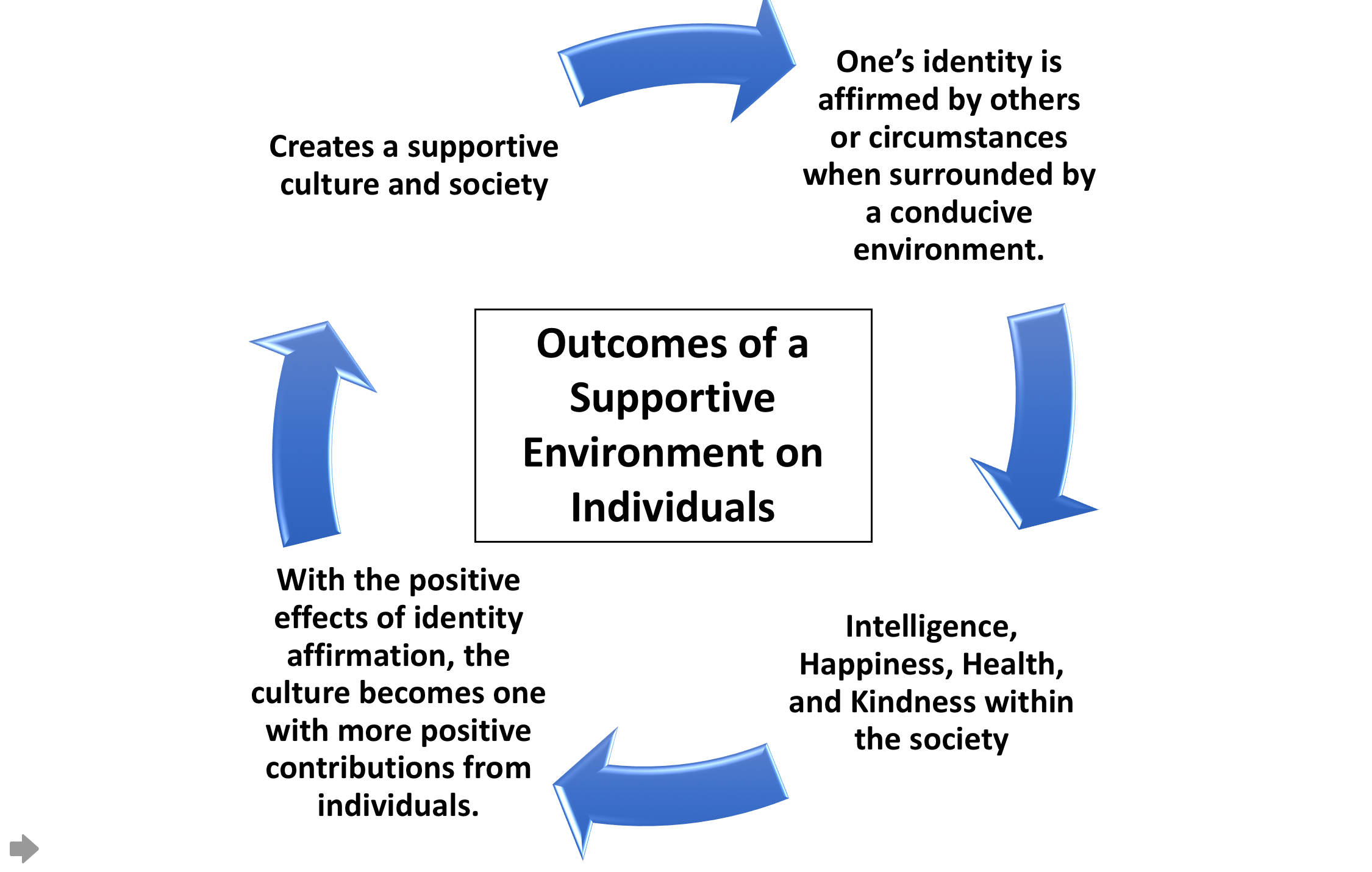
Cultural Psychology
Cultural psychology is the study of how cultures reflect and shape the psychological processes of their members.Heine, S. J. (2011). ''Cultural Psychology. ''New York: W. W. Norton & Company. It is based on the premise that mind and culture are inseparable and mutually constitutive, meaning that people are shaped by their culture and their culture is also shaped by them.Fiske, A.; Kitayama, S.; Markus, H.R.; & Nisbett, R.E. (1998)The cultural matrix of social psychology In D. Gilbert & S. Fiske & G. Lindzey (Eds.), The Handbook of Social Psychology (4th ed., pp. 915–81). San Francisco: McGraw-Hill. Cultural psychology aims to define culture, its nature and function, specifically in relation to psychological phenomena. Gerd Baumann has argued: "Culture is not a real thing, but an abstract and purely analytical notion. In itself «it» does not «cause» behavior, but denotes an abstraction from it, and is thus neither normative nor predictive but a heuristic means towards explain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |