|
Rating System
A rating system can be any kind of rating applied to a certain application domain. They are often created using a rating scale. Examples include: * Motion picture content rating system ** Motion Picture Association film rating system **Canadian motion picture rating system *Television content rating system * Video game content rating system *DC Comics rating system * Marvel Comics rating system * Elo rating system *Glicko rating system * Chess rating system * Rating system of the Royal Navy *Star rating * Sports rating system *Wine rating A wine rating is a score assigned by one or more wine critics to a wine tasted as a summary of that critic's evaluation of that wine. A wine rating is therefore a subjective quality score, typically of a numerical nature, given to a specific bottl ... * Texas Education Agency accountability ratings system {{set index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rating Scale
:''Concerning rating scales as systems of educational marks, see articles about education in different countries (named "Education in ..."), for example, Education in Ukraine.'' :''Concerning rating scales used in the practice of medicine, see articles about diagnoses, for example, Major depressive disorder.'' A rating scale is a set of categories designed to elicit information about a quantitative or a qualitative attribute. In the social sciences, particularly psychology, common examples are the Likert response scale and 1-10 rating scales in which a person selects the number which is considered to reflect the perceived quality of a product. Background A rating scale is a method that requires the rater to assign a value, sometimes numeric, to the rated object, as a measure of some rated attribute Types of rating scales All rating scales can be classified into one of these types: # Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) # Verbal Rating Scale (VRS) # Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) # Likert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motion Picture Content Rating System
A motion picture content rating system classifies films based on their suitability for audiences due to their treatment of issues such as sex, violence, or substance abuse; their use of profanity; or other matters typically deemed unsuitable for children or adolescents. Most countries have some form of rating system that issues determinations variously known as ''certifications'', ''classifications'', ''certificates'', or ''ratings''. Age recommendations, of either an advisory or restrictive capacity, are often applied in lieu of censorship; in some jurisdictions movie theaters may have a legal obligation to enforce restrictive ratings. In countries such as Australia and Singapore, an official government body decides on ratings; in other countries such as the United States, it is done by industry committees with little if any official government status. In most countries, however, films that are considered morally offensive have been censored, restricted, or banned. Even if the fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motion Picture Association Film Rating System
The Motion Picture Association film rating system is used in the United States and its territories to rate a motion picture's suitability for certain audiences based on its content. The system and the ratings applied to individual motion pictures are the responsibility of the Motion Picture Association (MPA), previously known as the Motion Picture Association of America (MPAA) from 1945 to 2019. The MPA rating system is a voluntary scheme that is not enforced by law; films can be exhibited without a rating, although most theaters refuse to exhibit non-rated or NC-17 rated films. Non-members of the MPA may also submit films for rating. Other media, such as television programs, music and video games, are rated by other entities such as the TV Parental Guidelines, the RIAA and the ESRB, respectively. Introduced in 1968, following the Hays Code of the classical Hollywood cinema era, the MPA rating system is one of various motion picture rating systems that are used to help parents d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Motion Picture Rating System
Motion picture ratings in Canada are mostly a provincial responsibility, and each province has its own legislation regarding exhibition and admission. For home video purposes, a single Canadian Home Video Rating System rating consisting of an average of the participating provincial ratings is displayed on retail packages, although various provinces may have rules on display and sale, especially for the R and A categories. There are currently four film classification offices rating commercially released movies in Canada, each an agency of a provincial government: * British Columbia Film Classification Office, a division of Consumer Protection BC, provides ratings for British Columbia, Manitoba, Ontario, and Saskatchewan. * Alberta Film Classification provides ratings for Alberta, the Northwest Territories, and Nunavut. * Régie du cinéma du Québec provides ratings for Quebec. * Maritime Film Classification Board, run by the Nova Scotia Alcohol & Gaming Authority, provides rati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Content Rating System
Television content rating systems are systems for Content rating, evaluating the content and reporting the suitability of television programs for Minor (law), minors. Many countries have their own television evaluation, rating system and countries' rating processes vary by local priorities. Programs are rated by the organization that manages the system, the broadcasting, broadcaster, or the content producers. A rating is usually set for each individual episode of a television series. The rating can change per episode, television network, network, rerun, and country. As such, program ratings are usually not meaningful unless when and where the rating is used is mentioned. Comparison table A comparison of current television content rating systems, showing age on the horizontal axis. Note however that the specific criteria used in assigning a classification can vary widely from one country to another. Thus a color code or age range cannot be directly compared from one country to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Game Content Rating System
A video game content rating system is a system used for the classification of video games based on suitability for target audiences. Most of these systems are associated with and/or sponsored by a government, and are sometimes part of the local motion picture rating system. The utility of such ratings has been called into question by studies that publish findings such as 90% of teenagers claim that their parents "never" check the ratings before allowing them to rent or buy video games, and as such, calls have been made to "fix" the existing rating systems. Video game content rating systems can be used as the basis for laws that cover the sales of video games to minors, such as in Australia. Rating checking and approval is part of the game localization when they are being prepared for their distribution in other countries or locales. These rating systems have also been used to voluntarily restrict sales of certain video games by stores, such as the German retailer Galeria Kaufhof's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DC Comics Rating System
The DC Comics rating system is a system for rating the content of comic books used by DC Comics. In 2011, DC Comics decided to withdraw from the Comics Code Authority and implement their own rating system for their comics. Rather than replicating the system used by Marvel Comics, DC Comics' system is more similar to video game ratings, specifically the ESRB. A few months later, Image Comics implemented a similar rating system to their own comics that followed the same system as DC. System The DC Comics Rating System assigns each comic book one of the following ratings: *E – EVERYONE – Appropriate for readers of all ages. May contain cartoon violence and/or some comic mischief. *T – TEEN – Appropriate for readers age 12 and older. May contain mild violence, language and/or suggestive themes. *T+ – TEEN PLUS – Appropriate for readers age 15 and older. May contain moderate violence, mild profanity, graphic imagery and/or suggestive themes. *M – MATURE – Appropriate fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marvel Comics Rating System
The Marvel Comics rating system is a system for rating the content of comic books, with regard to appropriateness for different age groups. In 2001, Marvel Comics withdrew from the Comics Code Authority and established its own rating system for its publications. This was precipitated by the CCA refusing approval of the seal due to the strong depiction of violence in ''X-Force'' #116, a comic written by Peter Milligan and drawn by Mike Allred. As well, by withdrawing from the CCA, this is seen as a move by editor-in-chief Joe Quesada to lure more high-profile creators to Marvel Comics. – ICv2 – 27 April 2001 Today's ratings are usually found on the comic's UPC box. System The Marv ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elo Rating System
The Elo rating system is a method for calculating the relative skill levels of players in zero-sum games such as chess. It is named after its creator Arpad Elo, a Hungarian-American physics professor. The Elo system was invented as an improved chess-rating system over the previously used Harkness system, but is also used as a rating system in association football, American football, baseball, basketball, pool, table tennis, and various board games and esports. The difference in the ratings between two players serves as a predictor of the outcome of a match. Two players with equal ratings who play against each other are expected to score an equal number of wins. A player whose rating is 100 points greater than their opponent's is expected to score 64%; if the difference is 200 points, then the expected score for the stronger player is 76%. A player's Elo rating is represented by a number which may change depending on the outcome of rated games played. After every game, the winni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glicko Rating System
The Glicko rating system and Glicko-2 rating system are methods of assessing a player's strength in games of skill, such as chess and Go. The Glicko rating system was invented by Mark Glickman in 1995 as an improvement on the Elo rating system, and initially intended for the primary use as a chess rating system. Glickman's principal contribution to measurement is "ratings reliability", called RD, for ''ratings deviation''. Overview Mark Glickman created the Glicko rating system in 1995 as an improvement on the Elo rating system. Both the Glicko and Glicko-2 rating systems are under public domain and have been implemented on game servers online (like Pokémon Showdown, Pokémon Go, Lichess, Free Internet Chess Server, Chess.com, Online Go Server (OGS), Counter Strike: Global Offensive, Quake Live, Team Fortress 2, Dota Underlords, Guild Wars 2, Splatoon 2, Dominion Online, TETR.IO, and competitive programming competitions. The Reliability Deviation (RD) measures the accuracy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Rating System
A chess rating system is a system used in chess to estimate the strength of a player, based on their performance versus other players. They are used by organizations such as FIDE, the US Chess Federation (USCF or US Chess), International Correspondence Chess Federation, and the English Chess Federation. Most of the systems are used to recalculate ratings after a tournament or match but some are used to recalculate ratings after individual games. Popular online chess sites such as chess.com, Lichess, and Internet Chess Club also implement rating systems. In almost all systems, a higher number indicates a stronger player. In general, players' ratings go up if they perform better than expected and down if they perform worse than expected. The magnitude of the change depends on the rating of their opponents. The Elo rating system is currently the most widely used. The first modern rating system was used by the Correspondence Chess League of America in 1939. Soviet player Andrey Khacha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
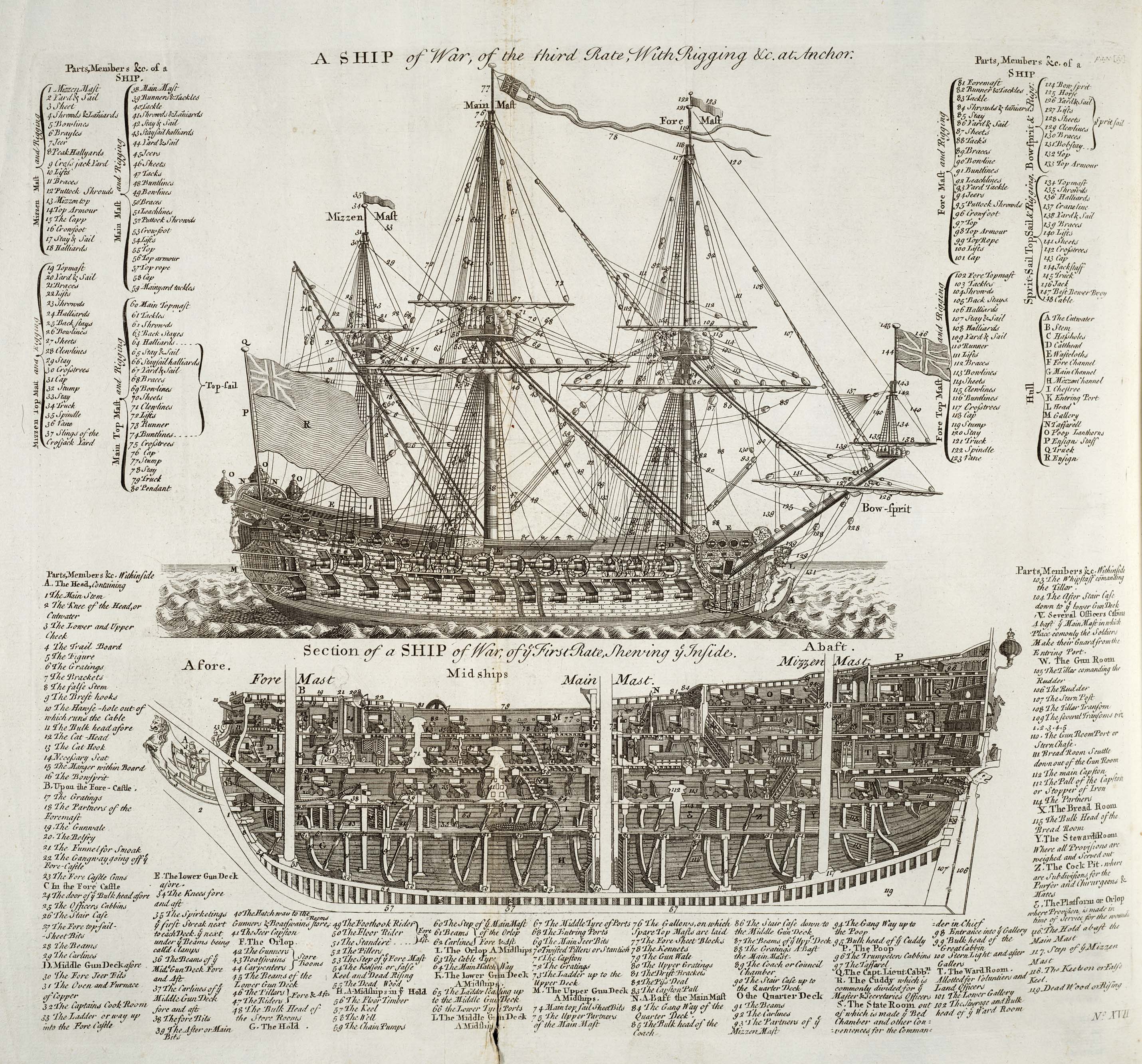
Rating System Of The Royal Navy
The rating system of the Royal Navy and its predecessors was used by the Royal Navy between the beginning of the 17th century and the middle of the 19th century to categorise sailing warships, initially classing them according to their assigned complement of men, and later according to the number of their carriage-mounted guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy formally came to an end in the late 19th century by declaration of the Admiralty. The main cause behind this declaration focused on new types of gun, the introduction of steam propulsion and the use of iron and steel armour which made rating ships by the number of guns obsolete. Origins and description The first movement towards a rating system may be seen in the 15th century and the first half of the 16th century, when the largest carracks in the Navy (such as the ''Mary Rose'', the '' Peter Pomegranate'' and the ''Henri Grâce à Dieu'') were denoted "great ships". This was only on the basis of their roughly-esti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)