|
Rating (other)
A rating is an evaluation or assessment of something, in terms of quality, quantity, or some combination of both. Rating or ratings may also refer to: Business and economics * Credit rating, estimating the credit worthiness of an individual, corporation or country * Ranally city rating system, a tool used to classify U.S. cities based on economic function * Telecommunications rating, the calculated cost of a phone call Entertainment * Arbitron ratings or Nielsen Audio, consumer research on radio broadcasting audiences in the United States * Content rating, the suitability of a TV broadcast, movie, comic book, or video game to its audience ** Motion picture rating system, categorizes films according to their suitability for adults and children ** Television content rating systems, categorizes TV shows based on suitability for audiences ** Video game content rating system, categorizes video games based on suitability for players * Audience measurement ** Nielsen ratings, measuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaluation
Evaluation is a systematic determination and assessment of a subject's merit, worth and significance, using criteria governed by a set of standards. It can assist an organization, program, design, project or any other intervention or initiative to assess any aim, realisable concept/proposal, or any alternative, to help in decision-making; or to ascertain the degree of achievement or value in regard to the aim and objectives and results of any such action that has been completed. The primary purpose of evaluation, in addition to gaining insight into prior or existing initiatives, is to enable reflection and assist in the identification of future change. Evaluation is often used to characterize and appraise subjects of interest in a wide range of human enterprises, including the arts, criminal justice, foundations, non-profit organizations, government, health care, and other human services. It is long term and done at the end of a period of time. Definition Evaluation is the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetane Rating
Cetane number (cetane rating) is an indicator of the combustion speed of diesel fuel and compression needed for ignition. It plays a similar role for diesel as octane rating does for gasoline. The CN is an important factor in determining the quality of diesel fuel, but not the only one; other measurements of diesel fuel's quality include (but are not limited to) energy content, density, lubricity, cold-flow properties and sulphur content.Werner Dabelstein, Arno Reglitzky, Andrea Schütze and Klaus Reders "Automotive Fuels" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2007, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Definition The cetane number (or CN) of a fuel is defined by finding a blend of cetane and isocetane with the same ignition delay. Cetane has a cetane number defined to be 100, while isocetane's measured cetane number is 15, replacing the former reference fuel alpha-methylnaphthalene, which was assigned a cetane number of 0. Once the blend is known, the cetane number is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Ratings (other)
Television ratings may refer to: * An audience measurement Audience measurement measures how many people are in an audience, usually in relation to radio listenership and television viewership, but also in relation to newspaper and magazine readership and, increasingly, web traffic on websites. Some ... technique ** Target rating point, a metric used in marketing and advertising ** By national organisations that compile audience measurement and television ratings *** AGB Nielsen Philippines – in the Philippines *** Broadcast Audience Research Council – in India *** Broadcasters' Audience Research Board – in the United Kingdom *** Nielsen TV ratings – in the United States *** Television ratings in Australia – in Australia * Television content rating systems, systems for evaluating the content and reporting the suitability of television programs for children or adults ** Australian Classification Board – in Australia ** TV Parental Guidelines – in the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rate (other)
Rate or rates may refer to: Finance * Rates (tax), a type of taxation system in the United Kingdom used to fund local government * Exchange rate, rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another Mathematics and science * Rate (mathematics), a specific kind of ratio, in which two measurements are related to each other (often with respect to time) * Rate function, a function used to quantify the probabilities of a rare event * Reaction rate The reaction rate or rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place, defined as proportional to the increase in the concentration of a product per unit time and to the decrease in the concentration of a reactant per uni ..., in chemistry the speed at which reactants are converted into products Military * Naval rate, a junior enlisted member of a navy * Rating system of the Royal Navy, a former method of indicating a British warship's firepower People * Ed Rate (1899–1990), American football play ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
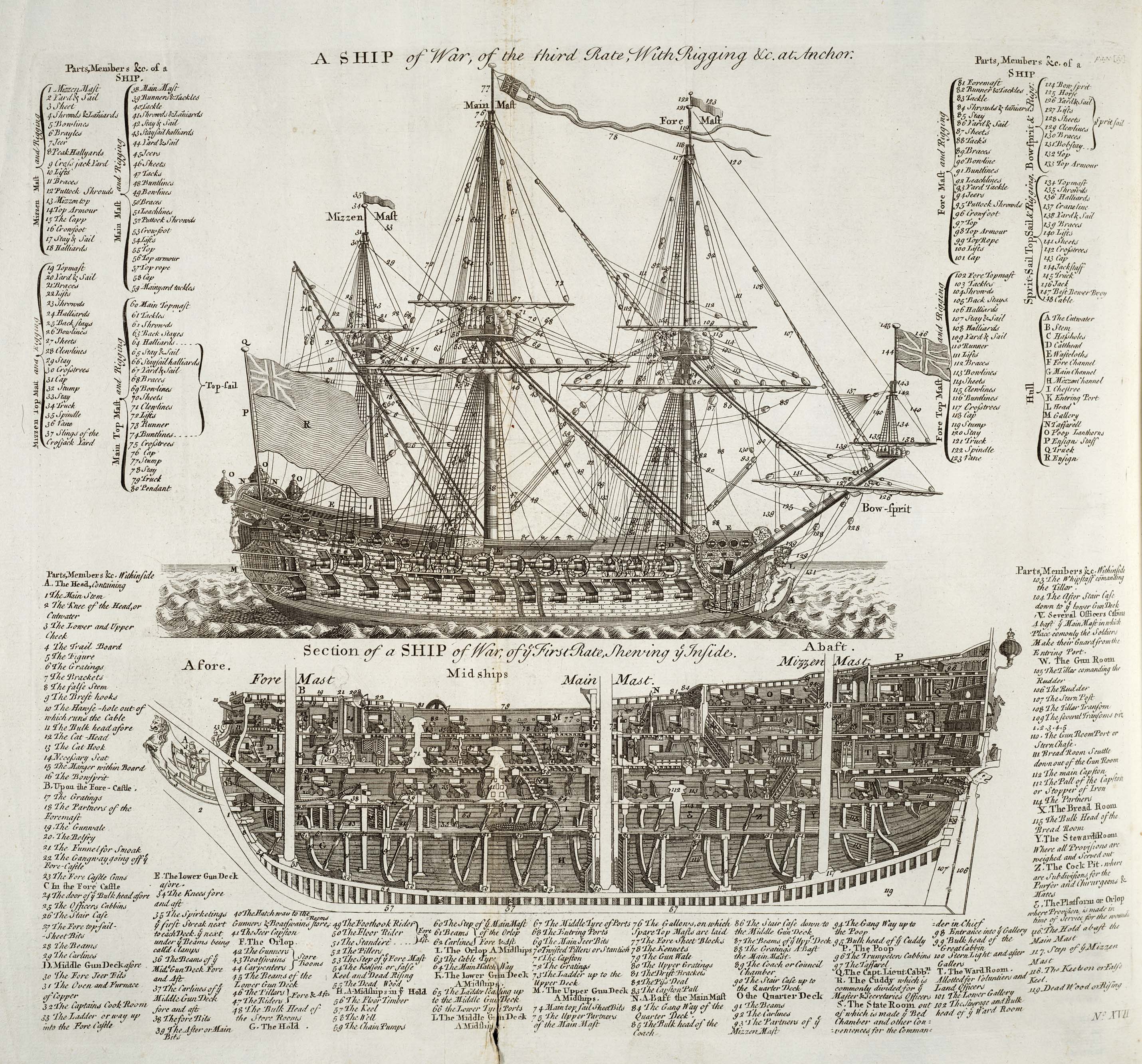
Rating System Of The Royal Navy
The rating system of the Royal Navy and its predecessors was used by the Royal Navy between the beginning of the 17th century and the middle of the 19th century to categorise sailing warships, initially classing them according to their assigned complement of men, and later according to the number of their carriage-mounted guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy formally came to an end in the late 19th century by declaration of the Admiralty. The main cause behind this declaration focused on new types of gun, the introduction of steam propulsion and the use of iron and steel armour which made rating ships by the number of guns obsolete. Origins and description The first movement towards a rating system may be seen in the 15th century and the first half of the 16th century, when the largest carracks in the Navy (such as the ''Mary Rose'', the '' Peter Pomegranate'' and the '' Henri Grâce à Dieu'') were denoted "great ships". This was only on the basis of their roughly-es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Care Ratings
Health care ratings are ratings or evaluations of health care. In the United States they have been an increasingly used tool to try to drive accountability among health care providers and in the context of classic supply/demand In economics, demand is the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. The relationship between price and quantity demand is also called the demand curve. Demand for a specific item ... view of Health economics, to help health care consumers make better choices. Reviews in 2008 and 2009 review of research on the effects of health care ratings found that there was evidence that public ratings drove hospitals to improve their performance, but there was limited evidence that they affected how consumers choose health care providers or insurance plans, or that they changed the performance of individual doctors or insurance companies. In may cases it is difficult to create health care ratings th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rating Site
A review site is a website on which reviews can be posted about people, businesses, products, or services. These sites may use Web 2.0 techniques to gather reviews from site users or may employ professional writers to author reviews on the topic of concern for the site. Early examples of review sites included ConsumerDemocracy.com, Complaints.com, planetfeedback.com, and Epinions.com. Business models Review sites are generally supported by advertising. Some business review sites may also allow businesses to pay for enhanced listings, which do not affect the reviews and ratings. Product review sites may be supported by providing affiliate links to the websites that sell the reviewed items, which pay the site on a per-click or per-sale basis. With the growing popularity of affiliate programs on the Internet, a new sort of review site has emerged: the affiliate product review site. This type of site is usually professionally designed and written to maximize conversions, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rating (wine)
A wine rating is a score assigned by one or more wine critics to a wine tasted as a summary of that critic's evaluation of that wine. A wine rating is therefore a subjective quality score, typically of a numerical nature, given to a specific bottle of wine. In most cases, wine ratings are set by a single wine critic, but in some cases a rating is derived by input from several critics tasting the same wine at the same time. A number of different scales for wine ratings are in use. Also, the practices used to arrive at the rating can vary. Over the last couple of decades, the 50–100 scale introduced by Robert M. Parker, Jr. has become commonly used. This or numerically similar scales are used by publications such as '' Wine Enthusiast'', ''Wine Spectator'', and ''Wine Advocate''. Other publications or critics, such as Jancis Robinson and Michael Broadbent, may use a 0–20 scale, or a 0–5 scale (often in terms of numbers of stars) either with or without half-star steps.J. Robin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rating (clinical Trials)
Within the field of clinical trial Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...s, rating is the process by which a human evaluator subjectively judges the response of a patient to a medical treatment. The rating can include more than one treatment response. The accessor is normally an independent observer other than the patient, but the accessor can also be the patient (a patient-reported outcome). Furthermore, some clinical outcomes can only be assessed by the patient (a "private phenomena"). Because the evaluation is subjective, this can result in both inter-rater or intra-rater reliability. When conducting clinical trials, ensuring rating consistency is important, but can prove to be quite difficult to obtain. Studies dealing with such indications as pain, mental disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elo Rating System
The Elo rating system is a method for calculating the relative skill levels of players in zero-sum games such as chess. It is named after its creator Arpad Elo, a Hungarian-American physics professor. The Elo system was invented as an improved chess-rating system over the previously used Harkness system, but is also used as a rating system in association football, American football, baseball, basketball, pool, table tennis, and various board games and esports. The difference in the ratings between two players serves as a predictor of the outcome of a match. Two players with equal ratings who play against each other are expected to score an equal number of wins. A player whose rating is 100 points greater than their opponent's is expected to score 64%; if the difference is 200 points, then the expected score for the stronger player is 76%. A player's Elo rating is represented by a number which may change depending on the outcome of rated games played. After every game, the wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rating (chess)
A chess rating system is a system used in chess to estimate the strength of a player, based on their performance versus other players. They are used by organizations such as FIDE, the US Chess Federation (USCF or US Chess), International Correspondence Chess Federation, and the English Chess Federation. Most of the systems are used to recalculate ratings after a tournament or match but some are used to recalculate ratings after individual games. Popular online chess sites such as chess.com, Lichess, and Internet Chess Club also implement rating systems. In almost all systems, a higher number indicates a stronger player. In general, players' ratings go up if they perform better than expected and down if they perform worse than expected. The magnitude of the change depends on the rating of their opponents. The Elo rating system is currently the most widely used. The first modern rating system was used by the Correspondence Chess League of America in 1939. Soviet player Andrey K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |