|
Ras El Ma Airfield
Ras el Ma Airfield is an abandoned World War II military airfield in Morocco, located in the southeast suburbs of Ras Kebdana. The airfield served as a support facility for the port, allowing Allied aircraft to be assembled and parepared for combat duty, then flown from the airstrip as replacements during the North African Campaign. The United States Army Air Force Twelfth Air Force also used the airfield to re-equip the 27th Bombardment Group with the A-36 Apache close air support variant of the P-51 Mustang in April 1943. Once the unit was successfully transitioned from its A-20 Havoc light bombers, it was reassigned back to combat duty at Korba, Tunisia ) , image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg , map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa , image_map2 = , capital = Tunis , largest_city = capital , .... References * Maurer, Maurer. ''Air Force Combat Units of World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelfth Air Force - Emblem (World War II)
Twelfth can mean: *The Twelfth Amendment to the United States Constitution *The Twelfth, a Protestant celebration originating in Ireland In mathematics: * 12th, an Ordinal number (linguistics), ordinal number; as in the item in an order twelve places from the beginning, following the eleventh and preceding the thirteenth * 1/12, a vulgar fraction, one part of a unit divided equally into twelve parts Music * The Musical note, note twelve scale degrees from the root (chord), root (current note, in a chord) ** The interval (music) (that is, gap) between the root and the twelfth note: a compound fifth (interval), fifth Currency *Uncia (coin), a Roman coin worth 12th of an As (Roman coin), As See also *12 (number) *Eleventh *Thirteenth {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-36 Apache
The North American A-36 (listed in some sources as "Apache" or "Invader", but generally called Mustang) was the ground-attack/dive bomber version of the North American P-51 Mustang, from which it could be distinguished by the presence of rectangular, slatted dive brakes above and below the wings. A total of 500 A-36 dive bombers served in the Mediterranean and Southeast Asia theaters during World War II before being withdrawn from operational use in 1944. The A-36 project was a stopgap measure intended to keep North American Aviation (NAA) assembly lines running during the first half of 1942 despite the US having exhausted its funds earmarked for fighter aircraft. When the order came for more P-51s in June 1942, the NAA workforce was thoroughly experienced. Design and development With the introduction of the North American Mustang Mk.I with the Royal Air Force's Army Co-operation Squadrons in February 1942, the new fighter began combat missions as a low-altitude reconnaissance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
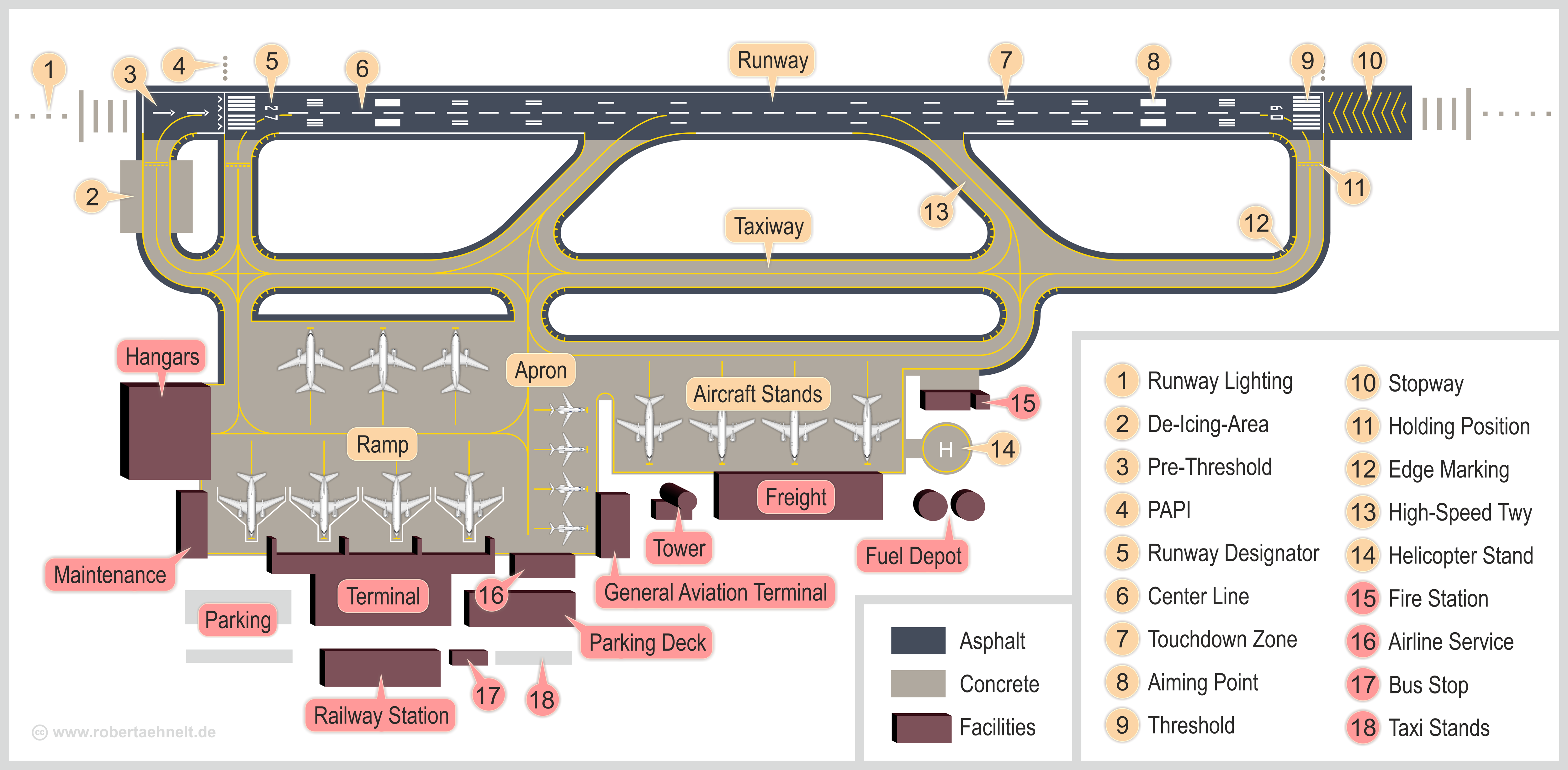
Airports Established In 1942
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Operating airports is extremely complicated, with a complex system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tourism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II Airfields In Morocco
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object while others analyze the world as a complex made up of many parts. In ''scientific cosmology'' the world or universe is commonly defined as " e totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". '' Theories of modality'', on the other hand, talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. ''Phenomenology'', starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons". In ''philosophy of mind'', the world is commonly contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. ''Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airfields Of The United States Army Air Forces In Morocco
An aerodrome (Commonwealth English) or airdrome (American English) is a location from which aircraft flight operations take place, regardless of whether they involve air cargo, passengers, or neither, and regardless of whether it is for public or private use. Aerodromes include small general aviation airfields, large commercial airports, and military air bases. The term ''airport'' may imply a certain stature (having satisfied certain certification criteria or regulatory requirements) that not all aerodromes may have achieved. That means that all airports are aerodromes, but not all aerodromes are airports. Usage of the term "aerodrome" remains more common in Ireland and Commonwealth nations, and is conversely almost unknown in American English, where the term "airport" is applied almost exclusively. A water aerodrome is an area of open water used regularly by seaplanes, floatplanes or amphibious aircraft for landing and taking off. In formal terminology, as defined by the I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunisia
) , image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg , map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa , image_map2 = , capital = Tunis , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , official_languages = Arabic Translation by the University of Bern: "Tunisia is a free State, independent and sovereign; its religion is the Islam, its language is Arabic, and its form is the Republic." , religion = , languages_type = Spoken languages , languages = Minority Dialects : Jerba Berber (Chelha) Matmata Berber Judeo-Tunisian Arabic (UNESCO CR) , languages2_type = Foreign languages , languages2 = , ethnic_groups = * 98% Arab * 2% Other , demonym = Tunisian , government_type = Unitary presidential republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Kais Saied , leader_ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korba Airfield
Korba Airfield is an abandoned military airfield in Tunisia, located about 3 km west of Hamadet Bir Messaouda in Nabul province; 13 km north of Korbra, and 60 km east-southeast of Tunis. Built by the US Army Corps of engineers, the airfield consisted of Pierced Steel Planking runways and parking and dispersal areas, with support structures quickly constructed out of wood or tents. Its last known use was by the United States Army Air Force Twelfth Air Force in 1943 during the Tunisian Campaign. Units which used the airfield were the following: * 27th Fighter Bomber Group, June–July 1943, A-36 Apache * 31st Fighter Group, 15 May-30 June 1943, Spitfire * 86th Bombardment Group, 30 June-20 July 1943, A-20 Havoc The airfield is also notable because many Italian Air Force airplanes landed at Korba in the days immediately following the armistice between Italy and the Allied armed forces in early September 1943. The Regia Aeronautica 8 Gruppo Macchi C.200 The M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-20 Havoc
The Douglas A-20 Havoc (company designation DB-7) is an American medium bomber, attack aircraft, night intruder, night fighter, and reconnaissance aircraft of World War II. Designed to meet an Army Air Corps requirement for a bomber, it was ordered by France for their air force before the USAAC decided it would also meet their requirements. French DB-7s were the first to see combat; after the fall of France, the bomber served with the Royal Air Force under the service name Boston. From 1941, night fighter and intruder versions were given the service name Havoc. In 1942 USAAF A-20s saw combat in North Africa. It served with several Allied air forces, principally the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF), the Soviet Air Forces (''VVS''), Soviet Naval Aviation (''AVMF''), and the Royal Air Force (RAF) of the United Kingdom. A total of 7,478 aircraft were built, of which more than a third served with Soviet units. It was also used by the air forces of Australia, South Africa, Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
27th Bombardment Group
7 (seven) is the natural number following 6 and preceding 8. It is the only prime number preceding a cube. As an early prime number in the series of positive integers, the number seven has greatly symbolic associations in religion, mythology, superstition and philosophy. The seven Classical planets resulted in seven being the number of days in a week. It is often considered lucky in Western culture and is often seen as highly symbolic. Unlike Western culture, in Vietnamese culture, the number seven is sometimes considered unlucky. It is the first natural number whose pronunciation contains more than one syllable. Evolution of the Arabic digit In the beginning, Indians wrote 7 more or less in one stroke as a curve that looks like an uppercase vertically inverted. The western Ghubar Arabs' main contribution was to make the longer line diagonal rather than straight, though they showed some tendencies to making the digit more rectilinear. The eastern Arabs developed the digit fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelfth Air Force
The Twelfth Air Force (12 AF; Air Forces Southern, (AFSOUTH)) is a Numbered Air Force of the United States Air Force Air Combat Command (ACC). It is headquartered at Davis–Monthan Air Force Base, Arizona. The command is the air component to United States Southern Command (USSOUTHCOM) conducting security cooperation and providing air, space, and cyberspace capabilities throughout Latin America and the Caribbean. Established on 20 August 1942 at Bolling Field, District of Columbia, 12th Air Force was a United States Army Air Forces combat air force deployed to the Mediterranean Theater of World War II. It engaged in operations in North Africa, the Mediterranean, and Western Europe. During the Cold War, 12 AF was one of the Numbered Air Forces of the United States Air Forces in Europe (USAFE) and later Tactical Air Command (TAC), Its units engaged in combat operations during the Vietnam War, as well as Operation Desert Storm. As a result of the War on Terror, most Twelfth Air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army Air Force
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II (1941–1945). It was created on 20 June 1941 as successor to the previous United States Army Air Corps and is the direct predecessor of the United States Air Force, today one of the six armed forces of the United States. The AAF was a component of the United States Army, which on 2 March 1942 was divided functionally by executive order into three autonomous forces: the Army Ground Forces, the United States Army Services of Supply (which in 1943 became the Army Service Forces), and the Army Air Forces. Each of these forces had a commanding general who reported directly to the Army Chief of Staff. The AAF administered all parts of military aviation formerly distributed among the Air Corps, General Headquarters Air Force, and the ground ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)



.jpg)

