|
Rare Earth Hypothesis
In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. According to the hypothesis, complex extraterrestrial life is an improbable phenomenon and likely to be rare throughout the universe as a whole. The term "Rare Earth" originates from '' Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe'' (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington. In the 1970s and 1980s, Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others, argued that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred spiral galaxy. From the principl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Blue Marble (remastered)
''The Blue Marble'' is an image of Earth taken on December 7, 1972, from a distance of around from the planet's surface. Taken by the crew of the Apollo 17 spacecraft on its way to the Moon, it is one of the most reproduced images in history. It mainly shows Earth from the Mediterranean Sea to Antarctica. This was the first time the Apollo trajectory made it possible to photograph the south polar ice cap, despite the Southern Hemisphere being heavily cloud cover, covered in clouds. In addition to the Arabian Peninsula and Madagascar, almost the entire coastline of Africa and most of the Indian Ocean are clearly visible, 1972 North Indian Ocean cyclone season#Cyclone Sixteen (16B), A Cyclone in the Indian Ocean is also visible, The South Asian mainland is on the eastern limb. NASA has also applied the name to a 2012 series of images which cover the entire globe at relatively high resolution. These were created by looking through satellite imagery, satellite pictures taken over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Drake
Frank Donald Drake (May 28, 1930 – September 2, 2022) was an American astrophysicist and astrobiologist. He began his career as a radio astronomer, studying the planets of the Solar System and later pulsars. Drake expanded his interests to the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI), beginning with Project Ozma in 1960, an attempt at extraterrestrial communications. He developed the Drake equation, which attempts to quantify the number of intelligent lifeforms that could potentially be discovered. Working with Carl Sagan, Drake helped to design the Pioneer plaque, the first physical message flown beyond the Solar System, and was part of the team that developed the Voyager record. Drake designed and implemented the Arecibo message in 1974, an extraterrestrial radio transmission of astronomical and biological information about Earth. Drake worked at the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Cornell University, University of California a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Habitable Zone
In astrobiology and planetary astrophysics, the galactic habitable zone is the region of a galaxy in which life might most likely develop. The concept of a galactic habitable zone analyzes various factors, such as metallicity (the presence of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium) and the rate and density of major catastrophes such as supernovae, and uses these to calculate which regions of a galaxy are more likely to form terrestrial planets, initially develop simple life, and provide a suitable environment for this life to evolve and advance. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may favor the birth and development of habitable planets more than smaller galaxies such as the Milky Way. In the case of the Milky Way, its galactic habitable zone is commonly believed to be an annulus (chubby ring) with an outer radius of about and an inner radius close to the Galactic Center (with both radii lacking hard boundaries). Galactic habitable-zone theory h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Paradox
The Fermi paradox is the discrepancy between the lack of conclusive evidence of advanced extraterrestrial life and the apparently high a priori likelihood of its existence, and by extension of obtaining such evidence. As a 2015 article put it, "If life is so easy, someone from somewhere must have come calling by now." Italian-American physicist Enrico Fermi's name is associated with the paradox because of a casual conversation in the summer of 1950 with fellow physicists Edward Teller, Herbert York, and Emil Konopinski. While walking to lunch, the men discussed recent UFO reports and the possibility of faster-than-light travel. The conversation moved on to other topics, until during lunch Fermi blurted out, "But where is everybody?" (although the exact quote is uncertain). There have been many attempts to resolve the Fermi paradox, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. According to this theory, space and time emerged together ago, and the universe has been expanding ever since the Big Bang. While the spatial size of the entire universe is unknown, it is possible to measure the size of the observable universe, which is approximately 93 billion light-years in diameter at the present day. Some of the earliest cosmological models of the universe were developed by ancient Greek and Indian philosophers and were geocentric, placing Earth at the center. Over the centuries, more precise astronomical observations led Nicolaus Copernicus to develop the heliocentric model with the Sun at the center of the Solar System. In developing the law of universal gravitation, Isaac Newton built upon Copernicus's work as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SETI
The search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI) is a collective term for scientific searches for intelligent extraterrestrial life, for example, monitoring electromagnetic radiation for signs of transmissions from civilizations on other planets. Scientific investigation began shortly after the advent of radio in the early 1900s, and focused international efforts have been ongoing since the 1980s. In 2015, Stephen Hawking and Israeli billionaire Yuri Milner announced a project called Breakthrough Listen. History Early work There have been many earlier searches for extraterrestrial intelligence within the Solar System. In 1896, Nikola Tesla suggested that an extreme version of his wireless electrical transmission system could be used to contact beings on Mars. In 1899, while conducting experiments at his Colorado Springs experimental station, he thought he had detected a signal from Mars since an odd repetitive static signal seemed to cut off when Mars set in the night ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraterrestrial Life
Extraterrestrial life, colloquially referred to as alien life, is life that may occur outside Earth and which did not originate on Earth. No extraterrestrial life has yet been conclusively detected, although efforts are underway. Such life might range from simple forms like prokaryotes to intelligent beings, possibly bringing forth civilizations that might be far more advanced than humankind. The Drake equation speculates about the existence of sapient life elsewhere in the universe. The science of extraterrestrial life is known as astrobiology. Speculation about the possibility of inhabited "worlds" outside the planet Earth dates back to antiquity. Multiple early Christian writers discussed the idea of a "plurality of worlds" as proposed by earlier thinkers such as Democritus; Augustine references Epicurus's idea of innumerable worlds "throughout the boundless immensity of space" (originally expressed in his Letter to Herodotus) in ''The City of God''. In his first century p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
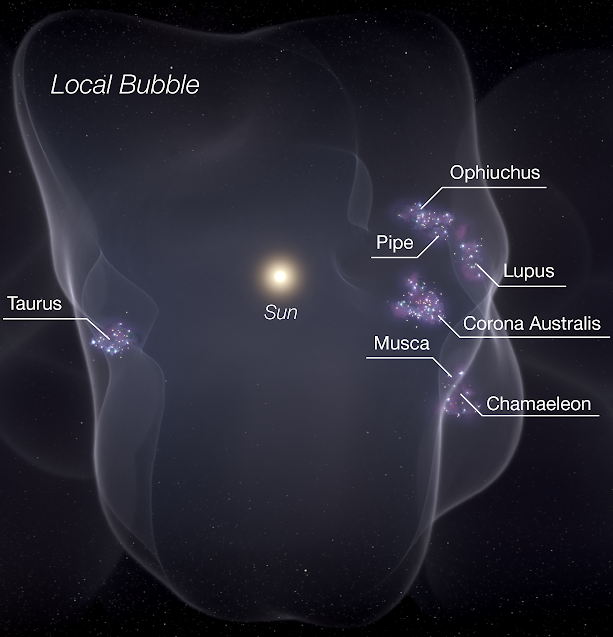
Local Bubble
The Local Bubble, or Local Cavity, is a relative cavity in the interstellar medium (ISM) of the Orion Arm in the Milky Way. It contains the closest of celestial neighbours and among others, the Local Interstellar Cloud (which contains the Solar System), the neighbouring G-Cloud, the Ursa Major Moving Group ( the closest stellar moving group) and the Hyades (the nearest open cluster). It is at least 300 light years across, and is defined by its neutral-hydrogen density of about 0.05 atoms/cm3, or approximately one tenth of the average for the ISM in the Milky Way (0.5 atoms/cm3), and one sixth that of the Local Interstellar Cloud (0.3 atoms/cm3). The exceptionally sparse gas of the Local Bubble is the result of supernovae that exploded within the past ten to twenty million years. Geminga, a pulsar in the constellation Gemini, was once thought to be the remnant of a single supernova that created the Local Bubble, but now multiple supernovae in subgroup B1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravity, gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It Formation and evolution of the Solar System, formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The solar mass, vast majority (99.86%) of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the Jupiter mass, remaining mass contained in the planet Jupiter. The four inner Solar System, inner system planets—Mercury (planet), Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars—are terrest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copernican Principle
In physical cosmology, the Copernican principle states that humans, on the Earth or in the Solar System, are not privileged observers of the universe, that observations from the Earth are representative of observations from the average position in the universe. Named for Copernican heliocentrism, it is a working assumption that arises from a modified cosmological extension of Copernicus' argument of a moving Earth. Origin and implications Hermann Bondi named the principle after Copernicus in the mid-20th century, although the principle itself dates back to the 16th-17th century paradigm shift away from the Ptolemaic system, which placed Earth at the center of the universe. Copernicus proposed that the motion of the planets could be explained by reference to an assumption that the Sun is centrally located and stationary in contrast to the geocentrism. He argued that the apparent retrograde motion of the planets is an illusion caused by Earth's movement around the Sun, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Of Mediocrity
The mediocrity principle is the philosophical notion that "if an item is drawn at random from one of several sets or categories, it's more likely to come from the most numerous category than from any one of the less numerous categories". The principle has been taken to suggest that there is nothing very unusual about the evolution of the Solar System, Earth's history, the evolution of biological complexity, human evolution, or any one nation. It is a heuristic in the vein of the Copernican principle, and is sometimes used as a philosophical statement about the place of humanity. The idea is to assume mediocrity, rather than starting with the assumption that a phenomenon is special, privileged, exceptional, or even superior. Extraterrestrial life The mediocrity principle suggests, given the existence of life on Earth, that should life exist elsewhere in the universe, it will typically exist on Earth-like planets. Measurement of distance to stars The mediocrity principle was i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)