|
Ranish Partition Manager
Ranish Partition Manager is a freeware hard disk partition editor, disk cloning utility, and boot manager, that gives a high level of control for creating multi-boot systems. It is available on the freeware live CD SystemRescueCD and the Ultimate Boot CD (not the Windows version). It runs under MS-DOS, PC DOS, DR-DOS, or FreeDOS. Features Partitioning *Unlike the partition editor bundled with Windows Vista and Windows 7, Ranish Partition Manager can make partition tables where both Windows XP and Windows Vista can be installed. However, it is possible to make a partition table with no errors in RPM, where the Windows XP installer cannot install XP (without deleting the extended partition value from the partition table). Editing this type of partition table with Vista's partition editor will result in mixed alignments. *Any number of changes can be made before saving to disk. *The latest beta (v2.44 beta) provides a workaround to overcome the limitation of 4 primary partitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeware
Freeware is software, most often proprietary, that is distributed at no monetary cost to the end user. There is no agreed-upon set of rights, license, or EULA that defines ''freeware'' unambiguously; every publisher defines its own rules for the freeware it offers. For instance, modification, redistribution by third parties, and reverse engineering are permitted by some publishers but prohibited by others. Unlike with free and open-source software, which are also often distributed free of charge, the source code for freeware is typically not made available. Freeware may be intended to benefit its producer by, for example, encouraging sales of a more capable version, as in the freemium and shareware business models. History The term ''freeware'' was coined in 1982 by Andrew Fluegelman, who wanted to sell PC-Talk, the communications application he had created, outside of commercial distribution channels. Fluegelman distributed the program via a process now termed '' share ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Partition
An extended boot record (EBR), or extended partition boot record (EPBR), is a descriptor for a logical partition under the common DOS disk drive partitioning system. In that system, when one (and only one) partition record entry in the master boot record (MBR) is designated an '' extended partition'', then that partition can be subdivided into a number of logical partitions. The actual structure of that extended partition is described by one or more EBRs, which are located inside the extended partition. The first (and sometimes only) EBR will always be located on the very first sector of the extended partition. Unlike primary partitions, which are all described by a single partition table within the MBR, and thus limited in number, each EBR precedes the logical partition it describes. If another logical partition follows, then the first EBR will contain an entry pointing to the next EBR; thus, multiple EBRs form a linked list. This means the number of logical drives that can be fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
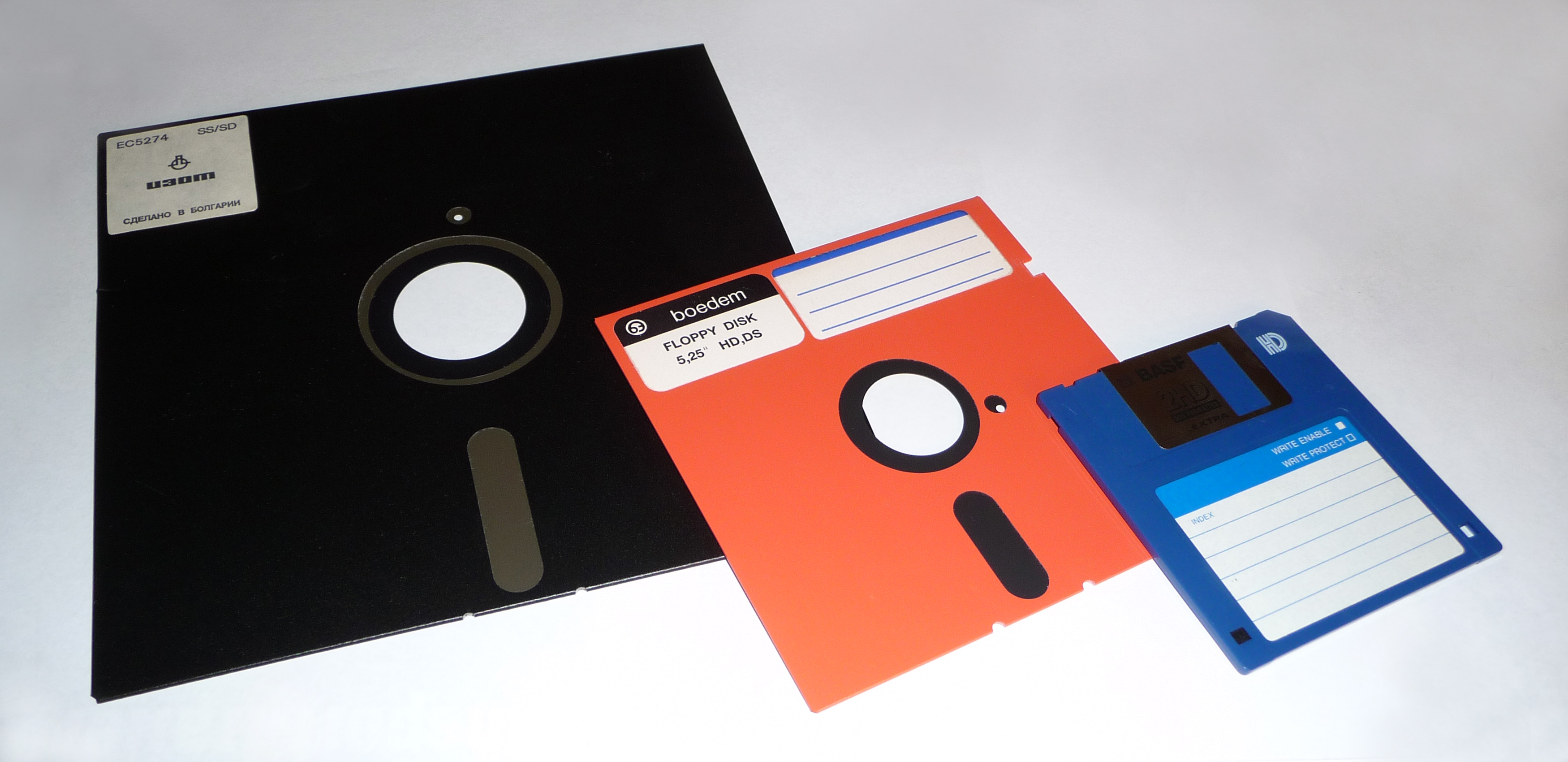
Floppy Disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch and then the 3½-inch became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare to non-existent. Some individuals and organizations continue to use older equipment to read or transfer data from floppy disks. Floppy di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Rescue CD
SystemRescue (Previously known as "SystemRescueCD") is a Linux distribution for x86 64 and x86 computers. The primary purpose of SystemRescue is to repair unbootable or otherwise damaged computer systems after a system crash. SystemRescue is not intended to be used as a permanent operating system. It runs from a Live CD, a USB flash drive or any type of hard drive. It was designed by a team led by François Dupoux, and is based on Arch Linux since version 6.0. Starting with version 6.0, it has systemd as its init system. Features SystemRescue is capable of graphics using the Linux framebuffer option for tools such as GParted. It has options such as connecting to the Internet through an ADSL modem or Ethernet and graphical web browsers such as Mozilla Firefox. SystemRescue features include: * GNU Parted and GParted to partition disks and resize partitions, including FAT32 and NTFS * fdisk to edit the disk partition table * PartImage - disk imaging software whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexedit
A hex editor (or ''binary file editor'' or ''byte editor'') is a computer program that allows for manipulation of the fundamental binary data that constitutes a computer file. The name 'hex' comes from 'hexadecimal', a standard numerical format for representing binary data. A typical computer file occupies multiple areas on the storage medium, whose contents are combined to form the file. Hex editors that are designed to parse and edit sector data from the physical segments of floppy or hard disks are sometimes called ''sector editors'' or ''disk editors''. Details With a hex editor, a user can see or edit the raw and exact contents of a file, as opposed to the interpretation of the same content that other, higher level application software may associate with the file format. For example, this could be raw image data, in contrast to the way image editing software would interpret and show the same file. Hex editors may be used to correct data corrupted by system or application p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Editor
A disk editor is a computer program that allows its user to read, edit, and write raw data (at character or hexadecimal, byte-levels) on disk drives (e.g., hard disks, USB flash disks or removable media such as a floppy disks); as such, they are sometimes called ''sector editors,'' since the read/write routines built into the electronics of most disk drives require to read/write data in chunks of sectors (usually 512 bytes). Many disk editors can also be used to edit the contents of a running computer's memory or a disk image. Unlike '' hex editors,'' which are used to edit files, a disk editor allows access to the underlying disk structures, such as the master boot record (MBR) or GUID Partition Table (GPT), file system, and directories. On some operating systems (like Unix or Unix-like) most hex editors can act as disk editors just opening block devices instead of regular files. Programmers can use disk editors to understand these structures and test whether their impl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Boot Record
A master boot record (MBR) is a special type of boot sector at the very beginning of partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept of MBRs was publicly introduced in 1983 with PC DOS 2.0. The MBR holds the information on how the disc's sectors are divided into partitions, each partition notionally containing a file system. The MBR also contains executable code to function as a loader for the installed operating system—usually by passing control over to the loader's second stage, or in conjunction with each partition's volume boot record (VBR). This MBR code is usually referred to as a boot loader. The organization of the partition table in the MBR limits the maximum addressable storage space of a partitioned disk to 2 TiB . Approaches to slightly raise this limit assuming 32-bit arithmetics or 4096-byte sectors are not officially supported, as they fatally break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Table
Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk, before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Partition
Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk, before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logical Drive
In computer data storage, a volume or logical drive is a single accessible storage area with a single file system, typically (though not necessarily) resident on a single partition of a hard disk. Although a volume might be different from a physical disk drive, it can still be accessed with an operating system's logical interface. However, a volume differs from a partition. Differences from partition A volume is not the same thing as a partition. For example, a floppy disk might be accessible as a volume, even though it does not contain a partition, as floppy disks cannot be partitioned with most modern computer software. Also, an OS can recognize a partition without recognizing any volume associated with it, as when the OS cannot interpret the filesystem stored there. This situation occurs, for example, when Windows NT-based OSes encounter disks with non-Microsoft OS partitions, such as the ext3 filesystem commonly used with Linux. Another example occurs in the Intel world w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder-head-sector
Cylinder-head-sector (CHS) is an early method for giving addresses to each physical block of data on a hard disk drive. It is a 3D-coordinate system made out of a vertical coordinate ''head'', a horizontal (or radial) coordinate ''cylinder'', and an angular coordinate ''sector''. Head selects a circular surface: a platter in the disk (and one of its two sides). Cylinder is a cylindrical intersection through the stack of platters in a disk, centered around the disk's spindle. Combined, cylinder and head intersect to a circular line, or more precisely: a circular strip of physical data blocks called ''track''. Sector finally selects which data block in this track is to be addressed, as the track is subdivided into several equally-sized portions, each of which is an arc of (360/n) degrees, where n is the number of sectors in the track. CHS addresses were exposed, instead of simple linear addresses (going from ''0'' to the ''total block count on disk - 1''), because early hard drive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logical Disk Manager
The Logical Disk Manager (LDM) is an implementation of a logical volume manager for Microsoft Windows NT, developed by Microsoft and Veritas Software. It was introduced with the Windows 2000 operating system, and is supported in Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10 and Windows 11. The MMC-based ''Disk Management'' snap-in () hosts the Logical Disk Manager. On Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, Microsoft deprecated LDM in favor of Storage Spaces. Logical Disk Manager enables disk volumes to be ''dynamic'', in contrast to the standard ''basic'' volume format. Basic volumes and dynamic volumes differ in their ability to extend storage beyond one physical disk. Basic partitions are restricted to a fixed size on one physical disk. Dynamic volumes can be enlarged to include more free space - either from the same disk or another physical disk. (For more information on the difference, see Basic and dynamic disks and volumes, below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |